 W
WEgyptian mythology is the collection of myths from ancient Egypt, which describe the actions of the Egyptian gods as a means of understanding the world around them. The beliefs that these myths express are an important part of ancient Egyptian religion. Myths appear frequently in Egyptian writings and art, particularly in short stories and in religious material such as hymns, ritual texts, funerary texts, and temple decoration. These sources rarely contain a complete account of a myth and often describe only brief fragments.
 W
WThis is an index of Egyptian mythology articles.
 W
WAn adder stone is a type of stone, usually glassy, with a naturally occurring hole through it. Such stones have been discovered by archaeologists in both Britain and Egypt. Commonly, they are found in Northern Germany at the coasts of the North and Baltic Seas.
 W
WAncient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world. The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom have given us most of the information regarding early Egyptian creation myths. These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world. The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. Thus, the world or more specifically Egypt was created in diverse ways according to different parts of the country. Some versions of the myth indicate spitting, others masturbation, as the act of creation. The union between the first divine couple brought forth another brother-sister pair, Geb and Nut, who in turn created Osiris, Isis, Seth and Nephthys. An extension to this basic framework was the Osiris myth involving god, his consort Isis, and their son Horus. The murder of Osiris by Seth, and the resulting struggle for power, won by Horus, provided a powerful narrative linking the ancient Egyptian ideology of kingship with the creation of the cosmos.
 W
WThe ankh or key of life is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol that was most commonly used in writing and in Egyptian art to represent the word for "life" and, by extension, as a symbol of life itself.
 W
WApep or Apophis was the ancient Egyptian deity who embodied chaos and was thus the opponent of light and Ma'at (order/truth). He appears in art as a giant serpent. His name is reconstructed by Egyptologists as *ʻAʼpāp(ī), as it was written ꜥꜣpp(y) and survived in later Coptic as Ⲁⲫⲱⲫ Aphōph. Apep was first mentioned in the Eighth Dynasty, and he was honored in the names of the Fourteenth Dynasty king 'Apepi and of the Greater Hyksos king Apophis.
 W
WAtef is the specific feathered white crown of the ancient Egyptian deity Osiris. It combines the Hedjet, the crown of Upper Egypt, with curly red ostrich feathers on each side of the crown for the Osiris cult. The feathers are identified as ostrich from their curl or curve at the upper ends, with a slight flare toward the base. They are the same feather as (singly) worn by Maat. They may be compared with the falcon tail feathers in two-feather crowns such as those of Amun, which are more narrow and straight without curve.
 W
WThe Atet was the solar barge of the sun god Ra in the mythology of the ancient Egyptians. It was also known as the Mandjet, the Boat of Millions of Years, and, during the night, as the Mesektet.
 W
WIn the creation myth of the Heliopolitan form of ancient Egyptian religion, Benben was the mound that arose from the primordial waters Nu upon which the creator deity Atum settled. The Benben stone is the top stone of the pyramid. It is also related to the obelisk.
 W
WThe Book of Caverns is an important ancient Egyptian netherworld book of the New Kingdom. Like all other netherworld books, it is also attested on the inside of kings’ tombs for the benefit of the deceased. It describes the journey of the sun god Ra through the six caverns of the underworld, focusing on the interaction between the sun god and the inhabitants of the netherworld, including rewards for the righteous and punishments for the enemies of the worldly order, those who fail their judgment in the afterlife. The Book of Caverns is one of the best sources of information about the Egyptian concept of hell.
 W
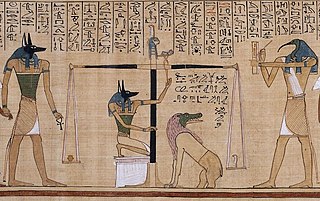
WThe Book of Gates is an ancient Egyptian funerary text dating from the New Kingdom. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased soul into the next world, corresponding to the journey of the sun through the underworld during the hours of the night. The soul is required to pass through a series of 'gates' at different stages in the journey. Each gate is associated with a different goddess, and requires that the deceased recognise the particular character of that deity. The text implies that some people will pass through unharmed, but that others will suffer torment in a lake of fire.
 W
WThe Book of the Dead is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw, is translated as Book of Coming Forth by Day or Book of Emerging Forth into the Light. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the Duat, or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years.
 W
WThe Book of the Earth is an Ancient Egyptian funerary text that has been called many names such as The Creation of the Sun Disk and the Book of Aker. The Book primarily appears on the tombs of Merneptah, Twosret, Ramesses III, Ramesses VI, and Ramesses VII and serves as a counterpart to the Book of Caverns.
 W
WThe Books of Breathing are several late ancient Egyptian funerary texts, intended to enable deceased people to continue to exist in the afterlife. The earliest known copy dates to about 350 BC. Other copies come from the Ptolemaic and Roman periods of Egyptian history, as late as the second century AD. It is a simplified form of the Book of the Dead.
 W
WIn Egyptian mythology, Buchis was the deification of the kꜣ of the war god Montu as a sacred bull that was worshipped in the region of Hermonthis.
 W
WButo, Butus or Butosus was an ancient city located 95 km east of Alexandria in the Nile Delta of Egypt. What in classical times the Greeks called Buto stood about midway between the Taly (Bolbitine) and Thermuthiac (Sebennytic) branches of the Nile, a few kilometers north of the east-west Butic River and on the southern shore of the Butic Lake.
 W
WThe curse of the pharaohs or the mummy's curse is a curse alleged to be cast upon anyone who disturbs the mummy of an ancient Egyptian, especially a pharaoh. This curse, which does not differentiate between thieves and archaeologists, is claimed to cause bad luck, illness, or death. Since the mid-20th century, many authors and documentaries have argued that the curse is 'real' in the sense of having scientifically explicable causes such as bacteria or radiation. However, the modern origins of Egyptian mummy curse tales, their development primarily in European cultures, the shift from magic to science to explain curses, and their changing uses—from condemning disturbance of the dead to entertaining horror film audiences—suggest that Egyptian curses are primarily a cultural, not exclusively scientific, phenomenon.
 W
WThe characteristic of cynocephaly, or cynocephalus, having the head of a dog—or of a jackal—is a widely attested mythical phenomenon existing in many different forms and contexts. The literal meaning of "cynocephaly" is "dog-headed"; however, that this refers to a human body with a dog head is implied. Such cynocephalics are known in mythology and legend from many parts of the world, including ancient Egypt, India, Greece, and China. Further mentions come from the medieval East and Europe. In modern popular culture cynocephalics are also encountered as characters in books, comics, and graphic novels. Cynocephaly is generally distinguished from lycanthropy (werewolfism) and dogs that can talk.
 W
WDuat is the realm of the dead in ancient Egyptian mythology. It has been represented in hieroglyphs as a star-in-circle: 𓇽. The god Osiris was believed to be the lord of the underworld. He was the first mummy as depicted in the Osiris myth and he personified rebirth and life after death. The underworld was also the residence of various other gods along with Osiris. The Duat was the region through which the sun god Ra traveled from west to east each night, and it was where he battled Apophis, who embodied the primordial chaos which the sun had to defeat in order to rise each morning and bring order back to the earth. It was also the place where people's souls went after death for judgment, though that was not the full extent of the afterlife. Burial chambers formed touching-points between the mundane world and the Duat, and the ꜣḫ "the effectiveness of the dead", could use tombs to travel back and forth from the Duat.
 W
WKV62 is the standard Egyptological designation for the tomb of young pharaoh Tutankhamun in the Valley of the Kings, now renowned for the wealth of valuable antiquities that it contained. Howard Carter discovered it in 1922 underneath the remains of workmen's huts built during the Ramesside Period; this explains why it was largely spared the desecration and tomb clearances at the end of the 20th Dynasty, although it was robbed and resealed twice in the period after its completion.
 W
WThe Ennead or Great Ennead was a group of nine deities in Egyptian mythology worshiped at Heliopolis: the sun god Atum; his children Shu and Tefnut; their children Geb and Nut; and their children Osiris, Isis, Seth, and Nephthys. The Ennead sometimes includes the son of Osiris and Isis, Horus.
 W
WThe flooding of the Nile has been an important natural cycle in Egypt since ancient times. It is celebrated by Egyptians as an annual holiday for two weeks starting August 15, known as Wafaa El-Nil. It is also celebrated in the Coptic Church by ceremonially throwing a martyr's relic into the river, hence the name, The Martyr's Finger. Ancient Egyptians believed that the Nile flooded every year because of Isis's tears of sorrow for her dead husband, Osiris.
 W
WThe horns of Ammon were a symbol of the Egyptian deity Ammon associated with the fossils shells of ancient snails and cephalopods, the latter now known as ammonite because of that historical connection.
 W
WThe Horus name is the oldest known and used crest of ancient Egyptian rulers. It belongs to the "great five names" of an Egyptian pharaoh. However, modern Egyptologists and linguists are starting to prefer the more neutral term: the "serekh name". This is because not every pharaoh placed the falcon, which symbolizes the deity Horus, atop his serekh.
 W
WKneph is a motif in ancient Egyptian religious art, variously a winged egg, a globe surrounded by one or more serpents, or Amun in the form of a serpent called Kematef. Some Theosophical sources tried to syncretize this motif with the deity Khnum, along with Serapis and Pluto. Under the Greek theonym Chnuphis, this figure adopts a serpent-bodied, lion-headed ("leontoeidic") visage, being particularly common in magical artifacts in Late Antiquity. It is by proxy frequently associated with the Gnostic Demiurge.
 W
WIn Egyptian mythology the Matet boat was the first of two boats traveled in by Ra, the sun god as he traveled the sky daily with the sun on his head. During the period between dawn and noon, Ra occupies the Matet boat. During the period between noon and dusk Ra travels in the Seqtet boat. Ra travels the underworld during the night where he encounters and battles many foes. Matet and Seqtet seem to have many different spellings and Ra himself is often mixed with another or sometimes several deities dependent upon the period and various locations throughout ancient Egypt.
 W
WMemphis (Menefer)(Arabic: مَنْف Manf pronounced [mænf]; Bohairic Coptic: ⲙⲉⲙϥⲓ; Greek: Μέμφις) was the ancient capital of Inebu-hedj, the first nome of Lower Egypt that was known as mḥw ("north").. Its ruins are located near the modern town of Mit Rahina, 20 km (12 mi) south of Giza in Greater Cairo, Egypt.
 W
WMenes was a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt credited by classical tradition with having united Upper and Lower Egypt and as the founder of the First Dynasty.
 W
WThe Nebty name was one of the "great five names" used by Egyptian pharaohs. It was also one of the oldest royal titles. The modern term "Two-Ladies-name" is a simple derivation from the translation of the Egyptian word nebty.
 W
WThe nomen of ancient Egyptian pharaohs was one of the "great five names". It was introduced by king Djedefre, third pharaoh of the 4th Dynasty, as an emendation to the traditional nswt-bity crest. The nomen was later separated from the prenomen to become an independent royal name.
 W
WThe Osiris myth is the most elaborate and influential story in ancient Egyptian mythology. It concerns the murder of the god Osiris, a primeval king of Egypt, and its consequences. Osiris's murderer, his brother Set, usurps his throne. Meanwhile, Osiris's wife Isis restores her husband's body, allowing him to posthumously conceive their son, Horus. The remainder of the story focuses on Horus, the product of the union of Isis and Osiris, who is at first a vulnerable child protected by his mother and then becomes Set's rival for the throne. Their often violent conflict ends with Horus's triumph, which restores Maat to Egypt after Set's unrighteous reign and completes the process of Osiris's resurrection.
 W
WThe prenomen, cartouche name or throne name of ancient Egypt was one of the five royal names of pharaohs. The first pharaoh to have a Sedge and Bee name was Den during the First Dynasty.
 W
WSerabit el-Khadim is a locality in the southwest Sinai Peninsula, Egypt, where turquoise was mined extensively in antiquity, mainly by the ancient Egyptians. Archaeological excavation, initially by Sir Flinders Petrie, revealed ancient mining camps and a long-lived Temple of Hathor, the Egyptian goddess who was favoured as a protector in desert regions.
 W
WIn ancient Egypt a shen ring was a circle with a line tangent to it, represented in hieroglyphs as a stylised loop of a rope. The word shen itself means, in ancient Egyptian, encircle, while the shen ring represented eternal protection.
 W
WThe ancient Egyptians believed that a soul was made up of many parts. In addition to these components of the soul, there was the human body.
 W
WThinis or This was the capital city of the first dynasties of ancient Egypt. Thinis is, as yet, undiscovered but well attested by ancient writers, including the classical historian Manetho, who cites it as the centre of the Thinite Confederacy, a tribal confederation whose leader, Menes, united Egypt and was its first pharaoh. Thinis began a steep decline in importance from Dynasty III, when the capital was relocated to Memphis, which was thought to be the first true and stable capital after unification of old Egypt by Menes. Thinis's location on the border of the competing Heracleopolitan and Theban dynasties of the First Intermediate Period and its proximity to certain oases of possible military importance ensured Thinis some continued significance in the Old and New Kingdoms. This was a brief respite and Thinis eventually lost its position as a regional administrative centre by the Roman period.
 W
WIn Ancient Egyptian texts, the "Two Ladies" was a religious euphemism for the goddesses Wadjet and Nekhbet, two deities who were patrons of the ancient Egyptians and worshiped by all after the unification of its two parts, Lower Egypt, and Upper Egypt. When the two parts of Egypt were joined together, there was no merger of these deities as often occurred with similar deities from various regions and cities. Both goddesses were retained because of the importance of their roles and they became known as the Two Ladies, who were the protectors of unified Egypt.
 W
WThe tyet, sometimes called the knot of Isis or girdle of Isis, is an ancient Egyptian symbol that came to be connected with the goddess Isis. Its hieroglyphic depiction is catalogued as V39 in Gardiner's sign list.