 W
WThe history of the United States from 1991 to 2008 began after the fall of the Soviet Union which signaled the end of the Cold War and left the U.S. unchallenged as the world's dominant superpower. The U.S. took a leading role in military involvement in the Middle East. The U.S. expelled an Iraqi invasion force from Kuwait, a Middle Eastern ally of the U.S., in the Persian Gulf War. On the domestic front, the Democrats won a return to the White House with the election of Bill Clinton in 1992. In the 1994 midterm election, the Republicans won control of Congress for the first time in 40 years. Strife between Clinton and the Republicans in Congress initially resulted in a federal government shutdown following a budget crisis, but later they worked together to pass welfare reform, the Children's Health Insurance Program, and a balanced budget. Charges from the Lewinsky scandal led to the 1998 impeachment of Clinton by the House of Representatives but he was later acquitted by the Senate. The U.S. economy boomed in the enthusiasm for high-technology industries in the 1990s until the NASDAQ crashed as the dot-com bubble burst and the early 2000s recession marked the end of the sustained economic growth.
 W
WThe history of the United States from 2008 to the present began with the collapse of the housing bubble, which led to the Great Recession, and helped the Democrats win the presidency in 2008 with the election of Barack Obama, the country's first African-American president. The government issued large loans and enacted economic stimulus packages that aimed to improve the economy. Obama's domestic initiatives also included the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, which by means of large reforms to the American healthcare system, created a National Health Insurance program. President Obama eventually withdrew combat troops from Iraq, and shifted the country's efforts in the War on Terror to Afghanistan, where a troop surge was initiated in 2009. In 2010, due to continued public discontent with the economic situation, unemployment, and federal spending, Republicans regained control of the House of Representatives and reduced the Democratic majority in the Senate. In 2011, Obama announced that al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden was killed by U.S. forces during a covert operation in Pakistan while the Iraq War was declared formally over the same year. The following year Obama was re-elected president. In June 2013, the Supreme Court struck down Section 3 of the Defense of Marriage Act, which resulted in the recognition of legally performed same-sex marriages by the federal government. In 2015, the Court ruled that all states must grant same-sex marriages as well as recognize others performed in different states in Obergefell v. Hodges.
 W
WThe Twenty-seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits any law that increases or decreases the salary of members of Congress from taking effect until the start of the next set of terms of office for representatives. The amendment is the most recent to be adopted, but one of the first proposed.
 W
WThe 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992. Democratic Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush, independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas, and a number of minor candidates. This election marked the end of a period of Republican dominance that began in 1968.
 W
WThe 1996 United States presidential election was the 53rd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1996. Incumbent Democratic President Bill Clinton defeated former Senate Majority Leader Bob Dole, the Republican nominee, and Ross Perot, the Reform Party nominee.
 W
WThe 1998 United States embassy bombings were attacks that occurred on August 7, 1998. More than 200 people were killed in nearly simultaneous truck bomb explosions in two East African cities, one at the United States Embassy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, the other at the United States Embassy in Nairobi, Kenya.
 W
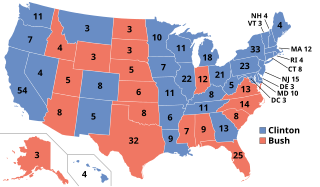
WThe 2000 United States presidential election was the 54th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 2000. Republican candidate George W. Bush, the governor of Texas and eldest son of the 41st president, George H. W. Bush, won the disputed election, defeating Democratic nominee Al Gore, the incumbent vice president. It was the fourth of five presidential elections, and the first in 112 years in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote and is considered one of the closest elections in US history.
 W
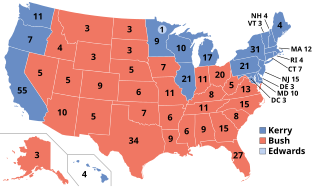
WThe 2004 United States presidential election was the 55th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 2004. The incumbent Republican President George W. Bush and his running mate Vice President Dick Cheney were elected to a second term, defeating the Democratic ticket of John Kerry, a United States Senator from Massachusetts and his running mate John Edwards, a United States Senator from North Carolina. Notably, it is to date the only presidential election since 1988 in which the Republican candidate won the popular vote. At the time Bush's popular vote total was the most votes ever received by a presidential candidate, a total that has since been surpassed 6 times in the last 4 presidential elections. Bush also became the only incumbent president to win reelection after losing the popular vote in the previous election. All others lost, most recently Donald Trump in 2020.
 W
WThe 2008 United States presidential election was the 56th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 2008. The Democratic ticket of Barack Obama, the junior U.S. Senator from Illinois, and Joe Biden, the senior U.S. Senator from Delaware, defeated the Republican ticket of John McCain, the senior Senator from Arizona, and Sarah Palin, the Governor of Alaska. Obama became the first African American ever to be elected to the presidency, as well as being only the third sitting United States Senator elected president, joining Warren G. Harding and John F. Kennedy.
 W
WThe 2012 United States presidential election was the 57th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 2012. The incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and his running mate, Vice President Joe Biden, were re-elected to a second term. They defeated the Republican ticket of businessman and former Governor Mitt Romney of Massachusetts and Representative Paul Ryan of Wisconsin.
 W
WThe 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state Hillary Clinton and U.S. senator from Virginia Tim Kaine. Trump took office as the 45th president, and Pence as the 48th vice president, on January 20, 2017. It was the fifth and most recent presidential election in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote.
 W
WThe 2020 United States presidential election was the 59th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. The Democratic ticket of former vice president Joe Biden and incumbent U.S. senator from California Kamala Harris defeated the Republican ticket of incumbent president Donald Trump and vice president Mike Pence. Trump became the first U.S. president since 1992 and the eleventh incumbent in the country's history to lose a bid for a second term, and Biden won the largest share of the popular vote against an incumbent since 1932. It was the ninth consecutive presidential election where the victorious candidate did not win a popular vote majority by a double-digit margin, continuing the longest series of such presidential elections in U.S. history that began in 1988. The election saw the highest voter turnout since 1900, with each of the two main tickets receiving more than 74 million votes, surpassing Barack Obama's record of 69.5 million votes from 2008. Biden received more than 81 million votes, the most votes ever cast for a candidate in a U.S. presidential election.
 W
WThe Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty (1972—2002) was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the limitation of the anti-ballistic missile (ABM) systems used in defending areas against ballistic missile-delivered nuclear weapons. Under the terms of the treaty, each party was limited to two ABM complexes, each of which was to be limited to 100 anti-ballistic missiles.
 W
WBalikatan is the name for the annual military exercises between the Philippines and the United States. It is a Tagalog word meaning "shoulder-to-shoulder". The April 2016 10-day exercises is the 32nd iteration of the Balikatan exercises. The exercises have been the cornerstone of Philippines–United States military relations since the U.S. bases in the Philippines closed.
 W
WThe Donald Trump administration has taken positions against marijuana and the easing of laws regarding marijuana. Although Trump indicated during his 2016 presidential campaign that he favored leaving the issue of legalization of marijuana to the states, his administration subsequently upheld the federal prohibition of cannabis, and Trump's 2021 fiscal budget proposal included removing protections for state medical marijuana laws. In 2018, the administration rescinded the 2013 Cole Memorandum, an Obama-era Justice Department policy that generally directed federal prosecutors not to pursue marijuana prosecutions in states where marijuana is legal as a matter of state law.
 W
WAccording to the government of the United States, China is said to have begun a widespread effort to acquire U.S. military technology and classified information and the trade secrets of U.S. companies. China is accused of stealing trade secrets and technology, often from companies in the United States, to help support its long-term military and commercial development. China has been accused of using a number of methods to obtain U.S. technology, including espionage, exploitation of commercial entities, and a network of scientific, academic and business contacts. Espionage cases include Larry Wu-Tai Chin, Katrina Leung, Gwo-Bao Min, Chi Mak and Peter Lee.
 W
WThe Christian Patriot movement is a tendency within the broader American Patriot movement that emphasizes Christian nationalism. Like the larger movement, it promotes a revisionist interpretation of American history in which the federal government has turned against the ideas of liberty and natural rights expressed in the American Revolution.
 W
WThe Cole Memorandum was a United States Department of Justice memorandum issued August 29, 2013, by United States Deputy Attorney General James M. Cole during the presidency of Barack Obama. The memorandum, sent to all United States Attorneys, governed federal prosecution of offenses related to marijuana. The memo stated that given its limited resources, the Justice Department would not enforce federal marijuana prohibition in states that "legalized marijuana in some form and ... implemented strong and effective regulatory and enforcement systems to control the cultivation, distribution, sale, and possession of marijuana," except where a lack of federal enforcement would undermine federal priorities.
 W
WA school shooting and attempted bombing occurred on April 20, 1999, at Columbine High School in Columbine, Colorado, United States. The perpetrators, twelfth grade (senior) students Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold, murdered 12 students and one teacher. Ten students were killed in the school library, where the pair subsequently commited suicide. Twenty-one additional people were injured by gunshots, and gunfire was also exchanged with the police. Another three people were injured trying to escape the school. At the time, it was the deadliest school shooting in U.S. history. The crime has inspired several copycats and "Columbine" has become a byword for school shootings.
 W
WDuty: Memoirs of a Secretary at War is a nonfiction book written by Robert M. Gates, a former U.S. Secretary of Defense. It was published in January 2014 by Alfred A. Knopf. The time period is from 2006 to 2011, and includes the George W. Bush administration (2006–2009), the Obama administration (2009–2011), the Afghan war, and the Iraq War.
 W
WThe Fifth Party System is the era of American national politics that began with the New Deal in 1932 under President Franklin D. Roosevelt. This era of Democratic Party-dominance emerged from the realignment of the voting blocs and interest groups supporting the Democratic Party into the New Deal coalition, following the Great Depression, with most black voters switching from the GOP to the Democratic Party and most conservative, white southern Democrats shifting to the Republican Party as the Democratic party became known as the party of civil rights. For this reason, it is often called the "New Deal Party System". It followed the Fourth Party System, usually called the Progressive Era, and was followed by the current Sixth Party System, though the beginning of the Sixth Party System is disputed.
 W
WIndivisible is a progressive movement in the United States initiated in 2016 as a reaction to the election of Donald Trump as President of the United States. The movement began with the online publication of a handbook written by Congressional staffers with suggestions for peacefully but effectively resisting the move to the right in the executive branch of the United States government under the Trump administration that was widely anticipated and feared by progressives. According to Peter Dreier, the goal of Indivisible is to "save American democracy" and "resume the project of creating a humane America that is more like social democracy than corporate plutocracy."
 W
WMutual Defense Treaty Between the United States and the Republic of Korea is a treaty between South Korea and the United States signed on 1 October 1953, two months after the signing of the Korean Armistice Agreement which brought a halt to the fighting in the Korean War. The agreement commits the two nations to provide mutual aid if either faces external armed attack and allows the United States to station military forces in South Korea in consultation with the South Korean government.
 W
WThe North American Free Trade Agreement was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994, and superseded the 1988 Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement between the United States and Canada. The NAFTA trade bloc formed one of the largest trade blocs in the world by gross domestic product.
 W
WThe presidency of Barack Obama began at noon EST on January 20, 2009, when Barack Obama was inaugurated as the 44th President of the United States, and ended on January 20, 2017. Obama, a Democrat from Illinois, took office following a decisive victory over Republican nominee John McCain in the 2008 presidential election. Four years later, in the 2012 election, he defeated Republican Mitt Romney to win re-election. He was the first African American president, the first multiracial president, the first non-white president, and the first president to have been born in Hawaii. Obama was succeeded by Republican Donald Trump, who won the 2016 presidential election.
 W
WThe presidency of Bill Clinton began at noon EST on January 20, 1993, when Bill Clinton was inaugurated as the 42nd President of the United States, and ended on January 20, 2001. Clinton, a Democrat from Arkansas, took office following a decisive victory over Republican incumbent President George H. W. Bush and Independent businessman Ross Perot in the 1992 presidential election. Four years later, in the 1996 election, he defeated Perot and Republican Bob Dole to win re-election. He was succeeded by Republican George W. Bush, who won the 2000 presidential election.
 W
WThe presidency of Donald Trump began at noon EST on January 20, 2017, when he was inaugurated as the 45th president of the United States, succeeding Barack Obama. A Republican, Trump was a businessman and reality television personality from New York City at the time of his 2016 presidential election victory over Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton. While Trump lost the popular vote, he won the Electoral College vote, 304 to 227, in a presidential contest that American intelligence agencies concluded was targeted by a Russian interference campaign. Trump made many false or misleading statements during his campaign and presidency. The statements were documented by fact-checkers, with political scientists and historians widely describing the phenomenon as unprecedented in modern American politics. Trump's approval rating was stable, hovering at high-30 to mid-40 percent throughout his presidency. Trump ultimately lost the 2020 presidential election to Joe Biden, making him the first US president since George H. W. Bush to serve only one term despite having sought a second term. Trump has refused to concede and instead filed many frivolous lawsuits, and pressuring Republican officials in an attempt to get a second term in office.
 W
WThe presidency of George H. W. Bush began at noon EST on January 20, 1989, when George H. W. Bush was inaugurated as the 41st President of the United States, and ended on January 20, 1993. Bush, a Republican from Texas, took office after a landslide victory over Democrat Michael Dukakis in the 1988 presidential election. Following his defeat, he was succeeded by Democrat Bill Clinton, who won the 1992 presidential election.
 W
WThe presidency of George W. Bush began at noon EST on January 20, 2001, when George W. Bush was inaugurated as the 43rd president of the United States, and ended on January 20, 2009. Bush, a Republican, took office following a very close victory over Democratic incumbent vice president Al Gore in the 2000 presidential election. Four years later, in the 2004 election, he defeated Democrat John Kerry to win re-election. Bush, the 43rd president, is the eldest son of the 41st president, George H. W. Bush. He was succeeded by Democrat Barack Obama, who won the 2008 presidential election.
 W
WThe presidency of Joe Biden will officially begin when Joe Biden is inaugurated on January 20, 2021. When he assumes office as the 46th president, Kamala Harris will concurrently assume office as the 49th and first female vice president.
 W
WRuby Ridge was the site of an 11-day siege in 1992 in Boundary County, Idaho, near Naples. It began on August 21, when deputies of the United States Marshals Service (USMS) initiated action to apprehend and arrest Randy Weaver under a bench warrant after his failure to appear on firearms charges. Given three conflicting dates for his court appearance, and suspecting a conspiracy against him, Weaver refused to surrender, and members of his immediate family, and family friend Kevin Harris, resisted as well. The Hostage Rescue Team of the Federal Bureau of Investigation became involved as the siege developed.
 W
WThe Sixth Party System is the era in United States politics following the Fifth Party System. As with any periodization, opinions differ on when the Sixth Party System may have begun, with suggested dates ranging from the late 1960s or 1970 to the 1990s and beyond. According to political scientists Mark D. Brewer and L. Sandy Maisel in 2020:It seems safe to state that the sixth American party system featured strong divisions between Republicans and Democrats, rooted in cleavages based on social class, social and cultural issues, race and ethnicity, and the proper size and scope of the federal government.
 W
WThe Treaty Between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on Strategic Offensive Reductions (SORT), also known as the Treaty of Moscow, was a strategic arms reduction treaty between the United States and Russia that was in force from June 2003 until February 2011 when it was superseded by the New START treaty. At the time, SORT was positioned as "represent[ing] an important element of the new strategic relationship" between the two countries with both parties agreeing to limit their nuclear arsenal to between 1,700 and 2,200 operationally deployed warheads each. It was signed in Moscow on 24 May 2002. After ratification by the U.S. Senate and the State Duma, SORT came into force on 1 June 2003. It would have expired on 31 December 2012 if not superseded by New START. Either party could have withdrawn from the treaty upon giving three months written notice to the other.
 W
WThe Taiwan Relations Act is an act of the United States Congress. Since the recognition of the People's Republic of China, the Act has defined the officially substantial but non-diplomatic relations between the people of the United States and the people of Taiwan.
 W
WThe Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security between the United States and Japan , also known in Japan as Anpo jōyaku (安保条約) or just Anpo (安保) for short, is a treaty establishing a military alliance between the United States and Japan. The treaty was first signed in 1951 at the San Francisco Presidio after the signing of the Treaty of San Francisco at the San Francisco War Memorial Opera House. Then, the Security Treaty was amended further in January 1960 between the US and Japan in Washington, DC.
 W
WU.S.–Japan Status of Forces Agreement is an agreement between Japan and the United States signed on 19 January 1960 in Washington, the same day as the revised U.S.-Japan Security Treaty. It is a status of forces agreement (SOFA) as stipulated in article VI of that treaty, which referred to "a separate agreement" governing the "use of [...] facilities and areas [granted to the U.S.] as well as the status of United States armed forces in Japan". It replaced the earlier "U.S.-Japan Administrative Agreement" that governed such issues under the original 1951 security treaty.
 W
WThe United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is the U.S. federal executive department responsible for public security, roughly comparable to the interior or home ministries of other countries. Its stated missions involve anti-terrorism, border security, immigration and customs, cyber security, and disaster prevention and management.
 W
WThe 2024 United States presidential election will be the 60th quadrennial presidential election. It will be the first presidential election to be run with population data from the 2020 census.
 W
WThe Agreement between the United States of America, the United Mexican States, and Canada, commonly known by its American English title United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA), is a free trade agreement concluded between Canada, Mexico, and the United States as a successor to the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The agreement has been characterized as "NAFTA 2.0," or "New NAFTA," since many provisions from NAFTA were incorporated and its changes were seen as largely incremental. On July 1, 2020, the USMCA entered into force in all member states.
 W
WThe Victims of Immigration Crime Engagement (VOICE) Office is a U.S. government agency established within the Department of Homeland Security under the Trump administration in February 2017. President Donald Trump directed it be established by Executive Order 13768.
 W
WThe Waco siege, also known as the Waco Massacre was the law enforcement siege of the compound that belonged to the religious sect Branch Davidians. It was carried out by American federal, Texas state law enforcement, and the U.S. military, between February 28 and April 19, 1993. The Branch Davidians were led by David Koresh and were headquartered at Mount Carmel Center ranch in the community of Axtell, Texas, 13 miles northeast of Waco. Suspecting the group of stockpiling illegal weapons, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF) obtained a search warrant for the compound and arrest warrants for Koresh and a select few of the group's members.
 W
WThe 1993 World Trade Center bombing was a terrorist attack on the World Trade Center, carried out on February 26, 1993, when a truck bomb detonated below the North Tower of the World Trade Center in New York City. The 1,336 lb (606 kg) urea nitrate–hydrogen gas enhanced device was intended to send the North Tower crashing into the South Tower, bringing both towers down and killing tens of thousands of people. It failed to do so, but killed six people, one of whom was pregnant and injured over one thousand. About 50,000 people were evacuated from the buildings that day.