 W
WThe Allotriges or ‘Allotrigones’, were a small ‘Celticized’ mountain people mentioned alongside the Plentauri by Ptolemy and Strabo, as inhabitants of the region roughly corresponding to present-day northwestern La Rioja, around the area of the Ebro sources.
 W
WThe Arevaci or Aravaci, were a Celtic people who settled in the central Meseta of northern Hispania and dominated most of Celtiberia from the 4th to late 2nd centuries BC. The Vaccaei were their allies.
 W
WThe Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the Hispano-Celtic inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community of Principality of Asturias, the modern province of León, and the northern part of the modern province of Zamora, and eastern Trás os Montes in Portugal. They were a horse-riding highland cattle-raising people who lived in circular huts of stone drywall construction. The Albiones were a major tribe from western Asturias. Isidore of Seville gave an etymology as coming from a river Asturia, identified by David Magie with Órbigo river in the plain of León, by others the modern Esla river.
 W
WThe Autrigones were a pre-Roman tribe that settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the western Basque Country and northern Burgos and the East of Cantabria, Spain. Their territory limited with the Cantabri territory at west, the Caristii at east, the Berones at the southeast and the Turmodigi at the south. It is discussed whether the Autrigones were Celts, theory supported by the existence of toponyms of Celtic origin, such as Uxama Barca and other with -briga endings and that eventually underwent a Basquisation along with other neighboring tribes such as the Caristii and Varduli
 W
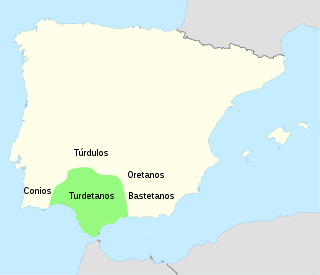
WThe Bastetani or Bastuli were an ancient Iberian (pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula. They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language. The relationship between the Iberian Bastetani and the Tartessian Mastieni is not entirely clear.
 W
WThe Belli, also designated Beli or Belaiscos were an ancient pre-Roman Celtic Celtiberian people who lived in the modern Spanish province of Zaragoza from the 3rd Century BC.
 W
WThe Berones were a pre-Roman Celtic people of ancient Spain, although they not were part of the Celtiberians, they lived north of the Celtiberians and close to the Cantabrian Conisci in the middle Ebro region between the Tirón and Alhama rivers.
 W
WThe Cantabri or Ancient Cantabrians, were a pre-Roman people, probably Celtic or pre-Celtic European, and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. These peoples and their territories were incorporated into the Roman Province of Hispania Tarraconensis in the year 19 BC, following the Cantabrian Wars.
 W
WThe Caristii were a pre-Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today are known as the historical territories of Biscay and Álava, in the Basque Country, northern Spain.
 W
WThe Carpetani were one of the Celtic pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, akin to the Celtiberians, dwelling in the central part of the meseta - the high central upland plain of the Iberian Peninsula.
 W
WThe Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting the central-eastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BC. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors. These tribes spoke the Celtiberian language and wrote it by adapting the Iberian alphabet. The numerous inscriptions that have been discovered, some of them extensive, have allowed scholars to classify the Celtiberian language as a Celtic language, one of the Hispano-Celtic languages that were spoken in pre-Roman and early Roman Iberia. Archaeologically, many elements link Celtiberians with Celts in Central Europe, but also show large differences with both the Hallstatt culture and La Tène culture.
 W
WThe Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the regions of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the coastal areas of Galicia. Classical authors give various accounts of the Celtici's relationships with the Gallaeci, Celtiberians and Turdetani.
 W
WThe Cessetani were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula. They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language. Their territory extended along the coast between the Coll de Balaguer and the Garraf Massif and was limited in the west by the Prades Mountains.
 W
WThe Contestani were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula. They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language.
 W
WThe Cratistii were an ancient pre-Roman, stock-raising people whose lands were situated along the upper Tagus valley, in the elevated plateau region of the western Cuenca and northeast Province of Teruel.
 W
WThe Gallaeci, Callaeci or Callaici were a large Celtic tribal federation who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now northern Portugal, Galicia, western Asturias and western Castile and León in Spain, before and during the Roman period. They spoke a Q-Celtic language related to Northeastern Hispano-Celtic, usually called Gallaic, Gallaecian, or Northwestern Hispano-Celtic. The region was annexed by the Romans in the time of Caesar Augustus during the Cantabrian Wars, a war which initiated the assimilation of the Gallaeci into Latin culture.
 W
WThe Germani were an obscure pre-Roman ancient people of the Iberian Peninsula which settled around the 4th century BC in western Oretania, an ancient region corresponding to the south of Ciudad Real and the eastern tip of Badajoz provinces.
 W
WThe Ilercavones were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula. They are believed to have spoken an Iberian language.
 W
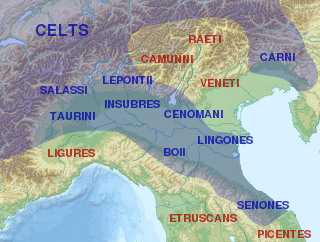
WThe Ligures were an ancient population that gave the name to Liguria, a region of north-western Italy.
 W
WThe Lobetani, were a small pre-Roman Iberian people of ancient Spain mentioned only once by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, situated around the mountainous Albarracín area of the southwest Province of Teruel.
 W
WThe Lusones were an ancient Celtiberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian Peninsula, who lived in the high Tajuña River valley, northeast of Guadalajara. They were eliminated by the Romans as a significant threat in the end of the 2nd century BC.
 W
WThe Olcades were an ancient stock-raising pre-Roman people from Hispania, who lived to the west of the Turboletae in the southeastern fringe of the Iberian system mountains.
 W
WThe Pellendones were an ancient pre-Roman Celtic people living on the Iberian Peninsula. From the early 4th century BC they inhabited the region near the source of the river Duero in what today is north-central Spain. The area comprises the north of Soria, the southeast of Burgos and the southwest of La Rioja provinces.
 W
WThe Plentauri or Pleutauri was a small, pre-Roman mountain people of the Iberian peninsula mentioned briefly by Strabo and Ptolemy who placed them in the Ebro sources area close to the Cantabrian range, roughly corresponding today to northwestern La Rioja.
 W
WThe Sedetani were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula. They are believed to have spoken a form of the Iberian language.
 W
WThe Titii or Tithii were a small and obscure Celtiberian people, whose lands were located along the middle Jalón and upper Tajuña valleys, somewhere between Alhama de Aragón in Zaragoza and Molina de Aragón in Guadalajara provinces.
 W
WThe Turboletae or Turboleti were an obscure pre-Roman people from ancient Spain, which lived in the northwest Teruel province since the early 3rd Century BC.
 W
WThe Turdetani were an ancient pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, living in the valley of the Guadalquivir, in what was to become the Roman Province of Hispania Baetica. Strabo considers them to have been the successors to the people of Tartessos and to have spoken a language closely related to the Tartessian language.
 W
WThe Turduli or Turtuli were an ancient people of southwesterns areas of the Iberian Peninsula, prior to its conquest by the Roman Empire. The Turduli who lived mainly in the south and centre of modern Portugal – in the east of the provinces of Beira Litoral, coastal Estremadura and Alentejo along the Guadiana valley, and in Extremadura and Andalusia in Spain.
 W
WThe Turmodigi were a pre-Roman ancient people, later mixed with the Celts people of northern Spain who occupied the area within the Arlanzón and Arlanza river valleys in the 2nd Iron Age.
 W
WThe Uraci or Duraci were a little-known Celtic people of pre-Roman Iberia who dwelt to the east of the Vaccaei and the Carpetani, occupying the southern Soria, northern Guadalajara and western Zaragoza provinces since the 4th century BC.
 W
WThe Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre-Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania. Their capital was Intercatia in Paredes de Nava.
 W
WThe Varduli were a pre-Roman tribe settled in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, in what today is the eastern region of the autonomous community of the Basque Country and western Navarre, in northern Spain. Their historical territory corresponds with current Basque-speaking areas, however it is debated whether the Varduli were actually Aquitanians, related to the Vascones, or if they were Celts, related to tribes such as the Cantabri and Celtiberians and which later underwent Basquisation.
 W
WThe Vettones were a pre-Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula of possibly Celtic ethnicity.