 W
WThe Chen dynasty, also known as the Southern Chen, was the fourth and last of the Southern Dynasties in China. Following the Liang dynasty, the Chen dynasty was founded by Chen Baxian. The Chen dynasty further strengthened and revitalized the economy and culture of Southern China, and even made territorial expansions northward, laying the foundation for future dynasties. It was succeeded by the Sui dynasty, a short-lived dynasty that was then destroyed by the Tang dynasty. The Chen royal family continued to hold powerful high-ranking positions in both the Sui and Tang governments.
 W
WDuanzhou or Duan Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China in modern Guangdong, China, centering on modern Zhaoqing. Duan Prefecture was a major production center of inkstones.
 W
WFeilai Temple is a Buddhist temple located on the bank of Bei River, in Qingyuan, Guangdong, China. Feilai Temple was originally built in 520, but because of natural disasters has been rebuilt numerous times since then. The present version was completed in June 2004. The temple has a construction area of 4,000 square metres (43,000 sq ft).
 W
WThe Four Gates Pagoda is a Sui dynasty stone Chinese pagoda located in central Shandong Province, China. It is thought to be the oldest remaining pavilion-style stone pagoda in China. The oldest extant brick-built pagoda in China is the 40-metre-tall (130 ft) Songyue Pagoda of 523 AD.
 W
WThe Guanghua Temple, also known as the South Mountain Guanghua Temple (南山广寺), is a Buddhist temple located at the foot of Mount Phoenix (凤凰山), about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) south of Putian City, Fujian Province, People's Republic of China.
 W
WThe Guoqing Temple is a Buddhist temple on Mount Tiantai, in Taizhou, Zhejiang Province, China. Originally built in 598 during the Sui Dynasty, and renovated during the reign of the Qing Yongzheng Emperor, the temple is located roughly 220 kilometres (140 mi) from the city of Hangzhou. It was the initial site for the creation of the Tiantai school of Mahayana Buddhism, founded by Zhiyi. The temple covers an area of some 23,000 m2 (250,000 sq ft) and features 600 rooms in a total of 14 different halls, including the Grand Hall of Sakyamuni, the Hall of Five Hundred Arhats and the Hall of Monk Jigong. The exterior of the building features Chinese pagodas such as the Sui Pagoda, the Seven Buddha Pagoda, and the Memorial Pagoda of Monk Yi Xing.
 W
WHangzhou or Hang Prefecture (589–1129) was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China located in modern northern Zhejiang, China, around modern Hangzhou. The prefecture was called Yuhang Commandery from 607 to 621 and from 742 to 758. Hang Prefecture was the capital of the Wuyue kingdom (907–978), inside which it was known as Xi Prefecture, and during its last years of the kingdom, as Qiantang Prefecture.
 W
WThe Hanging Temple, also Hengshan Hanging Temple, Hanging Monastery or Xuankong Temple is a temple built into a cliff near Mount Heng in Hunyuan County, Datong City, Shanxi Province, China. The closest city is Datong, 64 kilometres (40 mi) to the northwest. Along with the Yungang Grottoes, the Hanging Temple is one of the main tourist attractions and historical sites in the Datong area. Built more than 1,500 years ago, this temple is notable not only for its location on a sheer precipice but also because it is the only existing temple with the combination of three Chinese traditional religions: Buddhism, Taoism, and Confucianism. The structure is kept in place with oak crossbeams fitted into holes chiseled into the cliffs. The main supportive structure is hidden inside the bedrock. The monastery is located in the small canyon basin, and the body of the building hangs from the middle of the cliff under the prominent summit, protecting the temple from rain erosion and sunlight. Coupled with the repair of the dynasties, the color tattoo in the temple is relatively well preserved.
 W
WHualin Temple, also known as the Temple of the Five Hundred Genii or Gods, is a Buddhist temple in Guangzhou, China.
 W
WJingye Temple is a Buddhist temple located on the north slope of Zhongnan Mountains, in Chang'an District, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China. It is the cradle of Risshū.
 W
WThe Liang dynasty (502–557), also known as the Southern Liang, was the third of the Southern Dynasties during China's Southern and Northern Dynasties period. It was located in South China and succeeded by the Chen dynasty in 557. The small rump state Western Liang (555–587), located in Central China, continued until it was destroyed in 587 by the Sui dynasty.
 W
WThe Liang (555–587), known in historiography as the Western Liang (西梁) or the Later Liang (後梁) to distinguish it from the earlier Liang dynasty (502–557), was a small puppet state during the Northern and Southern dynasties period, located in the middle Yangtze region in today's central Hubei province. From 555 to 557 it was subservient to the Western Wei, from 557 to 581 to the Northern Zhou, and from 581 to 587 to the Sui dynasty before the Sui annexed it.
 W
WLinggu Temple is a famous Buddhist temple in Nanjing. It is now surrounded by a large park.
 W
WLishui is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Zhejiang province, People's Republic of China. It borders Quzhou, Jinhua and Taizhou to the north, Wenzhou to the southeast, and the province of Fujian to the southwest. The name of the city literally means "Beautiful Waters."
 W
WThe Longxing Monastery or Longxing Temple is an ancient Buddhist monastery located in the town of Zhengding in Hebei Province, China, approximately 15 kilometers north of the provincial capital of Shijiazhuang. It has been referred to as the "Best Temple south of Beijing".
 W
WLuzhou or Lu Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China centering on modern Hefei, Anhui, China. It existed (intermittently) from 581 to 1277.
 W
WMizhou or Mi Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China in modern southeastern Shandong, China. It existed (intermittently) from 585 until 1368 upon the foundation of the Ming dynasty.
 W
WThe Northern Qi, also called Later Qi and Gao Qi, was one of the Northern dynasties of imperial China history and ruled northeastern China from 550 to 577. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wenxuan, and it was ended following attacks from Northern Zhou.
 W
WThe Shuanglin Temple is a large Buddhist temple in the Shanxi Province of China. It is situated in the countryside of Qiaotou village about 6–7 kilometres (3.7–4.3 mi) southwest of the ancient city of Pingyao. It is among the many cultural monuments located in the Pingyao, which is a UNESCO World Heritage site inscribed in 1997. The temple is protected by the state administration.
 W
WThe Songyue Pagoda, constructed in AD 523, is located at the Songyue Monastery on Mount Song, in Henan province, China. Built during the Northern Wei Dynasty, this pagoda is one of the few intact sixth-century pagodas in China and is also the earliest known Chinese brick pagoda. Most structures from that period were made of wood and have not survived, although ruins of rammed earth fortifications still exist.
 W
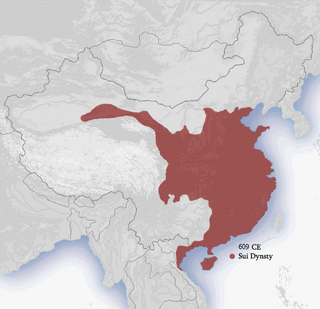
WThe Sui dynasty was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China of pivotal significance. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties and reinstalled the rule of ethnic Han in the entirety of China proper, along with sinicization of former nomadic ethnic minorities within its territory. It was succeeded by the Tang dynasty, which largely inherited its foundation.
 W
WTaogong Palace is a Taoist temple located on the west side of Linxiang Hill (临湘山), beside the Liuyang River, in Langli Subdistrict, Changsha County, Hunan, China. The temple covers a total area of 7,333.333 square metres (78,935.34 sq ft), with more than 1,852 square metres (19,930 sq ft) of floor space.
 W
WThe Temple of the Six Banyan Trees or Liurong Temple is a Buddhist temple in Guangzhou, China, originally built in AD 537.
 W
WThe Eastern Wei followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei, and ruled northern China from 534 to 550. As with Northern Wei, the ruling family of Eastern Wei were members of the Tuoba clan of the Xianbei.
 W
WThe Western Wei followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei, and ruled northern China from 535 to 557. As with the Northern Wei state that preceded it, the ruling family of Western Wei were members of the Tuoba clan of the Xianbei.
 W
WXingguo Temple, more commonly known as Zhangbafo, is a Buddhist temple located in Hubin Town, Binzhou, Shandong, China.
 W
WZhengzhou or Zheng Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China centering on modern Zhengzhou, Henan, China. It existed (intermittently) from 583 until 1913 after the foundation of the Republic.
 W
WThe Northern Zhou followed the Western Wei, and ruled northern China from 557 to 581 AD. The last of the Northern Dynasties of China's Northern and Southern dynasties period, it was eventually overthrown by the Sui Dynasty. Like the preceding Western and Northern Wei dynasties, the Northern Zhou emperors were of Xianbei descent.