 W
WThe history of the United States from 1980 until 1991 includes the last year of the Jimmy Carter presidency, eight years of the Ronald Reagan administration, and the first three years of the George H. W. Bush presidency, up to the collapse of the Soviet Union. Plagued by the Iran hostage crisis, runaway inflation, and mounting domestic opposition, Carter lost the 1980 presidential election to Republican Reagan.
 W
WThe 1980 United States presidential election was the 49th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 4, 1980. Republican nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democrat Jimmy Carter in a landslide victory. This was the second consecutive election in which the incumbent president was defeated after Carter himself defeated Gerald Ford four years earlier in 1976. Additionally, it was only the second time, and the first in nearly 100 years that a Republican candidate defeated an incumbent Democrat. Due to the rise of conservatism following Reagan's victory, some historians consider the election to be a political realignment that marked the start of the Reagan Era.
 W
WThe 1984 United States presidential election was the 50th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1984. Incumbent Republican President Ronald Reagan defeated former Vice President Walter Mondale, the Democratic candidate in a landslide victory. In electoral votes, the final count was 525-13.
 W
WThe 1988 United States presidential election was the 51st quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1988. The Republican nominee, incumbent Vice President George H. W. Bush, defeated the Democratic nominee, Governor Michael Dukakis of Massachusetts. This was the first presidential election since 1948, and the most recent to date, in which a party won a third presidential term.
 W
WOn October 23, 1983, two truck bombs struck buildings in Beirut, Lebanon, housing American and French service members of the Multinational Force in Lebanon (MNF), a military peacekeeping operation during the Lebanese Civil War. The attack killed 307 people: 241 U.S. and 58 French military personnel, six civilians, and two attackers.
 W
WThe Bitburg controversy concerned a ceremonial visit by Ronald Reagan, the incumbent President of the United States, to a German military cemetery in Bitburg, West Germany in May 1985. The visit was intended to commemorate the 40th anniversary of the end of World War II in Europe but aroused considerable criticism in the United States and around the world when it became known that 49 of the 2,000 German soldiers buried at the site had been members of the Waffen-SS, the military arm of Nazi Germany's Schutzstaffel (SS). The entire SS was judged to be a criminal organisation at the Nuremberg trials. The fact that Reagan had not been scheduled to visit former concentration camps compounded the controversy and a trip to Bergen-Belsen concentration camp was later added to his itinerary.
 W
WBlack Monday is the name commonly attached to the global, sudden, severe, and largely unexpected stock market crash on October 19, 1987. In Australia and New Zealand, the day is also referred to as Black Tuesday because of the time zone difference from the United States.
 W
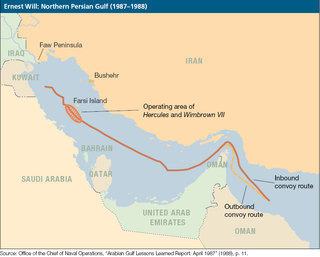
WThe Bridgeton incident was the mining of the supertanker SS Bridgeton near Farsi Island in the Persian Gulf on July 24, 1987. The ship was sailing in the first convoy of Operation Earnest Will, the U.S. response to Kuwaiti requests to protect its tankers from attack amid the Iran–Iraq War. The explosion of an Iranian mine in the Gulf's shipping channel damaged Bridgeton's outer hull but did not prevent it from completing its voyage.
 W
WThe Christian Patriot movement is a tendency within the broader American Patriot movement that emphasizes Christian nationalism. Like the larger movement, it promotes a revisionist interpretation of American history in which the federal government has turned against the ideas of liberty and natural rights expressed in the American Revolution.
 W
WOperation Earnest Will was the American military protection of Kuwaiti-owned tankers from Iranian attacks in 1987 and 1988, three years into the Tanker War phase of the Iran–Iraq War. It was the largest naval convoy operation since World War II.
 W
WThe Exxon Valdez oil spill occurred in Prince William Sound, Alaska, March 24, 1989, when Exxon Valdez, an oil tanker owned by Exxon Shipping Company, bound for Long Beach, California, struck Prince William Sound's Bligh Reef, 1.5 mi (2.4 km) west of Tatitlek, Alaska, at 12:04 a.m. and spilled 10.8 million US gallons (257,000 bbl) of crude oil over the next few days. It is considered the worst oil spill worldwide in terms of damage to the environment. The Valdez spill is the second largest in US waters, after the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill, in terms of volume released. Prince William Sound's remote location, accessible only by helicopter, plane, or boat, made government and industry response efforts difficult and severely taxed existing response plans. The region is a habitat for salmon, sea otters, seals and seabirds. The oil, originally extracted at the Prudhoe Bay Oil Field, eventually affected 1,300 miles (2,100 km) of coastline, of which 200 miles (320 km) were heavily or moderately oiled.
 W
WThe Fifth Party System is the era of American national politics that began with the New Deal in 1932 under President Franklin D. Roosevelt. This era of Democratic Party-dominance emerged from the realignment of the voting blocs and interest groups supporting the Democratic Party into the New Deal coalition, following the Great Depression, with most black voters switching from the GOP to the Democratic Party and most conservative, white southern Democrats shifting to the Republican Party as the Democratic party became known as the party of civil rights. For this reason, it is often called the "New Deal Party System". It followed the Fourth Party System, usually called the Progressive Era, and was followed by the current Sixth Party System, though the beginning of the Sixth Party System is disputed.
 W
WThe Helsinki Summit comprised a meeting between US President George H. W. Bush and Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev, taking place on September 9, 1990, just a few weeks before the reunification of Germany and just one month after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait as their fourth meeting following a meeting that included Ronald Reagan, in New York in December 1988. Furthermore, the collapse of communism and the pending reunification of Germany necessitated a third summit meeting of the Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe in order to formally end the Cold War.
 W
WThe Immigration Reform and Control Act was passed by the 99th United States Congress and signed into law by US President Ronald Reagan on November 6, 1986.
 W
WThe Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union. US President Ronald Reagan and Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev signed the treaty on 8 December 1987. The US Senate approved the treaty on 27 May 1988, and Reagan and Gorbachev ratified it on 1 June 1988.
 W
WThe 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake occurred on California’s Central Coast on October 17 at 5:04 p.m. local time. The shock was centered in The Forest of Nisene Marks State Park approximately 10 mi (16 km) northeast of Santa Cruz on a section of the San Andreas Fault System and was named for the nearby Loma Prieta Peak in the Santa Cruz Mountains. With an Mw magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), the shock was responsible for 63 deaths and 3,757 injuries. The Loma Prieta segment of the San Andreas Fault System had been relatively inactive since the 1906 San Francisco earthquake until two moderate foreshocks occurred in June 1988 and again in August 1989.
 W
WThe Malta Summit comprised a meeting between US President George H. W. Bush and Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev, taking place on December 2–3, 1989, just a few weeks after the fall of the Berlin Wall. It was their second meeting following a meeting that included Ronald Reagan, in New York in December 1988. During the summit, Bush and Gorbachev would declare an end to the Cold War although whether it was truly such is a matter of debate. News reports of the time referred to the Malta Summit as the most important since 1945, when British prime minister Winston Churchill, Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin and US President Franklin D. Roosevelt agreed on a post-war plan for Europe at the Yalta Conference.
 W
WOn March 27, 1980, a series of volcanic explosions and pyroclastic flows began at Mount St. Helens in Skamania County, Washington, United States. It initiated as a series of phreatic blasts from the summit then escalated on May 18, 1980, as a major explosive eruption. The eruption, which had a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 5, was the most significant to occur in the contiguous 48 U.S. states since the much smaller 1915 eruption of Lassen Peak in California. It has often been declared the most disastrous volcanic eruption in U.S. history.
 W
WMutual Defense Treaty Between the United States and the Republic of Korea is a treaty between South Korea and the United States signed on 1 October 1953, two months after the signing of the Korean Armistice Agreement which brought a halt to the fighting in the Korean War. The agreement commits the two nations to provide mutual aid if either faces external armed attack and allows the United States to station military forces in South Korea in consultation with the South Korean government.
 W
WOperation Praying Mantis was an attack on 18 April 1988, by U.S. forces within Iranian territorial waters in retaliation for the Iranian mining of the Persian Gulf during the Iran–Iraq War and the subsequent damage to an American warship.
 W
WThe presidency of George H. W. Bush began at noon EST on January 20, 1989, when George H. W. Bush was inaugurated as the 41st President of the United States, and ended on January 20, 1993. Bush, a Republican from Texas, took office after a landslide victory over Democrat Michael Dukakis in the 1988 presidential election. Following his defeat, he was succeeded by Democrat Bill Clinton, who won the 1992 presidential election.
 W
WThe presidency of Jimmy Carter began at noon on January 20, 1977, when Jimmy Carter was inaugurated as the 39th President of the United States, and ended on January 20, 1981. Carter, a Democrat from Georgia, took office after defeating incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford in the 1976 presidential election. Following his defeat, Carter was succeeded by Republican Ronald Reagan, who won the 1980 presidential election.
 W
WThe presidency of Ronald Reagan began at noon EST on January 20, 1981, when Ronald Reagan was inaugurated as the 40th President of the United States, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over Democratic incumbent President Jimmy Carter in the 1980 presidential election. Four years later, in the 1984 election, he defeated Democrat Walter Mondale to win re-election in a landslide. Reagan was succeeded by his Vice President, George H. W. Bush, who won the 1988 presidential election with Reagan's support. Reagan's 1980 election resulted from a dramatic conservative shift to the right in American politics, including a loss of confidence in liberal, New Deal, and Great Society programs and priorities that had dominated the national agenda since the 1930s.
 W
WThe Raid at Renacer Prison was an attack on the El Renacer prison in Gamboa, Panama, by units of the 82nd Airborne Division of the US Army on 20 December 1989, during the United States invasion of Panama. During the raid the U.S. military freed the sixty-four prisoners held in the detention facility and killed 5 soldiers of the Panama Defense Forces.
 W
WThe Reagan Doctrine was stated by United States President Ronald Reagan in his State of the Union address on February 6, 1985: "We must not break faith with those who are risking their lives--on every continent from Afghanistan to Nicaragua--to defy Soviet-supported aggression and secure rights which have been ours from birth." It was a strategy implemented by the Reagan Administration to overwhelm the global influence of the Soviet Union in the late Cold War. The doctrine was a centerpiece of United States foreign policy from the early 1980s until the end of the Cold War in 1991.
 W
WRonald Wilson Reagan was an American politician who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989 and became a highly influential voice of modern conservatism. Prior to his presidency, he was a Hollywood actor and union leader before serving as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 to 1975.
 W
WThe United States Refugee Act of 1980 is an amendment to the earlier Immigration and Nationality Act and the Migration and Refugee Assistance Act, and was created to provide a permanent and systematic procedure for the admission to the United States of refugees of special humanitarian concern to the U.S., and to provide comprehensive and uniform provisions for the effective resettlement and absorption of those refugees who are admitted. The act was completed on March 3, 1980, was signed by President Jimmy Carter on March 17, 1980 and became effective on April 1, 1980. This was the first comprehensive amendment of U.S. general immigration laws designed to face up to the realities of modern refugee situations by stating a clear-cut national policy and providing a flexible mechanism to meet the rapidly shifting developments of today's world policy. The main objectives of the act were to create a new definition of refugee based on the one created at the UN Convention and Protocol on the Status of Refugees, raise the limitation from 17,400 to 50,000 refugees admitted each fiscal year, provide emergency procedures for when that number exceeds 50,000, and to establish the Office of U.S. Coordinator for Refugee Affairs and the Office of Refugee Resettlement. Most importantly, it established explicit procedures on how to deal with refugees in the U.S. by creating a uniform and effective resettlement and absorption policy.
 W
WRonald Reagan, the 40th President of the United States, announced his candidacy for re-election as president in Washington, D.C. on November 3, 1983. On August 23, 1984, he again became the nominee of the Republican Party for the 1984 presidential election. After receiving the Republican nomination, he confirmed that Vice President George H. W. Bush would remain as his running mate.
 W
WUSS Simpson (FFG-56) was an Oliver Hazard Perry-class guided missile frigate of the United States Navy, named for Rear Admiral Rodger W. Simpson.
 W
WThe Sixth Party System is the era in United States politics following the Fifth Party System. As with any periodization, opinions differ on when the Sixth Party System may have begun, with suggested dates ranging from the late 1960s or 1970 to the 1990s and beyond. According to political scientists Mark D. Brewer and L. Sandy Maisel in 2020:It seems safe to state that the sixth American party system featured strong divisions between Republicans and Democrats, rooted in cleavages based on social class, social and cultural issues, race and ethnicity, and the proper size and scope of the federal government.
 W
WThe Taiwan Relations Act is an act of the United States Congress. Since the recognition of the People's Republic of China, the Act has defined the officially substantial but non-diplomatic relations between the people of the United States and the people of Taiwan.
 W
WThe Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security between the United States and Japan , also known in Japan as Anpo jōyaku (安保条約) or just Anpo (安保) for short, is a treaty establishing a military alliance between the United States and Japan. The treaty was first signed in 1951 at the San Francisco Presidio after the signing of the Treaty of San Francisco at the San Francisco War Memorial Opera House. Then, the Security Treaty was amended further in January 1960 between the US and Japan in Washington, DC.
 W
WU.S.–Japan Status of Forces Agreement is an agreement between Japan and the United States signed on 19 January 1960 in Washington, the same day as the revised U.S.-Japan Security Treaty. It is a status of forces agreement (SOFA) as stipulated in article VI of that treaty, which referred to "a separate agreement" governing the "use of [...] facilities and areas [granted to the U.S.] as well as the status of United States armed forces in Japan". It replaced the earlier "U.S.-Japan Administrative Agreement" that governed such issues under the original 1951 security treaty.
 W
WThe United States invasion of Grenada began at dawn on 25 October 1983. The U.S. and a coalition of six Caribbean nations invaded the island nation of Grenada, 100 miles (160 km) north of Venezuela. Codenamed Operation Urgent Fury by the U.S. military, it resulted in military occupation within a few days. It was triggered by the strife within the People's Revolutionary Government which resulted in the house arrest and execution of the previous leader and second Prime Minister of Grenada Maurice Bishop, and the establishment of the Revolutionary Military Council with Hudson Austin as Chairman. The invasion resulted in the appointment of an interim government, followed by democratic elections in 1984. The country has remained a democratic nation since then.
 W
WThe United States Invasion of Panama, codenamed Operation Just Cause, lasted over a month between mid-December 1989 and late January 1990. It occurred during the administration of President George H. W. Bush and ten years after the Torrijos–Carter Treaties were ratified to transfer control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by 1 January 2000. During the invasion, de facto Panamanian leader, general and dictator Manuel Noriega, who for a long time worked with the Central Intelligence Agency, was deposed citing racketeering and drug trafficking. Following the operation, the Panama Defense Forces were dissolved and President-elect Guillermo Endara was sworn into office.
 W
WThe USS Stark incident occurred during the Iran–Iraq War on 17 May 1987, when an Iraqi jet aircraft fired two Exocet missiles at the American frigate USS Stark. A total of thirty-seven United States Navy personnel were killed or later died as a result of the attack, and twenty-one were injured.