 W
WThe term French Louisiana refers to two distinct regions:first, to colonial French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by France during the 17th and 18th centuries; and, second, to modern French Louisiana, which stretches across the southern extreme of the present-day state of Louisiana.
 W
WLouisiana or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control 1682 to 1769 and 1801 (nominally) to 1803, the area was named in honor of King Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle. It originally covered an expansive territory that included most of the drainage basin of the Mississippi River and stretched from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico and from the Appalachian Mountains to the Rocky Mountains.
 W
WThe Arkansas Post was the first European settlement in the lower Mississippi River Valley and present-day Arkansas. Henri de Tonti established it in 1686 as a French trading post on the lower Arkansas River. The French and Spanish traded with the Quapaw people for years.
 W
WThe term cape has a different tradition of usage in the American Midwest along the Mississippi River. The middle Mississippi River Valley once formed part of the French Colonies of Quebec and Louisiana, also referred to as Upper Louisiana (Haute-Louisiane) or the Illinois Country. The Illinois Country also included the left bank of the Mississippi River in present-day Missouri.
 W
WThe Mississippi Company was a corporation holding a business monopoly in French colonies in North America and the West Indies. When land development and speculation in the region became frenzied and detached from economic reality, the Mississippi bubble became one of the earliest examples of an economic bubble.
 W
WCotton Gin Port is a ghost town in Monroe County, Mississippi, United States.
 W
WDuc du Maine was a slave ship that on June 6, 1719 brought the first African slaves to Louisiana. She had carried them from Senegambia.
 W
WFort Assumption was a French fortification constructed in 1739 on the fourth Chickasaw Bluff on the Mississippi River in Shelby County, present day Memphis, Tennessee. The fort was used as a base against the Chickasaw in the unsuccessful Indian-removal Campaign of 1739.
 W
WFort de Chartres was a French fortification first built in 1720 on the east bank of the Mississippi River in present-day Illinois. It was used as an administrative center for the province. Due generally to river floods, the fort was rebuilt twice, the last time in limestone in the 1750s in the era of French colonial control over Louisiana and the Illinois Country.
 W
WFort Maurepas, later known as Old Biloxi, was developed in colonial French Louisiana in April 1699 along the Gulf of Mexico. . Fort Maurepas was designated temporarily as the capital of Louisiana in 1719. The capital was moved from Mobile westward to Biloxi (present-day Mississippi} then to New Orleans in 1722 on the Mississippi River. Government buildings in the latter city were still under construction.
 W
WFort Orleans was a French fort in colonial North America, the first fort built by any European forces on the Missouri River. It was built near the mouth of the Grand River near present-day Brunswick. Intended to be the linchpin in the vast New France empire stretching from Montreal to New Mexico, the fort was occupied from 1723–1726. It was the first multi-year European settlement in what is today the U.S. state of Missouri.
 W
WFort Prudhomme, or Prud'homme, was a simple stockade fortification, constructed in late Feb. 1682 on one of the Chickasaw Bluffs of the Mississippi River in West Tennessee by Cavelier de La Salle's French canoe expedition of the Mississippi River Basin. The fortification was intended to provide shelter during the search for a member of the expedition who got lost at a stop while hunting, it was used by the expedition for only ten days. Fort Prudhomme was the first structure built by the French in Tennessee; its exact location is not known.
 W
WFort Rosalie was built by the French in 1716 within the territory of the Natchez Native Americans and it was part of the French colonial empire in the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi.
 W
WFort Toulouse, also called Fort des Alibamons and Fort Toulouse des Alibamons, is a historic fort near the city of Wetumpka, Alabama, United States, that is now maintained by the Alabama Historical Commission. The French founded the fort in 1717, naming it for Louis-Alexandre de Bourbon, comte de Toulouse. In order to counter the growing influence of the British colonies of Georgia and Carolina, the government of French Louisiana erected a fort on the eastern border of the Louisiana Colony in what is now the state of Alabama.
 W
WThe French Colonial Historic District is a historic district that encompasses a major region of 18th-century French colonization in southwestern Illinois. The district is anchored by Fort de Chartres and Fort Kaskaskia, two important French settlements and military posts in what was then the Illinois Country. The Kaskaskia village site is also included within the district; it includes the Pierre Menard House, the only surviving building from Illinois' first state capital. Over a dozen French houses in Prairie du Rocher are also part of the district, including the poteaux-sur-sol Creole House and the 1735 Meilliere House. In addition to the French sites, the district also includes several Native American archaeological sites, such as the Modoc Rock Shelter, the Kolmer Site, the Waterman Site, and the Henke Site.
 W
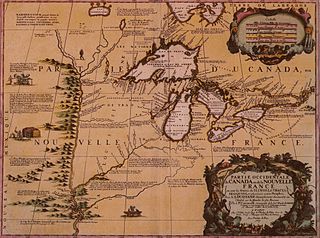
WThe Illinois Country — sometimes referred to as Upper Louisiana — was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s in what is now the Midwestern United States. While these names generally referred to the entire Upper Mississippi River watershed, French colonial settlement was concentrated along the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers in what is now the U.S. states of Illinois and Missouri, with outposts in Indiana. Explored in 1673 from Green Bay to the Arkansas River by the Canadien expedition of Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, the area was claimed by France. It was settled primarily from the Pays d'en Haut in the context of the fur trade. Over time, the fur trade took some French to the far reaches of the Rocky Mountains, especially along the branches of the broad Missouri River valley. The French name, Pays des Illinois, means "Land of the Illinois [plural]" and is a reference to the Illinois Confederation, a group of related Algonquian native peoples.
 W
WPierre Le Moyne d'Iberville was a soldier, ship captain, explorer, colonial administrator, knight of the order of Saint-Louis, adventurer, privateer, trader, member of Compagnies Franches de la Marine and founder of the French colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal of French colonist parents.
 W
WThe Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from France in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, most of it inhabited by American Indians; for the majority of the area, what the United States bought was the "preemptive" right to obtain Indian lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The total cost of all subsequent treaties and financial settlements over the land has been estimated to be around 2.6 billion dollars.
 W
WThe Mississippi Company was a corporation holding a business monopoly in French colonies in North America and the West Indies. When land development and speculation in the region became frenzied and detached from economic reality, the Mississippi bubble became one of the earliest examples of an economic bubble.
 W
WMissouri French or Illinois Country French also known as français vincennois, français Cahok, and nicknamed "Paw-Paw French " often by individuals outside the community but not exclusively, is a variety of the French language formerly spoken in the upper Mississippi River Valley in the Midwestern United States, particularly in eastern Missouri. The language is one of the major varieties of French that developed in the United States and at one point was widely spoken in areas of Bonne Terre, Valles Mines, Desloge, De Soto, Ste. Genevieve, Old Mines, Saint Louis, Richwoods, Prairie du Rocher, Cahokia, Kaskaskia, and Vincennes as well as several other locations. Speakers of Missouri French may call themselves "créoles" as they are descendants of the early French settlers of Illinois Country.
 W
WDeed from the Five Nations to the King, of their Beaver Hunting Ground, more commonly known as the Nanfan Treaty, was an agreement made between the representatives of the Iroquois Confederacy with John Nanfan, the acting colonial governor of New York, on behalf of The Crown. The treaty was conducted in Albany, New York, on July 19, 1701, and amended by both parties on September 14, 1726.
 W
WNew Orleans is a consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With an estimated population of 390,144 in 2019, it is the most populous city in Louisiana. Serving as a major port, New Orleans is considered an economic and commercial hub for the broader Gulf Coast region of the United States.
 W
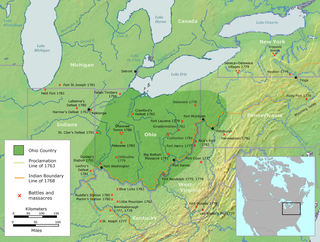
WThe Ohio Country was a name used in the mid- to late 18th century for a region of North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and north of the upper Ohio and Allegheny Rivers extending to Lake Erie. The area encompassed roughly all of present-day states of Ohio, northwestern West Virginia, Western Pennsylvania, and a wedge of southeastern Indiana.
 W
WFort Maurepas, later known as Old Biloxi, was developed in colonial French Louisiana in April 1699 along the Gulf of Mexico. . Fort Maurepas was designated temporarily as the capital of Louisiana in 1719. The capital was moved from Mobile westward to Biloxi (present-day Mississippi} then to New Orleans in 1722 on the Mississippi River. Government buildings in the latter city were still under construction.
 W
WThe Old Mobile Site was the location of the French settlement La Mobile and the associated Fort Louis de La Louisiane, in the French colony of New France in North America, from 1702 until 1712. The site is located in Le Moyne, Alabama, on the Mobile River in the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta. The settlement served as the capital of French Louisiana from 1702 until 1711, when the capital was relocated to the site of present-day Mobile, Alabama. The settlement was founded and originally governed by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville. Upon the death of d'Iberville, the settlement was governed by his younger brother, Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville. The site can be considered a French colonial counterpart to the English settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. The settlement site and fort were listed on the National Register of Historic Places on May 6, 1976. The Old Mobile Site was determined eligible for designation as a National Historic Landmark on January 3, 2001.
 W
WThe Cathedral-Basilica of Saint Louis, King of France, also called St. Louis Cathedral, is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New Orleans and is the oldest cathedral in continuous use in what would become the United States. It is dedicated to Saint Louis, also known as King Louis IX of France. The first church on the site was built in 1718; the third, under the Spanish rule, built in 1789, was raised to cathedral rank in 1793. The original St. Louis Cathedral was burned during the great fire of 1788 and was expanded and largely rebuilt and completed in the 1850s, with little of the 1789 structure remaining.
 W
WSt. Martinville is a city in, and the parish seat of, St. Martin Parish, Louisiana, United States. It lies on Bayou Teche, sixteen miles south of Breaux Bridge, eighteen miles southeast of Lafayette, and nine miles north of New Iberia. The population was 6,114 at the 2010 census, down from 6,989 in 2000. It is part of the Lafayette Metropolitan Statistical Area.
 W
WSlavery in New France was practiced by some of the indigenous populations, which enslaved outsiders as captives in warfare, but it was European colonization that made commercial chattel slavery become common in New France. By 1750, two thirds of the enslaved peoples in New France were indigenous, and by 1843, most enslaved people were black.
 W
WThe Illinois Country — sometimes referred to as Upper Louisiana — was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s in what is now the Midwestern United States. While these names generally referred to the entire Upper Mississippi River watershed, French colonial settlement was concentrated along the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers in what is now the U.S. states of Illinois and Missouri, with outposts in Indiana. Explored in 1673 from Green Bay to the Arkansas River by the Canadien expedition of Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, the area was claimed by France. It was settled primarily from the Pays d'en Haut in the context of the fur trade. Over time, the fur trade took some French to the far reaches of the Rocky Mountains, especially along the branches of the broad Missouri River valley. The French name, Pays des Illinois, means "Land of the Illinois [plural]" and is a reference to the Illinois Confederation, a group of related Algonquian native peoples.
 W
WThe Villasur expedition of 1720 was a Spanish military expedition intended to check New France's growing influence on the North American Great Plains, led by Lieutenant-General Pedro de Villasur. Pawnee and Otoe Indians attacked the expedition in Nebraska, killing 36 of the 40 Spaniards, 10 of their Indian allies, and a French guide. The survivors retreated to their base in New Mexico.