 W
WThe Territory of Arizona was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863 until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Arizona. It was created from the western half of the New Mexico Territory during the American Civil War.
 W
WConfederate Arizona, officially the Territory of Arizona, and commonly known as the Arizona Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the Confederate States that existed from August 1, 1861, to May 26, 1865, when the Trans-Mississippi Department, commanded by General E. Kirby Smith, surrendered at Shreveport, Louisiana. Effective Confederate control of Arizona Territory, however, ended after the Battle of Glorieta Pass in March 1862.
 W
WThe Arizona Pioneers' Home, also known as the Home for Arizona Pioneers and State Hospital for Disabled Miners, is a retirement home in Prescott, Arizona, established to provide housing for early Arizona pioneers. The home is operated and funded by the state of Arizona. The building is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WThe Bascom Massacre was a confrontation between Apache Indians and the United States Army under Lt. George Nicholas Bascom in the Arizona Territory in early 1861. It has been considered to have directly precipitated the decades-long Apache Wars between the United States and several tribes in the southwestern United States. War was coming with the Chiricahua Apache. The affair led to an open break and open hostilities, but Cochise had not previously been peaceful, he had been prudent and avoided raiding Americans. He had, however, stolen livestock from the Overland Mail, from Fort Buchanan and had twice been forced to return stolen stock by Capt. Richard S. Ewell, who swore that if he had to deal with Cochise again, he would strike a blow.
 W
WBig Bug is a ghost town in Yavapai County, Arizona. The former settlement is located twelve miles southeast of Prescott and was established in 1862.
 W
WThe Battle of the Catalina River was a military engagement fought on March 21, 1784 during the Spanish conquest of the present day Arizona. The combatants were Apache and Navajo warriors, Spanish soldiers and Tucson militia.
 W
WCottonwood Island, a large island in the Colorado River, within Cottonwood Valley, in Clark County, Nevada. Cottonwood Island was a low-lying island about 10 miles long and up to 3 miles wide. It was forested by cottonwoods and also after the spring flood, cluttered with driftwood from the riparian woodlands along the upper watershed of the Colorado River, washed down and caught in the first wide valley where the river slowed and spread out. Cottonwood Island was important as a source wood and of fuel for steamboats on that river and for the early mills and mines in El Dorado Canyon.
 W
WDesert Station is a historic locale, the site of a later station of the Butterfield Overland Mail, in what is now Maricopa County, Arizona.
 W
WEstado de Occidente was a Mexican state established in 1824. The constitution was drafted in that year and the government was initially established with its capital at El Fuerte, Sinaloa. The first governor was Juan Miguel Riesgo. The state consisted of modern Sonora and Sinaloa, and also modern Arizona more or less south of the Gila River.
 W
WFort Defiance is a census-designated place (CDP) in Apache County, Arizona, United States. It is also located within the Navajo Nation. The population was 3,624 at the 2010 census.
 W
WThe Gadsden Purchase, is a 29,670-square-mile (76,800 km2) region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lands south of the Gila River and west of the Rio Grande where the U.S. wanted to build a transcontinental railroad along a deep southern route, which the Southern Pacific Railroad later completed in 1881–1883. The purchase also aimed to resolve other border issues.
 W
WFrancisco Hermenegildo Tomás Garcés, O.F.M., was a Spanish Franciscan friar who served as a missionary and explorer in the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. He explored much of the southwestern region of North America, including present day Sonora and Baja California in Mexico, and the U.S. states of Arizona and California. He was killed along with his companion friars during an uprising by the Native American population, and they have been declared martyrs for the faith by the Catholic Church. The cause for his canonization was opened by the Church.
 W
WGriswell's or Griswell's Station was a stagecoach station of the Butterfield Overland Mail located along the Gila River in Arizona. It was located 12 miles east of Peterman's Station and 15 miles west of Flap Jack Ranch Station.
 W
WThe Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, officially titled the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits and Settlement between the United States of America and the Mexican Republic, is the peace treaty signed on February 2, 1848, in the Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo between the United States and Mexico that ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The treaty was ratified by the United States on March 10 and by Mexico on May 19. The ratifications were exchanged on May 30, and the treaty was proclaimed on July 4, 1848.
 W
WEusebio Francisco Kino, often referred to as Father Kino, was an Italian Jesuit, missionary, geographer, explorer, cartographer and astronomer born in the Territory of the Bishopric of Trent, then part of the Holy Roman Empire. For the last 24 years of his life he worked in the region then known as the Pimería Alta, modern-day Sonora in Mexico and southern Arizona in the United States. He explored the region and worked with the indigenous Native American population, including primarily the Tohono O'Odham, Sobaipuri and other Upper Piman groups. He proved that the Baja California Peninsula is not an island by leading an overland expedition there. By the time of his death he had established 24 missions and visitas.
 W
WThe Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the Intervención Estadounidense en México, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1845 U.S. annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered Mexican territory since the government did not recognize the Velasco treaty signed by Mexican General Antonio López de Santa Anna when he was a prisoner of the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was de facto an independent country, but most of its citizens wished to be annexed by the United States. Domestic sectional politics in the U.S. were preventing annexation since Texas would have been a slave state, upsetting the balance of power between northern free states and southern slave states. In the 1844 United States presidential election, Democrat James K. Polk was elected on a platform of expanding U.S. territory in Oregon and Texas. Polk advocated expansion by either peaceful means or by armed force, with the 1845 annexation of Texas as furthering that goal. For Mexico, this was a provocation, but Polk went further, sending U.S. Army troops to the area; he also sent a diplomatic mission to Mexico to try to negotiate the sale of territory. U.S. troops' presence was provocative and designed to lure Mexico into starting the conflict, putting the onus on Mexico and allowing Polk to argue to Congress that a declaration of war should be issued. Mexican forces attacked U.S. forces, and the United States Congress declared war.
 W
WMurderer's Grave Station is a historic locale, later called Kinyon Station and Kenyon Station was a stagecoach station of the Butterfield Overland Mail located along the Gila River in Arizona. The site was located 20 miles east of Oatmans Flat Station and 15 miles west of Gila Ranch Station. It was located along the Gila River near the present site of the Painted Rock Reservoir
 W
WThe Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of New Mexico, making it the longest-lived organized incorporated territory of the United States, lasting approximately 62 years.
 W
WThe Viceroyalty of New Spain was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. It covered a huge area that included much of North America, northern parts of South America and several Pacific Ocean archipelagos, namely Philippines and Guam. It originated in 1521 after the fall of Tenochtitlan, the main event of the Spanish conquest, and officially created on 18 August 1521 as a kingdom, the first of four viceroyalties Spain created in the Americas. Its first viceroy was Antonio de Mendoza y Pacheco, and the capital of the kingdom was Mexico City, established on the ancient Tenochtitlan.
 W
WOatman Flat Station, later Fourr's Stage Station, was a stagecoach station of the Butterfield Overland Mail located along the Gila River in Maricopa County, Arizona. The site was located 20 miles (32 km) east of Flap-Jack Ranch and 20 miles (32 km) west of Murderer's Grave Station, near the Gila River at Oatman Flat. It is to the east of the Oatman Grave, where the family of Olive Oatman was buried following their massacre on the Southern Emigrant Trail by Yavapai in 1851.
 W
WJuan de Oñate y Salazar was a Spanish conquistador from New Spain, explorer, and colonial governor of the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in the viceroyalty of New Spain. He led early Spanish expeditions to the Great Plains and Lower Colorado River Valley, encountering numerous indigenous tribes in their homelands there. Oñate founded settlements in the province, now in the Southwestern United States. A monument in Alcalde, New Mexico was removed on June 15, 2020.
 W
WPah-Ute County is a former county in the northwest corner of Arizona Territory that existed from 1865 until 1871, at which point most of the area was transferred to Nevada. The remainder was merged into Mohave County. The majority of the territory is now in Clark County, Nevada, which includes the city of Las Vegas. Due to the transfer of most of the county's land to Nevada, Pah-Ute is sometimes referred to as Arizona's "Lost County". Pah-Ute is an historic spelling of the tribal name Paiute.
 W
WThe Peralta Stones are a set of engraved stones. Some people believe they indicate the location of the famed Lost Dutchman's Gold Mine, in Arizona, United States. The Dutchman was a German immigrant named Jacob Waltz.
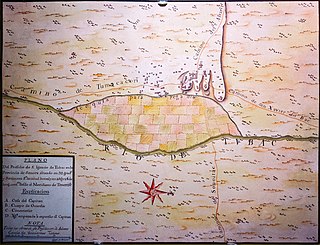 W
WThe Pima Revolt, or the O'odham Uprising and the Pima Outbreak, was a revolt of Pima native Americans in 1751 against colonial forces in Spanish Arizona and one of the major northern frontier conflicts in early New Spain.
 W
WThe Pimería Alta was an area of the 18th century Sonora y Sinaloa Province in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, that encompassed parts of what are today southern Arizona in the United States and northern Sonora in Mexico.
 W
WThe Battle of the Pinal Mountains was one of many small battles to occur between Apache warriors and Spanish colonists. The exact date of the battle is unknown but happened on one day in mid June, 1788, in the Pinal Mountains of east central Arizona.
 W
WPlanchas de Plata, sometimes called Bolas de Plata is a historic silver-mining district near Nogales, Sonora, Mexico, and a few miles south of the border with the US state of Arizona. Native silver was discovered here in 1736 by Antonio Siraumea, a Yaqui Indian, on the Rancho Arizona of Bernardo de Urrea. Historian Donald Garate believes Urrea's Arizona Ranch to be the likely source of the name of the present US state of Arizona, and he claimed the origin of the name of the ranch was the Basque phrase "aritz ona". Other historians have, however, debated this. For more detail on the etymology of the name Arizona, see Arizona.Toward the end of last October, between the Guevavi Mission and the ranchería called Arizona, some balls and slabs of silver were discovered, one of which weighed more than one hundred arrobas, a sample of which I am sending to you, Most Illustrious Lord. --Captain Juan Bautista de Anza to Bishop Benito Crespo, January 7, 1737.
 W
WThe Provincias Internas, also known as the Comandancia y Capitanía General de las Provincias Internas, was an administrative district of the Spanish Empire created in 1776 to provide more autonomy for the frontier provinces of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, present-day northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States. The goal of its creation was to establish a unified government in political, military and fiscal affairs. Nevertheless, the Commandancy General experienced significant changes in its administration because of experimentation to find the best government for the frontier region as well as bureaucratic in-fighting. Its creation was part of the Bourbon Reforms and was part of an effort to invigorate economic and population growth in the region to stave off encroachment on the region by foreign powers. During its existence, the Commandancy General encompassed the Provinces of Sonora y Sinaloa, Nueva Vizcaya, Las Californias, Nuevo México, Nuevo Santander, Nuevo Reyno de León, Coahuila and Texas.
 W
WSalado culture, or Salado Horizon, was a human culture in the upper Salt River of the Tonto Basin in southeastern Arizona from approximately 1150 CE through the 15th century.
 W
WSan Rafael, is a ghost town in Pima County, Arizona, United States.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Fort Defiance was a military engagement fought during the United States period of the Navajo Wars. On August 30, 1860, about 1,000 Navajo warriors assaulted the United States Army garrison of Fort Defiance in New Mexico Territory, now within present day Arizona. The Navajo achieved a surprise attack but was ultimately repulsed by 150 American defenders of the 3rd Infantry under Captain Oliver L. Shepherd. The Americans formed in the center of the buildings and withstood the Navajo attack. The natives retreated with a loss of around seven dead and several wounded while the Americans suffered one man killed in action and three wounded. The second Navajo assault on Fort Defiance was one of the largest battles fought within the borders of Arizona. It was also one of the reasons why the militia commander Lieutenant Colonel Manuel Antonio Chaves ordered an unauthorized campaign into Navajo territory in 1860 and 1861.
 W
WSteamboats on the Colorado River operated from the river mouth at the Colorado River Delta on the Gulf of California in Mexico, up to the Virgin River on the Lower Colorado River Valley in the Southwestern United States from 1852 until 1909, when the construction of the Laguna Dam was completed. The shallow draft paddle steamers were found to be the most economical way to ship goods between the Pacific Ocean ports and settlements and mines along the lower river, putting in at landings in Sonora state, Baja California Territory, California state, Arizona Territory, New Mexico Territory, and Nevada state. They remained the primary means of transportation of freight until the advent of the more economical railroads began cutting away at their business from 1878 when the first line entered Arizona Territory.
 W
WThe First Battle of Terrenate on July 7, 1776 was a military engagement during the Spanish period of Arizona. It was fought between Spanish soldiers and Apache warriors, near the Presidio Santa Cruz de Terrenate in the present day southern Arizona.
 W
WThe following timeline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of Arizona.
 W
WPrior to the adoption of its name for a U.S. state, Arizona was traditionally defined as the region south of the Gila River to the present-day Mexican border, and between the Colorado River and the Rio Grande. It encompasses present-day Southern Arizona and the New Mexico Bootheel plus adjacent parts of Southwestern New Mexico. This area was transferred from Mexico to the United States in the Gadsden Purchase of 1853. Mining and ranching were the primary occupations of traditional Arizona's inhabitants, though growing citrus fruits had long been occurring in Tucson.
 W
WThe Fourth Battle of Tucson was a raid during the lengthy wars between Spanish colonists in Arizona and its region and Apache Indians. At break of day, on March 21, 1784, a force of no more than 500 Apaches and Navajos attacked Spanish cavalry guards protecting a herd of livestock at the Presidio San Augustin del Tucson in southern Arizona.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Tucson or the May Day Attack was a battle in Tucson, Arizona, and the neighboring pueblo. It occurred during the Mexican Apache Wars on May 1, 1782, between a small garrison of Spanish soldiers and hundreds of Apache warriors.
 W
WThe V Bar V Heritage Site is the largest known petroglyph site in the Verde Valley of central Arizona, and one of the best-preserved. The rock art site consists of 1,032 petroglyphs in 13 panels. Acquired by the Coconino National Forest in 1994, the site is protected and kept open to the public by the US Forest Service. Volunteers from the Verde Valley Archaeological Society and the Friends of the Forest provide interpretive tours and on-site management.