 W
WThe Battle of Alamance, which took place on May 16, 1771, was the final battle of the War of the Regulation, a rebellion in colonial North Carolina over issues of taxation and local control, considered by some to be the opening salvo of the American Revolution. Named for nearby Great Alamance Creek, the battle took place in what was then Orange County and has since become Alamance County in the central Piedmont area, about 6 miles (9.7 km) south of present-day Burlington, North Carolina.
 W
WThe Anglo–Cherokee War, was also known from the Anglo-European perspective as the Cherokee War, the Cherokee Uprising, or the Cherokee Rebellion. The war was a conflict between British forces in North America and Cherokee Indian tribes during the French and Indian War. The British and the Cherokee had been allies at the start of the war, but each party had suspected the other of betrayals. Tensions between British-American settlers and the Cherokee increased during the 1750s, culminating in open hostilities in 1758.
 W
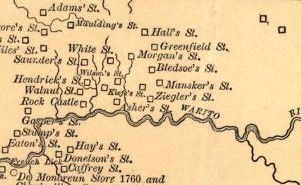
WBledsoe's Station, also known as Bledsoe's Fort, was an 18th-century, fortified, frontier, white settlement located in what is now Castalian Springs, Sumner County, Tennessee. The fort was built by long hunter and Sumner County pioneer Isaac Bledsoe in the early 1780s to protect Upper Cumberland settlers and migrants from hostile Native American attacks. While the fort is no longer standing, its location has been verified by archaeological excavations. The site is now part of Bledsoe's Fort Historical Park, a public park established in 1989 by Sumner County residents and Bledsoe's descendants.
 W
WThe Charles Robertson Grant, also known more simply as the Watauga Grant, was a transaction for the sale of land by the Cherokee Nation to Charles Robertson.
 W
WCherokee history is the written and oral lore, traditions, and historical record maintained by the living Cherokee people and their ancestors. In the 21st century, leaders of the Cherokee people define themselves as those persons enrolled in one of the three federally recognized Cherokee tribes: The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians, The Cherokee Nation, and The United Keetoowah Band of Cherokee Indians. The first live predominantly in North Carolina; the latter two tribes are based in Oklahoma. The Cherokee people have extensive written records, including detailed genealogical records, preserved in the Cherokee language, the Cherokee syllabary, and in the English language.
 W
WThe Cherokee Nation was a legal, autonomous, tribal government in North America recognized from 1794 to 1907. It was often referred to simply as "The Nation" by its inhabitants. The government was disbanded in 1907, after its land rights had been extinguished, prior to the admission of Oklahoma as a state. During the late 20th century, the Cherokee people reorganized, instituting a government with sovereign jurisdiction known as the Cherokee Nation.
 W
WChiaha was a Native American chiefdom located in the lower French Broad River valley in modern East Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. They lived in raised structures within boundaries of several stable villages. These overlooked the fields of maize, beans, squash, and tobacco, among other plants which they cultivated. Chiaha was the northern extreme of the paramount Coosa chiefdom's sphere of influence in the 16th century when the Spanish expeditions of Hernando de Soto and Juan Pardo passed through the area. The Chiaha chiefdom included parts of modern Jefferson and Sevier counties, and may have extended westward into Knox, Blount and Monroe counties.
 W
WFort Adair was a stockade fortification that served as a supply depot for early settlers migrating west. The structure was constructed in 1788 or around 1791 at Grassy Valley, an early European settlement in the Appalachian Ridge-and-Valley region of East Tennessee. The presence of a supply station encouraged more Europeans to settle in the vicinity. The town of Fountain Head was founded around Fort Adair by settlers of Grassy Valley and later renamed to Fountain City. Since its annexation in 1962, Fountain City is a neighborhood of northern Knoxville, Tennessee.
 W
WFort Blount was a frontier fort and federal outpost located along the Cumberland River in Jackson County, Tennessee, United States. Situated at the point where Avery's Trace crossed the river, the fort provided an important stopover for migrants and merchants travelling from the Knoxville area to the Nashville area in the 1790s. After the fort was abandoned around 1800, the community of Williamsburg developed on the site and served as county seat for the newly formed Jackson County from 1807 and 1819. The fort and now vanished village sites were added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.
 W
WFort Nashborough was the stockade established in early 1779 in the French Lick area of the Cumberland River valley, as a forerunner to the settlement that would become the city of Nashville, Tennessee. The log stockade was square in shape and covered 2 acres (8,100 m2). It contained 20 log cabins and was protection for the settlers against wild animals and Indians. Today, a reconstructed fortification, maintained by Nashville Parks and Recreation, stands near the site of the original structure.
 W
WFort Watauga, more properly Fort Caswell, was an American Revolutionary War fort that once stood at the Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. The fort was originally built in 1775–1776 by the area's frontier government, the Watauga Association, to help defend Watauga settlers from Native American attacks, which were in part instigated by the British. Fort Watauga was originally named Fort Caswell after North Carolina Governor Richard Caswell.
 W
WThe Great Grant Deed, also known as The Great Grant, was a transaction for the sale of property by the Cherokee Nation to Richard Henderson and Company. The grant is also known as the Lousia purchase or the Transylvania purchase. The transaction occurred at Sycamore Shoals on the Watauga River on March 17, 1775. The Great Grant was for lands forming Henderson's new Transylvania Colony comprising much of what is now the state of Kentucky.
 W
WIcehouse Bottom is a prehistoric Native American site in Monroe County, Tennessee, located on the Little Tennessee River in the southeastern United States. Native Americans were using the site as a semi-permanent hunting camp as early as 7500 BC, making it one of the oldest-known habitation areas in what is now the state of Tennessee. Analysis of the site's Woodland period artifacts shows evidence of an extensive trade network that reached to indigenous peoples in Georgia, North Carolina, and Ohio. This was later an area of known Cherokee settlements, the historic people encountered by Anglo-European settlers in the 18th and 19th centuries.
 W
WJames White's Fort, also known as White's Fort, was an 18th-century settlement that became Knoxville, Tennessee, in the United States. The name also refers to the fort, itself.
 W
WKingston Pike is a highway in Knox County, Tennessee, United States, that connects Downtown Knoxville with West Knoxville, Farragut, and other communities in the western part of the county. The road follows a merged stretch of U.S. Route 11 (US 11) and US 70. From its initial construction in the 1790s until the development of the Interstate Highway System in the 1960s, Kingston Pike was the main traffic artery in western Knox County, and an important section of several cross-country highways. The road is now a major commercial corridor, containing hundreds of stores, restaurants, and other retail establishments.
 W
WLong Meadow is an historic house in Carters Valley in Hawkins County, Tennessee, near Surgoinsville. It was built in 1762 and is considered to be Tennessee's oldest wooden structure. It was erected on land that its builder, William Young, had received through a royal land grant. The house was originally a log structure, with several additions added in the 19th century.
 W
WA longhunter was an 18th-century explorer and hunter who made expeditions into the American frontier wilderness for as much as six months at a time. Historian Emory Hamilton asserts that "The Long Hunter was peculiar to Southwest Virginia only, and nowhere else on any frontier did such hunts ever originate" although the term has been used loosely to describe any unofficial American explorer of the period. Most long hunts started in the Holston River Valley near Chilhowie, Virginia. The hunters came from there and the adjacent valley of the Clinch River, where they were land owners or residents. The parties of two or three men usually started their hunts in October and ended toward the end of March or early in April.
 W
WMansker's Station, also called Mansker's Fort was a station along Avery's Trace in Middle Tennessee. It was built by Kasper Mansker.
 W
WThe Province of North Carolina was a British colony that existed in North America from 1712 to 1776, created as a proprietary colony. The power of the British government was vested in a governor of North Carolina, but the colony declared independence from Great Britain in 1776. The Province of North Carolina had four capitals: Bath (1712–1722), Edenton (1722–1743), Brunswick (1743–1770), and New Bern. The colony later became the states of North Carolina and Tennessee, and parts of the colony combined with other territory to form the states of Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi.
 W
WThe Old Stone Fort is a prehistoric Native American structure located in Coffee County, Tennessee, in the Southeastern United States. The structure was most likely built between 80 and 550 AD during the Middle Woodland period. It is the most complex hilltop enclosure found in the South and was likely used for ceremonial purposes rather than defense.
 W
WOverhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the west side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 18th-century European traders and explorers from British colonies along the Atlantic coast, as they had to cross the mountains to reach these settlements.
 W
WJuan Pardo was a Spanish explorer who was active in the later half of the sixteenth century. He led a Spanish expedition through what is now North and South Carolina and into eastern Tennessee on the orders of Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, who had built Fort San Felipe (1566), and established Santa Elena, on present-day Parris Island; these were the first Spanish settlements in what is now South Carolina. While leading an expedition deeper in-country, Pardo founded Fort San Juan at Joara, the first European settlement (1567–1568) in the interior of North Carolina.
 W
WThe Path Grant Deed is a document regarded as a first step toward the American westward migration across the Appalachian Mountains, resulting from negotiations at Sycamore Shoals in March 1775. The land acquired within the boundaries of the Path Grant allowed Daniel Boone to develop the Wilderness Road free from attack or claims by the Cherokee. The Path Grant was recorded on November 15, 1794 by the Hawkins County, Tennessee registrar in Deed Book #1, pages 147-151
 W
WThe Royal Colonial Boundary of 1665 marked the border between the Colony of Virginia and the Province of Carolina from the Atlantic Ocean westward across North America. The line follows the parallel 36°30′ north latitude that later became a boundary for several U.S. states as far west as the Oklahoma Panhandle, and also came to be associated with the Missouri Compromise of 1820.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort Loudoun was an engagement during the Anglo-Cherokee War fought from February 1760 to August 1760 between the warriors of the Cherokee led by Ostenaco and the garrison of Fort Loudoun composed of British and colonial soldiers commanded by Captain Paul Demeré.
 W
WHernando de Soto was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula, and played an important role in Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States. He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River.
 W
WThe Territory South of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Southwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1790, until June 1, 1796, when it was admitted to the United States as the State of Tennessee. The Southwest Territory was created by the Southwest Ordinance from lands of the Washington District that had been ceded to the U.S. federal government by North Carolina. The territory's lone governor was William Blount.
 W
WThe Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals since prehistoric times, and Cherokees gathered there. As Europeans began settling the Trans-Appalachian frontier, the shoals proved strategic militarily, as well as shaped the economies of Tennessee and Kentucky. Today, the shoals are protected as a National Historic Landmark and are maintained as part of Sycamore Shoals State Historic Park.
 W
WTanasi was a historic Overhill Cherokee village site in present-day Monroe County, Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. The village was the namesake for the state of Tennessee. Abandoned by the Cherokee in the 19th century, since 1979 the town site has been submerged by the Tellico Lake impoundment of the Little Tennessee River. Tanasi served as the de facto capital of the Cherokee from as early as 1721 until 1730, when the capital shifted to Great Tellico.
 W
WThe Tellico Blockhouse was an early American outpost located along the Little Tennessee River in what developed as Vonore, Monroe County, Tennessee. Completed in 1794, the blockhouse was a US military outpost that operated until 1807; the garrison was intended to keep peace between the nearby Overhill Cherokee towns and encroaching early Euro-American pioneers in the area in the wake of the Cherokee–American wars. The Tellico Blockhouse was the site where several treaties were negotiated between the United States and the Cherokee, by which the latter ceded large portions of land in present-day Tennessee and Georgia in order to try to gain peace. The US provided various financial incentives for these actions. During this period, the blockhouse was the site of official liaisons between the United States government and the Cherokee.
 W
WThe Transylvania Colony, also referred to as the Transylvania Purchase, was a short-lived, extra-legal colony founded during 1775 by land speculator Richard Henderson, who controlled the North Carolina-based Transylvania Company. Henderson and his investors had reached an agreement to purchase a vast tract of Cherokee lands west of the southern and central Appalachian Mountains through the acceptance of the Treaty of Sycamore Shoals with most leading Cherokee chieftains then controlling these lands. In exchange for the land the tribes received goods worth, according to the estimates of some scholars, about 10,000 British pounds. To further complicate matters, this early American frontier land was also claimed at the same time by both the Province of Virginia and the North Carolina colony.
 W
WThe War of the Regulation, also known as the Regulator movement, was an uprising in British America's Carolina colonies, lasting from around 1765 to 1771, in which citizens took up arms against colonial officials, whom they viewed as corrupt. Though the rebellion did not change the power structure, some historians consider it a catalyst to the American Revolutionary War. Others like John Spencer Bassett take the view that the Regulators did not wish to change the form or principle of their government, but simply wanted to make the colony's political process more equal. They wanted better economic conditions for everyone, instead of a system that heavily benefited the colonial officials and their network of plantation owners mainly near the coast. Bassett interprets the events of the late 1760s in Orange and surrounding counties as "...a peasants' rising, a popular upheaval."
 W
WThe Watauga Association was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. Although it lasted only a few years, the Watauga Association provided a basis for what later developed into the state of Tennessee and likely influenced other western frontier governments in the trans-Appalachian region. North Carolina annexed the Watauga settlement area, by then known as the Washington District, in November 1776. Within a year, the area was placed under a county government, becoming Washington County, North Carolina, in November 1777. This area covers the present day Washington County, Carter County, and other areas now located in the northeast part of the state of Tennessee.