 W
WThe Anti-Comintern Pact, officially the Agreement against the Communist International, was an anti-Communist pact concluded between Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan on 25 November 1936, and was directed against the Communist International (Comintern). It was signed by German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop and Japanese ambassador to Germany Kintomo Mushakoji. Italy, Spain and other countries joined it until November 1941.
 W
WThe Balkan Pact, or Balkan Entente, was a treaty signed by Greece, Turkey, Romania and Yugoslavia on 9 February 1934 in Athens, aimed at maintaining the geopolitical status quo in the region following World War I. To present a united front against Bulgarian designs on their territories, the signatories agreed to suspend all disputed territorial claims against each other and their immediate neighbors which followed in the aftermath of the war and a rise in various regional ethnic minority tensions. Other nations in the region that had been involved in related diplomacy refused to sign the document, including Italy, Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary and the Soviet Union. The pact became effective on the day that it was signed. It was registered in the League of Nations Treaty Series on 1 October 1934.
 W
WThe Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, is an international agreement governing copyright, which was first accepted in Berne, Switzerland, in 1886.
 W
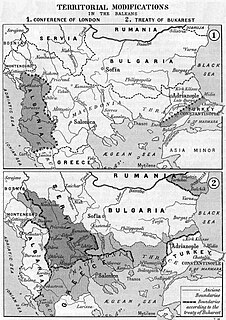
WThe Treaty of Bucharest was concluded on 10 August 1913, by the delegates of Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, Montenegro and Greece. The Treaty was concluded in the aftermath of the Second Balkan War and amended the previous Treaty of London, which ended the First Balkan War. About one month later, the Bulgarians signed a separate border treaty with the Ottomans, who had regained some territory west of the Enos-Midia Line during the second war.
 W
WThe Treaty of Bucharest of 1916 was signed between Romania and the Entente Powers on 4 /17 August 1916 in Bucharest. The treaty stipulated the conditions under which Romania agreed to join the war on the side of the Entente, particularly territorial promises in Austria-Hungary. The signatories bound themselves to keep secret the contents of the treaty until a general peace was concluded.
 W
WThe Treaty of Bucharest (1918) was a peace treaty between Romania on the one side and the Central Powers on the other, following the stalemate reached after the campaign of 1917 left Romania isolated after Russia's unilateral exit from World War I.
 W
WThe Treaty of Buftea was a preliminary peace treaty between the Kingdom of Romania on one side and the Central Powers on the other.
 W
WThe Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place due to the start of World War I.
 W
WThe Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place due to the start of World War I.
 W
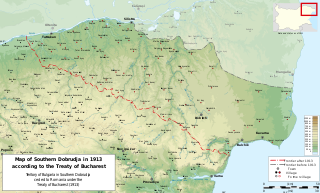
WThe Treaty of Craiova was signed on 7 September 1940 and ratified on 13 September 1940 by the Kingdom of Bulgaria and the Kingdom of Romania. Under its terms, Romania had to allow Bulgaria to retake Southern Dobruja, which Romania had gained after the 1913 Second Balkan War. Bulgaria had to pay 1 million lei as compensation for the investment provided to the region by Romania.
 W
WThe First Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded in Armies in the Field, held on 22 August 1864, is the first of four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. It defines "the basis on which rest the rules of international law for the protection of the victims of armed conflicts." After the first treaty was adopted in 1864, it was significantly revised and replaced in 1906, 1929, and finally 1949. It is inextricably linked to the International Committee of the Red Cross, which is both the instigator for the inception and enforcer of the articles in these conventions.
 W
WThe Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place due to the start of World War I.
 W
WThe International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice through setting international labour standards. Founded in 1918 under the League of Nations, it is the first and oldest specialised agency of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 2,700 staff from over 150 nations, of whom 900 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.
 W
WThe International Opium Convention, signed at The Hague on January 23, 1912 during the First International Opium Conference, was the first international drug control treaty. It was registered in League of Nations Treaty Series on January 23, 1922. The United States convened a 13-nation conference of the International Opium Commission in 1909 in Shanghai, China, in response to increasing criticism of the opium trade. The treaty was signed by Germany, the United States, China, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Persia, Portugal, Russia, and Siam. The Convention provided, "The contracting Powers shall use their best endeavours to control, or to cause to be controlled, all persons manufacturing, importing, selling, distributing, and exporting morphine, cocaine, and their respective salts, as well as the buildings in which these persons carry such an industry or trade."
 W
WThe Kellogg–Briand Pact is a 1928 international agreement in which signatory states promised not to use war to resolve "disputes or conflicts of whatever nature or of whatever origin they may be, which may arise among them". There were no mechanisms for enforcement. Parties failing to abide by this promise "should be denied of the benefits furnished by [the] treaty". It was signed by Germany, France, and the United States on 27 August 1928, and by most other states soon after. Sponsored by France and the U.S., the Pact renounced the use of war and calls for the peaceful settlement of disputes. Similar provisions were incorporated into the Charter of the United Nations and other treaties, and it became a stepping-stone to a more activist American policy. It is named after its authors, United States Secretary of State Frank B. Kellogg and French foreign minister Aristide Briand. The pact was concluded outside the League of Nations and remains in effect.
 W
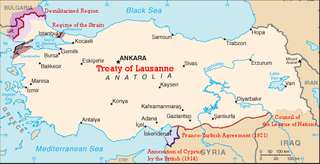
WThe Treaty of Lausanne was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. It officially settled the conflict that had originally existed between the Ottoman Empire and the Allied French Republic, British Empire, Kingdom of Italy, Empire of Japan, Kingdom of Greece, and the Kingdom of Romania since the onset of World War I. The original text of the treaty is in French. It was the result of a second attempt at peace after the failed Treaty of Sèvres. The earlier treaty had been signed in 1920, but later rejected by the Turkish national movement who fought against its terms. The Treaty of Lausanne ended the conflict and defined the borders of the modern Turkish Republic. In the treaty, Turkey gave up all claims to the remainder of the Ottoman Empire and in return the Allies recognized Turkish sovereignty within its new borders. It provided for the Greek-Turkish population exchange and allowed unrestricted civilian passage through the Turkish Straits.
 W
WThe Litvinov Protocol is the common name of an international peace treaty concluded in Moscow on February 9, 1929. Named after the chief Soviet diplomat moving the negotiations forward, Maxim Litvinov, the treaty provided for immediate implementation of the Kellogg-Briand Pact by its signatories, thereby formally renouncing war as a part of national foreign policy.
 W
WThe Metre Convention, also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations. The treaty created the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), an intergovernmental organization under the authority of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) and the supervision of the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM), that coordinates international metrology and the development of the metric system.
 W
WThe Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly-sur-Seine, France.
 W
WThe Paris Peace Treaties were signed on 10 February 1947 following the end of World War II in 1945. The Paris Peace Conference lasted from 29 July until 15 October 1946. The victorious wartime Allied powers negotiated the details of peace treaties with Italy, Romania, Hungary, Bulgaria and Finland. The treaties allowed the defeated Axis powers to resume their responsibilities as sovereign states in international affairs and to qualify for membership in the United Nations.
 W
WThe Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana, from Romania to Hungary.
 W
WThe Svalbard Treaty recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. The treaty regulates the demilitarisation of the archipelago. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities on the islands. As of 2012, Norway and Russia are making use of this right.
 W
WThe Tighina Agreement was an agreement between Germany and Romania about administration, economy and security issues of the Transnistria Governorate that entered into force on 30 August 1941. It was signed during World War II, while the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union was taking place. The Tiraspol Agreement in which Romania received the region had entered in force shortly before, on 19 August.
 W
WThe Tiraspol Agreement was an agreement between Germany and Romania signed on 19 August 1941 in the city of Tiraspol regarding the Romanian administration of the region of Transnistria, which became the Transnistria Governorate. It fell under the rule of Gheorghe Alexianu, under immediate subordination of Ion Antonescu, the Conducător (leader) of Romania. It was signed during World War II, while the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union was taking place. The Tighina Agreement in which specific issues of the region were discussed entered in force shortly after, on 30 August. The agreement allowed full Romanian control over the territory between the Dniester and Southern Bug rivers, with the exception of the city of Odessa. The latter was ceded to Romania in the Tighina Agreement with some privileges for Germany.
 W
WThe Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye was signed on 10 September 1919 by the victorious Allies of World War I on the one hand and by the Republic of German-Austria on the other. Like the Treaty of Trianon with Hungary and the Treaty of Versailles with Germany, it contained the Covenant of the League of Nations and as a result was not ratified by the United States but was followed by the US–Austrian Peace Treaty of 1921.
 W
WThe Treaty of Trianon was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon Palace in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formally ended World War I between most of the Allies of World War I and the Kingdom of Hungary. French diplomats played the major role in designing the treaty, with a mind to establishing French-led coalition of the newly formed nations. It regulated the status of the independent Hungarian state and defined its borders generally within the ceasefire lines established in November–December 1918 and left Hungary as a landlocked state that included 93,073 square kilometres (35,936 sq mi), 28% of the 325,411 square kilometres (125,642 sq mi) that had constituted the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary. The new Kingdom had a population of 7.6 million, 36% compared to the pre-war kingdom's population of 20.9 million. Though the areas that were allocated to neighbouring countries had a majority of non-Hungarians, in them lived 3.3 million Hungarians – 31% – who were now in a minority status. The treaty limited Hungary's army to 35,000 officers and men, and the Austro-Hungarian Navy ceased to exist. These decisions and their consequences has been the cause of deep resentment in Hungary ever since.
 W
WThe Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive military alliance that was eventually joined by Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria and Yugoslavia as well as by the German client state of Slovakia. Yugoslavia's accession provoked a coup d'état in Belgrade two days later. Germany, Italy and Hungary responded by invading Yugoslavia. The resulting Italo-German client state, known as the Independent State of Croatia, joined the pact on 15 June 1941.