 W
WIndus script font is a Private Use Areas (PUA) font, developed by National Fund for Mohenjo-daro and launched on International Conference on Mohenjo-daro & Indus Valley Civilisation on 8 February 2017.
 W
WThe Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread, its sites spanning an area stretching from northeast Afghanistan, through much of Pakistan, and into western and northwestern India. It flourished in the basins of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial, mostly monsoon-fed, rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the seasonal Ghaggar-Hakra river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.
 W
WThe Arctic Home in the Vedas is a 1903 book on the origin of Aryanic People by Indian nationalist, teacher, and an independence activist Bal Gangadhar Tilak. It propounded the idea that the North Pole was the original home of Aryans during the pre-glacial period which they had to leave due to the ice deluge around 8000 B.C. and had to migrate to the Northern parts of Europe and Asia in search of lands for new settlements. In support to his theory, Tilak presented certain Vedic hymns, Avestic passages, Vedic chronology and Vedic calendars with interpretations of the contents in detail.
 W
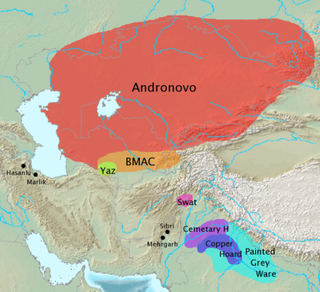
WThe Cemetery H culture was a Bronze Age culture in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, from about 1900 BC until about 1300 BC. It was a regional form of the late phase of the Harappan civilisation.
 W
WThe Chautang, originating in Siwalik Hills, is a tributary of Sarsuti river which in turn is tributary of Ghaggar river in of Haryana state of India.
 W
WDancing Girl is a prehistoric bronze sculpture made in lost-wax casting about c. 2300-1750 BCE in the Indus Valley Civilisation city of Mohenjo-daro, which was one of the earliest cities. The statue is 10.5 centimetres (4.1 in) tall, and depicts a naked young woman or girl with stylized proportions standing in a confident, naturalistic pose. Dancing Girl is well-regarded as a work of art, and is a cultural artefact of the Indus Valley Civilisation.
 W
WThe Tangri River, also called the Dangri River, which originates in the Shivalik Hills, is a tributary of the Ghaggar River in the Haryana state of India.
 W
WThe Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage and as the Hakra downstream of the barrage. The Hakra river is hydraulically connected to the Nara River provided it has adequate flow to maintain surface flow. After the construction of the Otu Barrage, the downstream Hakra river dried up fully but subsurface flow is maintained to the Nara river which becomes later the delta channel of the Indus River before joining the sea via Kori Creek in Gujarat state.
 W
WThe Kaushalya river, a tributary of Ghaggar river, is a river in Panchkula district of Haryana state of India.
 W
WThe Markanda river in Himachal Pradesh and Haryana states of India is a tributary of Ghaggar river, flowing through Sirmaur District, Ambala district and Shahabad Markanda town in Kurukshetra district. The Markanda river's ancient name was Aruna.
 W
WThe Ghazi Shah Mound is most ancient archaeological site located in Johi Tehsil Dadu District Sindh, Pakistan. It was explored by N. G. Majumdar and Louis Flam has also studied and surveyed this ancient site. It is very earliest site of Indus Valley Civilization dates back to 4000 to 6000 years.
 W
WHakra Ware culture is a material culture which is contemporaneous with the early Harappan Ravi phase culture of the Indus Valley. Hakra Ware culture is characterized by handmade vessels with mud and grit applied to the surface. The Hakra Wares culture also made structures in the form of subterranean dwelling pits, cut into the natural soil. The walls and floor of these pits were plastered with the yellowish alluvium of the Hakra valley. The first example was found near Jalilpur on the Ravi River about 80 miles (130 km) southwest of Harrappa in 1972. According to Rao, Hakra Ware has been found at Bhirrana, and is pre-Harappan, dating to the 8th–7th millennium BCE.
 W
WHarappa is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about 24 km (15 mi) west of Sahiwal. The site takes its name from a modern village located near the former course of the Ravi River which now runs 8 km (5.0 mi) to the north. The current village of Harappa is less than 1 km (0.62 mi) from the ancient site. Although modern Harappa has a legacy railway station from the British Raj period, it is a small crossroads town of 15,000 people today.
 W
WHarappa architecture is the architecture of the Indus Valley Civilization, an ancient society of people who lived during circa 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE in the Indus Valley of modern-day India and Pakistan.
 W
WInamgaon is a post-Harappan agrarian village and archaeological site located in Maharashtra, western India. Situated along the right bank of the Ghod River, it is considered to be the 'regional centre' of the Bhima Valley.
 W
WThe Indus River is one of the main rivers of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in the Indian subcontinent. It flows through China, India, and Pakistan. Originating in the Tibetan Plateau in the vicinity of Lake Manasarovar, the river runs a course through the Ladakh region of India towards Gilgit-Baltistan, and then flows in a southerly direction along the entire length of Pakistan to merge into the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi in Sindh. The Indus is the longest river of Pakistan.
 W
WThe Indus script is a corpus of symbols produced by the Indus Valley Civilization. Most inscriptions containing these symbols are extremely short, making it difficult to judge whether or not these symbols constituted a script used to record a language, or even symbolise a writing system. In spite of many attempts, the 'script' has not yet been deciphered, but efforts are ongoing. There is no known bilingual inscription to help decipher the script, and the script shows no significant changes over time. However, some of the syntax varies depending upon location.
 W
WIndus–Mesopotamia relations are thought to have developed during the second half of 3rd millennium BCE, until they came to a halt with the extinction of the Indus valley civilization after around 1900 BCE. Mesopotamia had already been an intermediary in the trade of lapis lazuli between South Asia and Egypt since at least about 3200 BCE, in the context of Egypt-Mesopotamia relations.
 W
WMeluḫḫa or Melukhkha is the Sumerian name of a prominent trading partner of Sumer during the Middle Bronze Age. Its identification remains an open question, but most scholars associate it with the Indus Valley Civilization.
 W
WMohenjo Daro is a 2016 Indian Hindi-language period action-adventure film written and directed by Ashutosh Gowariker. It is produced by Siddharth Roy Kapur for UTV Motion Pictures and Sunita Gowariker for Ashutosh Gowariker Productions (AGPPL), and features Hrithik Roshan and Pooja Hegde in the lead roles. It is a cinematic presentation based on the ancient Indus Valley civilization, and its city Mohenjo-daro, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
 W
WMohenjo-daro is an archaeological site in the province of Sindh, Pakistan. Built around 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation, and one of the world's earliest major cities, contemporaneous with the civilizations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Minoan Crete, and Norte Chico. Mohenjo-daro was abandoned in the 19th century BCE as the Indus Valley Civilization declined, and the site was not rediscovered until the 1920s. Significant excavation has since been conducted at the site of the city, which was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. The site is currently threatened by erosion and improper restoration.
 W
WThe Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a 4th millennium BC to 2nd millennium BC Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh. It is considered a candidate for association with the early Indo-Aryan or Vedic culture.
 W
WThe Pashupati Seal is a steatite seal that was discovered at the Mohenjo-daro archaeological site of the Indus Valley Civilization. The seal depicts a seated figure that is possibly tricephalic. It was once thought to be ithyphallic, an interpretation that is now mostly discarded. The man has a horned headdress and is surrounded by animals. He may represent a horned deity. The seal is kept in the National Museum of India in New Delhi.
 W
WThe Rakhigarhi Indus Valley Civilisation Museum, with a research center and hostel for researchers, is a proposed museum to be built in Rakhigarhi village in Hisar district of Haryana state in India.
 W
WThe Sahibi river, also called the Sabi River, is an ephemeral, rain-fed river flowing through Rajasthan, Haryana and Delhi states in India. It drains into Yamuna in Delhi, where its channeled course is also called the Najafgarh drain, which also serves as Najafgarh drain bird sanctuary. Sahibi is a seasonal river which is 300 km long and flows from Aravalli hills in Rajasthan to Haryana, of which 100 km is in Haryana.
 W
WThe ancient Indus Valley Civilization of historic India, including current day India and Sindh, Pakistan, was prominent in infrastructure, hydraulic engineering, and had many water supply and sanitation devices that were the first of their kind.
 W
WThe Sarsuti river, originating in Siwalik Hills and flowing through the palaeochannel of Yamuna, is a tributary of Ghaggar river in of Haryana state of India. Its course is dotted with archaeological and religious sites dating back to post-Harrapan Mahabharata sites from Vedic period, such as Kapal Mochan, Kurukshetra, Thanesar, Brahma Sarovar, Jyotisar, Bhor Saidan and Pehowa.
 W
WVastu shastra is a traditional Indian system of architecture originating in India. Texts from the Indian subcontinent describe principles of design, layout, measurements, ground preparation, space arrangement, and spatial geometry. Vastu Shastras incorporate traditional Hindu and Buddhist beliefs. The designs aim to integrate architecture with nature, the relative functions of various parts of the structure, and ancient beliefs utilising geometric patterns (yantra), symmetry, and directional alignments.
 W
WA war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, breaking their ranks and instilling terror. Elephantry are military units with elephant-mounted troops.