 W
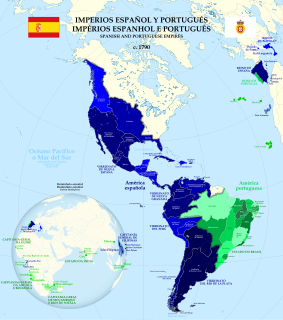
WThe Spanish colonization of the Americas began under the Crown of Castile and spearheaded by the Spanish conquistadors. The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions in South America and the Caribbean. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer this vast territory. The main motivations for colonial expansion were profit and the spread of Catholicism through indigenous conversions.
 W
WThe Storming of the Teocalli by Cortez and his troops is an 1848 oil on canvas painting by the German American history painter, Emanuel Leutze.
 W
WPedro de Alvarado y Contreras was a Spanish conquistador and governor of Guatemala. He participated in the conquest of Cuba, in Juan de Grijalva's exploration of the coasts of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Gulf of Mexico, and in the conquest of Mexico led by Hernán Cortés. He is considered the conquistador of much of Central America, including Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador. Although renowned for his skill as a soldier, Alvarado is known also for the cruelty of his treatment of native populations, and mass murders committed in the subjugation of the native peoples of Mexico.
 W
WThe Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía. The conflict begun at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquest attempt establishing cities and forcing Mapuches into servitude. It subsequently evolved over time into phases, drawn-out sieges, slave-hunting expeditions, pillaging raids, punitive expeditions, and renewed Spanish attempts to secure lost territories. Abduction of women and war rape was common on both sides.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the events by Spanish conquerors, their indigenous allies, and the defeated Aztecs. It was not solely a contest between a small contingent of Spaniards defeating the Aztec Empire but rather the creation of a coalition of Spanish invaders with tributaries to the Aztecs, and most especially the Aztecs' indigenous enemies and rivals. They combined forces to defeat the Mexica of Tenochtitlan over a two-year period. For the Spanish, the expedition to Mexico was part of a project of Spanish colonization of the New World after twenty-five years of permanent Spanish settlement and further exploration in the Caribbean.
 W
WThe Battle of Acajutla was a battle on June 8, 1524, between the Spanish conquistador Pedro de Alvarado and the standing army of Cuscatlan Pipils, an indigenous state, in the neighborhood of present-day Acajutla, near the coast of western El Salvador.
 W
WThe Battle of Cempoala was fought on 27 May 1520 at Cempoala, Mexico between the forces of Pánfilo de Narváez and the forces of Hernán Cortés, which were supported by a small number of indigenous soldiers.
 W
WAfter the assassination of Francisco Pizarro, in retaliation for his father's execution in 1538, Diego de Almagro II, El Mozo, continued to press claims as the rightful ruler of Peru and as leader of his father's supporters. His claims were largely unsuccessful, however, as Pizarro was succeeded as governor by Cristóbal Vaca de Castro, despite claims from his brother Gonzalo Pizarro, whose claims to join arms against the Almagristas and "El Mozo" largely remained unanswered.
 W
WThe Battle of Jaquijahuana was fought between the forces of Gonzalo Pizarro and Pedro de la Gasca, on April 9, 1548, during the Revolt of the Encomenderos by the Spanish conquistadores.
 W
WJuan Rodríguez Cabrillo was an Iberian maritime explorer best known for investigations of the West Coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the first European to explore present-day California, navigating along the coast of California in 1542–1543.
 W
WThe 'Battle' of Cajamarca also spelled Cajamalca was the ambush and seizure of the Inca ruler Atahualpa by a small Spanish force led by Francisco Pizarro, on November 16, 1532. The Spanish killed thousands of Atahualpa's counselors, commanders, and unarmed attendants in the great plaza of Cajamarca, and caused his armed host outside the town to flee. The capture of Atahualpa marked the opening stage of the conquest of the pre-Columbian civilization of Peru.
 W
WSpanish conquest of the Chibchan Nations refers to the conquest by the Spanish monarchy of the Chibcha language-speaking nations, mainly the Muisca and Tairona that inhabited present-day Colombia, beginning the Spanish colonization of the Americas.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of El Salvador was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Mesoamerican polities in the territory that is now incorporated into the modern Central American nation of El Salvador. El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America, and is dominated by two mountain ranges running east–west. Its climate is tropical, and the year is divided into wet and dry seasons. Before the conquest the country formed a part of the Mesoamerican cultural region, and was inhabited by a number of indigenous peoples, including the Pipil, the Lenca, the Xinca, and Maya. Native weaponry consisted of spears, bows and arrows, and wooden swords with inset stone blades; they wore padded cotton armour.
 W
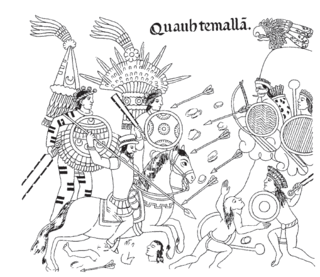
WThe Spanish conquest of Guatemala was a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, in which Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries.
 W
WHistoria general de las Indias is the account by Francisco López de Gómara of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. The first printing was in December 1552, in the workshop of Agustín Millán in Zaragoza, published under the title La istoria de las Indias
 W
WHistoria verdadera de la conquista de la Nueva España is a first-person narrative written in 1576 by military adventurer, conquistador, and colonist settler Bernal Díaz del Castillo (1492–1581), who served in three Mexican expeditions; those of Francisco Hernández de Córdoba (1517) to the Yucatán peninsula; the expedition of Juan de Grijalva (1518), and the expedition of Hernán Cortés (1519) in the Valley of Mexico; the history relates his participation in the fall of Emperor Moctezuma II, and the subsequent defeat of the Aztec Empire.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, also known as Conquest of Peru, was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military skirmishes, 168 Spanish soldiers under conquistador Francisco Pizarro, his brothers, and their native allies captured the Sapa Inca Atahualpa in the 1532 Battle of Cajamarca. It was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory in 1572 and colonization of the region as the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest of the Inca Empire, led to spin-off campaigns into present-day Chile and Colombia, as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin.
 W
WIndian auxiliaries or indios auxiliares is the term used in old Spanish chronicles and historical texts for the indigenous peoples who were integrated into the armies of the Spanish conquistadors with the purpose of supporting their advance and combat operations during the Conquest of America. They acted as guides, translators, or porters and in this role were also called yanakuna, particularly within the old Inca Empire and Chile. The term was also used for formations composed of indigenous warriors or Indios amigos, which they used for reconnaissance, combat, and as reserve in battle. The auxiliary Indians remained in use after the conquest, during some revolts, in border zones and permanent military areas, as in Chile in the Arauco War.
 W
WThe King's Fifth (1966) is a children's historical novel by Scott O'Dell that was the inspiration for the cartoon TV series The Mysterious Cities of Gold. It describes, from the point of view of a teenage Spanish Conquistador, how the European search for gold in the New World of the Americas affected people's lives and minds. The title refers to the one fifth share of spoils expected by the Spanish Crown.
 W
WThe Lienzo de Quauhquechollan is a 16th-century lienzo of the Nahua, a group of indigenous peoples of Mexico. It is one of two surviving Nahua pictorial records recounting the Spanish conquest of Guatemala and the earliest surviving maps of what is now Guatemala.
 W
WMabila was a small fortress town known to the paramount chief Tuskaloosa in 1540, in a region of present-day central Alabama. The exact location has been debated for centuries, but southwest of present-day Selma, Alabama, is one possibility.
 W
WThe Manche Chʼol were a former Chʼol-speaking Maya people inhabiting the extreme south of what is now the Petén Department of modern Guatemala, the area around Lake Izabal, and southern Belize. The Manche Chʼol took the name Manche from the name of their main settlement. They were the last group of eastern Cholan-speakers to remain independent and ethnically distinct. It is likely that they were descended from the inhabitants of Classic period Maya cities in the southeastern Maya region, such as Nim Li Punit, Copán and Quiriguá.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of the Maya was a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas, in which the Spanish conquistadores and their allies gradually incorporated the territory of the Late Postclassic Maya states and polities into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Maya occupied a territory that is now incorporated into the modern countries of Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras and El Salvador; the conquest began in the early 16th century and is generally considered to have ended in 1697.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of the Muisca took place from 1537 to 1540. The Muisca were the inhabitants of the central Andean highlands of Colombia before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. They were organised in a loose confederation of different rulers; the zipa of Bacatá, with his headquarters in Funza, the zaque of Boyacá, with his headquarters in Hunza, the iraca of the sacred City of the Sun Sugamuxi, the Tundama of Tundama, and several independent caciques. The leaders of the Confederation at the time of conquest were zipa Tisquesusa, zaque Quemuenchatocha, iraca Sugamuxi and Tundama in the northernmost portion of their territories. The Muisca were organised in small communities of circular enclosures, with a central square where the bohío of the cacique was located. They were called "Salt People" because of their extraction of salt in various locations throughout their territories, mainly in Zipaquirá, Nemocón, and Tausa. For the main part self-sufficient in their well-organised economy, the Muisca traded with the European conquistadors valuable products as gold, tumbaga, and emeralds with their neighbouring indigenous groups. In the Tenza Valley, to the east of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense where the majority of the Muisca lived, they extracted emeralds in Chivor and Somondoco. The economy of the Muisca was rooted in their agriculture with main products maize, yuca, potatoes, and various other cultivations elaborated on elevated fields. Agriculture had started around 3000 BCE on the Altiplano, following the preceramic Herrera Period and a long epoch of hunter-gatherers since the late Pleistocene. The earliest archaeological evidence of inhabitation in Colombia, and one of the oldest in South America, has been found in El Abra, dating to around 12,500 years BP.
 W
WLa Noche Triste was an important event during the Spanish conquest of Mexico, wherein Hernán Cortés, his army of Spanish conquistadors, and their native allies were driven out of the Aztec capital at Tenochtitlan.
 W
WThe Battle of Otumba was a battle during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. The battle was fought at Otumba de Gómez Farías, Mexico in 1520.
 W
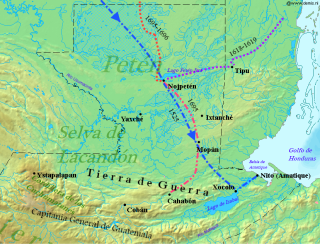
WThe Spanish conquest of Petén was the last stage of the conquest of Guatemala, a prolonged conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas. A wide lowland plain covered with dense rainforest, Petén contains a central drainage basin with a series of lakes and areas of savannah. It is crossed by several ranges of low karstic hills and rises to the south as it nears the Guatemalan Highlands. The conquest of Petén, a region now incorporated into the modern republic of Guatemala, climaxed in 1697 with the capture of Nojpetén, the island capital of the Itza kingdom, by Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi. With the defeat of the Itza, the last independent and unconquered native kingdom in the Americas fell to European colonisers.
 W
WRelación breve de la conquista de la Nueva España is the account of friar Francisco de Aguilar, who in his youth took part in the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire as a conquistador under the command of Hernán Cortés.
 W
WThe Fall of Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Aztec Empire, was a decisive event in the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. It occurred in 1521 following extensive manipulation of local factions and exploitation of pre-existing divisions by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés, who was aided by the support of his indigenous allies and his interpreter and companion La Malinche.
 W
WTlaxcala was a pre-Columbian city and state in central Mexico.
 W
WThe Villasur expedition of 1720 was a Spanish military expedition intended to check New France's growing influence on the North American Great Plains, led by Lieutenant-General Pedro de Villasur. Pawnee and Otoe Indians attacked the expedition in Nebraska, killing 36 of the 40 Spaniards, 10 of their Indian allies, and a French guide. The survivors retreated to their base in New Mexico.