 W
WThe Hindenburg Line was a German defensive position built during the winter of 1916–1917 on the Western Front during the First World War. The line ran from Arras to Laffaux, near Soissons on the Aisne. In 1916, the Battle of Verdun and the Battle of the Somme left the German western armies exhausted and on the Eastern Front, the Brusilov Offensive had inflicted huge losses on the Austro-Hungarian armies and forced the Germans to take over more of the front. The declaration of war by Romania had placed additional strain on the German army and war economy.
 W
WOperation Alberich was the code name of a German military operation in France during the First World War. Two salients had been formed during the Battle of the Somme in 1916 between Arras and Saint-Quentin and from Saint-Quentin to Noyon. Alberich was planned as a strategic withdrawal to new positions on the shorter and more easily defended Hindenburg Line. General Erich Ludendorff was reluctant to order the withdrawal and hesitated until the last moment.
 W
WThe Drocourt-Quéant Line was a set of mutually supporting defensive lines constructed by Germany between the French towns of Drocourt and Quéant during World War I. This defensive system was part of the northernmost section of the Hindenburg Line, a vast German defensive system that ran through northeastern France.
 W
WFlanders Fields is a common English name of the World War I battlefields in an area straddling the Belgian provinces of West Flanders and East Flanders as well as the French department of Nord-Pas-de-Calais, part of which makes up the area known as French Flanders.
 W
WGrivesnes is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WGueudecourt is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WLe Hamel is a commune in the Somme department and Hauts-de-France region of northern France.
 W
WHancourt is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WHangard is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. The commune is centered on Hangard village.
 W
WHawthorn Ridge Redoubt was a German front-line fortification, west of the village of Beaumont Hamel on the Somme. The redoubt was built after the end of the Battle of Albert, and as French and later British attacks on the Western Front became more formidable, the Germans added fortifications and trench positions near the original lines around Hawthorn Ridge. At 7:20 a.m. on 1 July 1916, the British fired a huge mine beneath the Hawthorn Ridge Redoubt. Sprung ten minutes before zero hour, it was one of 19 mines detonated on the first day of the Battle of the Somme; the detonation of this mine was filmed by Geoffrey Malins. The attack on the redoubt by part of the 29th Division of VIII Corps was a costly failure.
 W
WThe Hohenzollern Redoubt was a strongpoint of the German 6th Army on the Western Front during the First World War, at Auchy-les-Mines near Loos-en-Gohelle in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France. Named after the House of Hohenzollern, the redoubt was fought for by German and British forces. Engagements took place from the Battle of Loos (25 September – 14 October 1915) to the beginning of the Battle of the Somme on 1 July 1916, including the Action of the Hohenzollern Redoubt in 1915 and the British Attack at the Hohenzollern Redoubt from 2 to 18 March 1916.
 W
WThe Hohenzollern Redoubt action, 2–18 March 1916 was fought on the Western Front during the First World War. The Hohenzollern Redoubt was a German defensive position north of Loos-en-Gohelle (Loos), a mining town north-west of Lens in France. The Redoubt was fought over by the British and German armies from the Battle of Loos to the beginning of the Battle of the Somme on 1 July 1916. Over the winter of 1915–1916, the 170th Tunnelling Company RE dug several galleries under the German lines in the area of the redoubt, which had changed hands several times since September 1915. In March 1916, the west side was held by the British and the east side was occupied by the Germans, with the front near a new German trench known as The Chord. No man's land had become a crater field and the Germans had an unobstructed view of the British positions from the Fosse 8 slag heap. The British front line was held by outposts to reduce the number of troops vulnerable to mine explosions and the strain of knowing that the ground could erupt at any moment.
 W
WThe Loss of the Kink Salient occurred during a local attack on 11 May 1916, by the 3rd Bavarian Division on the positions of the 15th (Scottish) Division. The attack took place at the west end of the Hohenzollern Redoubt near Loos, on the Western Front during the First World War. An unprecedented bombardment demolished the British front line, then specially trained German assault units rushed the survivors and captured the British front line and the second line of defence; British tunnellers were trapped in their galleries and taken prisoner.
 W
WThe First attack on Bullecourt was a military operation on the Western Front during the First World War. The 1st Anzac Corps of the British Fifth Army attacked in support of the Third Army, engaged in the Battle of Arras. The Report of the Battles Nomenclature Committee (1921) called operations subsidiary to the main Battle of Arras the Flanking Operation to the Arras Offensive.
 W
WThe German attack on Lagnicourt on 15 April 1917 was a military operation on the Western Front during the First World War. Four German divisions conducted a spoiling attack on the positions of the 1st Anzac Corps of the British Fifth Army. The attack was intended to delay the advance of the Fifth Army towards the Hindenburg Line, cause as many casualties and destroy as much equipment, particularly artillery, as possible.
 W
WLesbœufs is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WThe Lochnagar mine south of the village of La Boisselle in the Somme département was an underground explosive charge, secretly planted by the British during the First World War, to be ready for 1 July 1916, the first day on the Somme. The mine was dug by the Tunnelling Companies of the Royal Engineers under a German field fortification known as Schwabenhöhe.
 W
WMaricourt is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. It is twinned with Brundall, Norfolk, England.
 W
WMolliens-au-Bois is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WMontauban-de-Picardie is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Its inhabitants are called "Montalbanais".
 W
WIn World War I, the small commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle, located some 22 miles (35 km) north-east of Amiens in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France, was the site of intense and sustained fighting between German and Allied forces. Between 1914 and 1916, the Western Front ran through the commune, and the villages were completely destroyed. After the Armistice of 11 November 1918, the former inhabitants returned and gradually rebuilt most of the infrastructure as it had been before the war.
 W
WOvillers-la-Boisselle is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WPozières is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
 W
WRouge Bouquet is a part of the Forêt de Parroy near the French village of Baccarat that was the site of a German artillery bombardment of American trench positions on 7 March 1918 at 15:20 on the Chausailles sector of the Western Front during World War I. The bombardment resulted in the burial of 21 men of the 165th Infantry Regiment, 42nd Rainbow Division of which only a few survived. The 22 men, including their platoon commander 1st Lieutenant John Norman, were assembled in a dugout when a German artillery shell landed on the roof of the dugout. A rescue effort by Major William J. "Wild Bill" Donovan was begun in haste attempting to dig the men but their efforts were hampered by mud-slides and continued enemy shelling. Two men were rescued and five dead were recovered before efforts had to be halted. The voices of other men could be heard for a while, but the remaining fifteen men died before rescue efforts could resume. Donovan was awarded the French Croix de Guerre for his actions during the attempted rescue.
 W
WThe Capture of Schwaben Redoubt was a tactical incident in the Battle of the Somme, 1916 during the First World War. The redoubt was a German strong point 500–600 yd (460–550 m) long and 200 yd (180 m) wide, built in stages since 1915, near the village of Thiepval and overlooking the River Ancre. It formed part of the German defensive system in the Somme sector of the Western Front during the First World War and consisting of a mass of machine-gun emplacements, trenches and dug-outs. The redoubt was defended by the 26th Reserve Division, from Swabia in south-west Germany, which had arrived in the area during the First Battle of Albert in 1914. Troops of the 36th (Ulster) Division captured the redoubt on 1 July 1916, until forced out by German artillery-fire and counter-attacks after dark.
 W
WThe Siegfried Line, known in German as the Westwall, was a German defensive line built during the 1930s opposite the French Maginot Line. It stretched more than 630 km (390 mi); from Kleve on the border with the Netherlands, along the western border of the old German Empire, to the town of Weil am Rhein on the border to Switzerland – and featured more than 18,000 bunkers, tunnels and tank traps.
 W
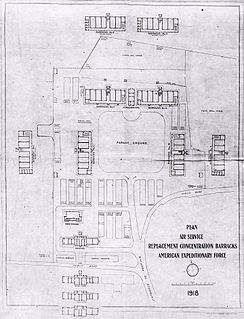
WThe Air Service Replacement Concentration Barracks is a former military facility in the vicinity of Saint-Maixent-l'École, Poitou-Charentes, France. It was used by the Air Service, United States Army as the Air Service Replacement Concentration Barracks during World War I. From the facility, Air Service personnel were sent into combat on the Western Front.
 W
WLe Vernet Internment Camp, or Camp Vernet, was a concentration camp in Le Vernet, Ariège, near Pamiers, in the French Pyrenees. Built in 1918 as a barracks but after WWI used as an internment camp for prisoners of war. From February 1939 to June 1944, it was used as an internment camp, first for Republican refugees fleeing Spain after Franco's victory in the Spanish Civil War, in particular some 12,000 refugees, including soldiers of Durruti Column and others of the International Brigades, under the legitimate French government and then, as of May-June 1940, under the Vichy government after German occupation during the Second World War. Starting in 1940, apart from the prisoners coming from the Spanish Civil War, the Vichy government used it to house prisoners considered suspect or dangerous to the government, including members of the resistance and opponents of the Hitler, Mussolini and Pétain regimes. From 1942 until June 1944, it was used as a holding camp for Jewish families awaiting deportation to other camps. The last transport out of the camp in June 1944 took the prisoners to Dachau concentration camp.
 W
WThe German attack on Vimy Ridge was a local attack on the Western Front on 21 May 1916, during the First World War. The Germans intended to prevent mines being blown under German positions by capturing the British front line and mine gallery entrances. After the Third Battle of Artois The French Tenth Army had held positions on the western slope of Vimy Ridge and the German 6th Army occupied positions on the steeper eastern slope. During the Battle of Verdun, the Tenth Army was withdrawn and the British First Army and Third Army on either flank, took over the French positions.
 W
WThe Y Sap mine was an underground explosive charge, secretly planted by the British during the First World War and ready for 1 July 1916, the first day on the Somme. The mine was dug by the Tunnelling Companies of the Royal Engineers under a German machine-gun nest known as Blinddarm (appendix) in the front line, on the north side of the village of La Boisselle in the Somme département. The mine was named after Y Sap, the British trench from which the gallery was driven. It was one of 19 mines on the British sector to be blown at the start of the battle.
 W
WThe Zone Rouge is a chain of non-contiguous areas throughout northeastern France that the French government isolated after the First World War. The land, which originally covered more than 1,200 square kilometres (460 sq mi), was deemed too physically and environmentally damaged by conflict for human habitation. Rather than attempt to immediately clean up the former battlefields, the land was allowed to return to nature. Restrictions within the Zone Rouge still exist today, although the control areas have been greatly reduced.