 W
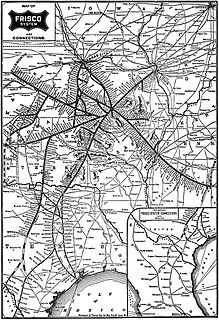
WThe Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison, Kansas, Topeka, Kansas, and Santa Fe, New Mexico. The railroad reached the Kansas–Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farmland from the land grants that it was awarded by Congress.
 W
WIn August 1999, the United States Postal Service issued a set of 33¢ postage stamps entitled All Aboard! 20th Century American Trains to "pay tribute to American industry and design, and specifically to the heritage of our railroads." Artist Ted Rose created five watercolor images depicting the following celebrated American named passenger trains from the 1930s and 1940s:the Congressional of the Pennsylvania Railroad; the Daylight of the Southern Pacific Railroad; the Hiawatha of the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad; the Super Chief of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway; and the 20th Century Limited of the New York Central Railroad.
 W
WThe Ashfork Bainbridge Steel Dam, the first large steel dam in the world, and one of only three ever built in the United States, was constructed in 1898 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF) to supply water for railway operations near Ash Fork, Arizona. It is named for the town of Ash Fork, and for Francis H. Bainbridge, a civil engineer and graduate of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI), a member of the Rensselaer Society of Engineers, and an engineer for ATSF. The dam has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 1976.
 W
WModesta Avila was an American protester in Orange County, California, who became the county's first convicted felon and first state prisoner. Avila had only received a minor warning in 1889 for placing an obstruction on the tracks to protest against the Santa Fe Railroad being built through her property without adequate compensation, but she continued to taunt the authorities, and was eventually arrested four months later.
 W
WThe Big Domes were a fleet of streamlined dome cars built by the Budd Company for the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in 1954. Budd built a total of 14 cars in two batches. The Santa Fe operated all 14 on various streamlined trains until it conveyed its passenger trains to Amtrak in 1971. The Santa Fe retained one as a business car and sold the remaining 13 to the Auto-Train Corporation, which operated them for another ten years. All but two have been preserved in varying condition.
 W
WCajon Pass is a mountain pass between the San Bernardino Mountains and the San Gabriel Mountains in Southern California. It was created by the movements of the San Andreas Fault. Located in the Mojave Desert, the pass is an important link from the Greater San Bernardino Area to the Victor Valley, and northeast to Las Vegas.
 W
WColton Crossing is a railway crossing situated in Colton, California, directly south of Interstate 10. First built in 1883, it was the site of one of the most intense frog wars in railroad construction history, leading to a personal confrontation between famed lawman Virgil Earp and California Governor Robert Waterman. The crossing was the intersection of the tracks for the former ATSF and former Southern Pacific (SP) railroads. Southern Pacific is now Union Pacific and the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway is now BNSF, and both the UP and BNSF still utilize their respective's predecessor's tracks. The Union Pacific tracks runs east-west at the crossing while the BNSF tracks operate north-south. Metrolink trains and Amtrak's Southwest Chief also use the BNSF tracks through the crossing while Amtrak's Sunset Limited utilize the UP tracks for that service. The Union Pacific tracks come from the east through the Coachella Valley and into the yard in West Colton. On the other hand, the BNSF tracks from the indirect west and direct south continue through the crossing and on to the yard in San Bernardino, which then head up north to Cajon Pass and eventually Barstow on the journey to Chicago.
 W
WCorwith Yards, a railroad intermodal freight terminal located at Pershing Road & Kedzie Avenue in the southwest side of Chicago, Illinois, in the neighborhood of Brighton Park, is a landmark in the history of railroad freight transport. At the time it was built by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in 1887, it was the world's largest railway yard. With adjacent parking and buildings it covers nearly a square mile of land. In the late 19th century Corwith Yards was the end of the line for trains of livestock loaded at AT&SF stations such as Dodge City, Kansas, and bound for the Union Stock Yards, as well as grain and other cargo from the western United States.
 W
WCompleted in 1904, the Crown King Branch of the Bradshaw Mountain Railroad, also known as Murphy's Impossible Railroad, linked the town of Crown King with the end of the Prescott and Eastern Railroad at Mayer, Arizona.
 W
WThe Fort Madison Toll Bridge is a tolled, swinging truss bridge over the Mississippi River that connects Fort Madison, Iowa, and unincorporated Niota, Illinois. Rail traffic occupies the lower deck of the bridge, while two lanes of road traffic occupy the upper deck. The double-decker bridge, about a mile long with a swing span of 525 feet (160 m), was the longest and largest double-deck swing-span bridge in the world, when constructed in 1927.It replaced an inadequate combination roadway/single-track bridge completed in 1887. The main river crossing consists of four 270-foot (82 m) Baltimore through truss spans and a swing span made of two equal arms, 266 feet (81 m) long. In 1999, it was listed in the National Register of Historic Places under the title, Fort Madison Bridge, ID number 99001035. It was also documented by the Library of Congress Historic American Engineering Record, survey number HAER IA-62. Construction and photographic details were recorded at the time in Scientific American magazine.
 W
WThe Fort Worth and Rio Grande Railway, chartered under the laws of Texas on June 1, 1885, was part of a plan conceived by Buckley Burton Paddock and other Fort Worth civic leaders to create a transcontinental route linking New York, Fort Worth, and the Pacific port of Topolobampo, which they believed would stimulate the growth and development of southwest Texas in general, and the economy of Fort Worth in particular.
 W
WThe Fred Harvey Company was the owner of the Harvey House chain of restaurants, hotels, and other hospitality industry businesses alongside railroads in the western United States. It was founded in 1876 by Fred Harvey to cater to the growing number of train passengers. When Harvey died in 1901, his family inherited 45 restaurants and 20 dining cars in 12 states. During World War II, Harvey Houses opened again to serve soldiers as they traveled in troop trains across the U.S. By 1968, when it was sold to Amfac, Inc., the Fred Harvey Company was the sixth largest food retailer in the United States. It left behind a lasting legacy of good food, dedication to customers, decent treatment of employees, and preservation of local traditions.
 W
WThe Hi-Level was a type of bilevel intercity railroad passenger car used in the United States. Car types included coaches, dining cars, and lounge cars. Most passenger spaces were on the upper level, which featured a row of windows on both sides. Boarding was on the lower level; passengers climbed up a center stairwell to reach the upper level. Vestibules on the upper level permitted passengers to walk between cars; some coaches had an additional stairwell at one end to allow access to single-level equipment. Santa Fe and Budd considered but never created a sleeping car.
 W
WThe Southern Transcon is a railroad corridor between Southern California and Chicago, Illinois, and serves as a BNSF Railway main line made up of 11 rail lines between Southern California and Chicago. Completed in its current alignment in 1908 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, when it opened the Belen Cutoff in New Mexico and bypassed the steep grades of Raton Pass, it now serves as a mostly double-tracked intermodal corridor.
 W
WThe Northwestern Pacific Railroad is a railroad covering the 62 mi (100 km) stretch between Schellville and Windsor with freight and Sonoma–Marin Area Rail Transit (SMART) commuter trains. Formerly, it was a regional railroad that served the entire North Coast of California, with a main line running 271 miles (436 km) from Schellville to Eureka, along with an additional portion of the line running from the Ignacio Wye to the edge of San Rafael. The portion of the NWP main line between the Ignacio Wye in Marin County and the depot in Healdsburg is owned by SMART. The Schellville–Ignacio and Healdsburg–Eureka portions are owned by the North Coast Railroad Authority (NCRA). Private contractor NWPco operates freight service under NCRA lease. California's 2018 Great Redwood Trail Act repurposes the abandoned railroad right-of-way from Eureka to the San Francisco Bay in Marin County for future use as the "Great Redwood Trail" rail-trail.
 W
WThe Oakland Terminal Railway was a terminal railroad in West Oakland, California. The OTR was jointly acquired in 1943 by the Western Pacific Railroad and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway to take over the Key System's freight railroad known as the Oakland Terminal Railroad. Today, the OTR is now the West Oakland Pacific Railroad that operates on 10 miles of track. OTR was jointly owned by the Union Pacific Railroad and BNSF Railway. The railroad operated in the industrial area around the Oakland Army Base.
 W
WOcean Wave was a steamboat that was operated from 1891 to 1897 on the Columbia River, from 1897 to 1899 on Puget Sound and from 1899 to 1911 as a ferry on San Francisco Bay. Ocean Wave is perhaps best known for transporting summer vacationers from Portland, Oregon to seaside resorts near Ilwaco, Washington during its service on the Columbia River. This vessel is also known for being the first ferry placed in service by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
 W
WThe Pleasure Domes are a fleet of six streamlined dome lounge cars built by Pullman-Standard for the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in 1950. The cars were used exclusively on the Super Chief from their introduction in 1950 until the end of Santa Fe passenger service in 1971. Amtrak retained all six cars and continued to operate them until 1980 when they were retired. All six were preserved. The Pleasure Dome, with its famed "Turquoise Room" private dining room, contributed to the Super Chiefs reputation for elegance and luxury. The name is derived from a line in Samuel Taylor Coleridge's poem Kubla Khan.
 W
WRailroad Wars were business rivalries between railroad companies, which occurred frequently in American history. Although they were usually little more than legal disputes inside a courtroom, they sometimes turned into armed conflicts. There has been competition between railroad companies since the beginning of railroading in the United States, but violent confrontations were most common in the final quarter of the 19th century, particularly in the Old West.
 W
WRatón Pass is a 7,834 ft (2,388 m) elevation mountain pass on the Colorado-New Mexico border in the western United States. Ratón is Spanish for "mouse". It is located on the eastern side of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains between Trinidad, Colorado and Raton, New Mexico, approximately 180 miles (290 km) northeast of Santa Fe. The pass crosses the line of volcanic mesas that extends east from the Sangre de Cristo Mountains along the state line, and furnishes the most direct land route between the valley of the Arkansas River to the north and the upper valley of the Canadian River, leading towards Santa Fe, to the south. The pass now carries Interstate 25 and railroad tracks.
 W
WRedondo Junction, California is the site of the current Amtrak maintenance facility. It is located 3.5 miles south of the Union Station passenger Terminal, Southwest of Boyle Heights near Washington Boulevard and the Los Angeles River.
 W
WThe Royal Gorge is a canyon of the Arkansas River located west of Cañon City, Colorado. The canyon begins at the mouth of Grape Creek about 2 mi (3.2 km) west of central Cañon City and continues in a west-northwesterly direction for approximately 6 mi (9.7 km) until ending near U.S. Route 50. Being one of the deepest canyons in Colorado, it is also known as the Grand Canyon of the Arkansas (River), with a maximum depth of 1,250 ft (380 m). The canyon is also very narrow, measuring from 50 ft (15 m) wide at its base to 300 ft (91 m) wide at its top, as it carves a path through the granite formations below Fremont Peak and YMCA Mountain, which rise above the north and south rims, respectively.
 W
WThe San Bernardino Line is a Metrolink line running between Downtown Los Angeles east through the San Gabriel Valley and the Inland Empire to San Bernardino. It is one of the three initial lines on the original Metrolink system.
 W
WThe Sibley Railroad Bridge is a three-span through truss single-track railroad bridge belonging to the BNSF Railway between Jackson County, Missouri, and Ray County, Missouri, at Sibley. The bridge carries the BNSF Marceline Subdivision over the Missouri River. It is the only single-track segment of the subdivision. The original 1887-88 bridge was a three-span Whipple through truss and was later reconstructed with Parker through truss spans. Besides the freight trains of BNSF Railway, it is also used by Amtrak's Southwest Chief.
 W
WThe Southern Transcon is a railroad corridor between Southern California and Chicago, Illinois, and serves as a BNSF Railway main line made up of 11 rail lines between Southern California and Chicago. Completed in its current alignment in 1908 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, when it opened the Belen Cutoff in New Mexico and bypassed the steep grades of Raton Pass, it now serves as a mostly double-tracked intermodal corridor.
 W
WThe Surf Line is a railroad line that runs from San Diego north to Orange County along California's Pacific Coast. It was so named because much of the line is near the Pacific Ocean, within less than 100 ft (30 m) in some places. The tracks are now owned by the Southern California Regional Rail Authority and the North County Transit District, and hosts Metrolink's Orange County Line and Inland Empire–Orange County Line, the San Diego Coaster, and Amtrak Pacific Surfliner passenger trains. The BNSF Railway operates freight over the line using trackage rights.
 W
WThe Tehachapi Loop is a 3,779 feet long spiral, or helix, on the Union Pacific Railroad Mojave Subdivision through Tehachapi Pass, of the Tehachapi Mountains in Kern County, south-central California. The line connects Bakersfield and the San Joaquin Valley to Mojave in the Mojave Desert.