 W
WThe Applegate Trail was an emigrant trail through the present-day U.S. states of Idaho, Nevada, California, and Oregon used in the mid-19th century by emigrants on the American frontier. It was originally intended as a less dangerous alternative to the Oregon Trail by which to reach the Oregon Territory. Much of the route was coterminous with the California Trail.
 W
WThe Barbary Coast Trail is a marked trail that connects 20 historic sites and several local history museums in San Francisco, California. Approximately 180 bronze medallions and arrows embedded in the sidewalk mark the 3.8-mile (6.1 km) trail.
 W
WNewhall Pass is a low mountain pass in Los Angeles County, California. Historically called Fremont Pass and San Fernando Pass, with Beale's Cut, it separates the Santa Susana Mountains from the San Gabriel Mountains. Although the pass was originally discovered in August 1769 by Catalan explorer Gaspar de Portolà, it eventually was named for Henry Newhall, a significant businessman in the area during the 19th century.
 W
WButterfield Overland Mail was a stagecoach service in the United States operating from 1858 to 1861. It carried passengers and U.S. Mail from two eastern termini, Memphis, Tennessee, and St. Louis, Missouri, to San Francisco, California. The routes from each eastern terminus met at Fort Smith, Arkansas, and then continued through Indian Territory (Oklahoma), Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Mexico, and California ending in San Francisco. On March 3, 1857, Congress authorized the U.S. postmaster general, at that time Aaron V. Brown, to contract for delivery of the U.S. mail from St. Louis to San Francisco. Prior to this, U.S. Mail bound for the Far West had been delivered by the San Antonio and San Diego Mail Line since June 1857.
 W
WState Route 99 (SR 99), commonly known as Highway 99 or, simply, as 99, is a north–south state highway in the U.S. state of California, stretching almost the entire length of the Central Valley. From its southern end at Interstate 5 (I-5) near Wheeler Ridge to its northern end at SR 36 near Red Bluff, SR 99 goes through the densely populated eastern parts of the valley. Cities served include Bakersfield, Delano, Tulare, Visalia, Kingsburg, Selma, Fresno, Madera, Merced, Turlock, Modesto, Manteca, Stockton, Sacramento, Yuba City, and Chico.
 W
WState Route 154 is a state highway in the U.S. state of California that runs from Los Olivos to Santa Barbara, crossing the San Marcos Pass in the Santa Ynez Mountains. Before U.S. Route 101 was built through the Gaviota Pass, SR 154 was the main throughway to Santa Barbara and the tri city area including use as a stagecoach route in early years. After being replaced by US 101 as the primary route between the Santa Ynez Valley and Santa Barbara, SR 154 now serves as a scenic bypass.
 W
WThe California Trail was an emigrant trail of about 3,000 mi (4,800 km) across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail followed the same corridor of networked river valley trails as the Oregon Trail and the Mormon Trail, namely the valleys of the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater rivers to Wyoming. In the present states of Wyoming, Idaho, and Utah, the California and Oregon trails split into several different trails or cutoffs.
 W
WThe California Trail was an emigrant trail of about 3,000 mi (4,800 km) across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail followed the same corridor of networked river valley trails as the Oregon Trail and the Mormon Trail, namely the valleys of the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater rivers to Wyoming. In the present states of Wyoming, Idaho, and Utah, the California and Oregon trails split into several different trails or cutoffs.
 W
WThe Conejo Grade, also known as the Camarillo Grade, is a 7% grade incline with a summit elevation of 841.1 feet (256.4 m). It is a section of US 101 linking Thousand Oaks and cities of the Conejo Valley, with Camarillo and the cities on the Oxnard Plain. A Caltrans inspection station for trucks is stationed at the upper terminus of the grade.
 W
WEbbetts Pass, named after John Ebbets, is a high mountain pass through the Sierra Nevada range in Alpine County, California. Ebbetts is the eastern of two passes in the area traversed by State Route 4. The western pass is the Pacific Grade Summit. The pass is registered as a California Historical Landmark. The Pacific Crest Trail, a 2,650-mile (4,260 km) long National Scenic Trail crosses State Route 4 at Ebbetts Pass.
 W
WEl Camino Real, sometimes associated with Calle Real, usually refers to the 600-mile (965-kilometer) road connecting the 21 Spanish missions in California, along with a number of sub-missions, four presidios, and three pueblos, stretching at its southern end from the San Diego area Mission San Diego de Alcalá, all of the way up to the trail's northern terminus at Mission San Francisco Solano in Sonoma, just north of San Francisco Bay.
 W
WEmigrant Gap is a gap in a ridge on the California Trail as it crosses the Sierra Nevada, to the west of what is now known as Donner Pass. Here the cliffs are so steep that, back in the 1840s, the pioneers on their way to California had to lower their wagons on ropes in order to continue.
 W
WFoote's Crossing Road originates in North Columbia, California and winds through the Tahoe National Forest to connect with the community of Alleghany, California. It is a Registered Historic Place.
 W
WNewhall Pass is a low mountain pass in Los Angeles County, California. Historically called Fremont Pass and San Fernando Pass, with Beale's Cut, it separates the Santa Susana Mountains from the San Gabriel Mountains. Although the pass was originally discovered in August 1769 by Catalan explorer Gaspar de Portolà, it eventually was named for Henry Newhall, a significant businessman in the area during the 19th century.
 W
WThe Great Sierra Wagon Road was a route through the Sierra Nevada in California, built to bring supplies to the Great Sierra Mine on Tioga Hill in the high country of what was to become Yosemite National Park. The road was built in 1882 by the Great Sierra Silver Mining Company, extending over 56.25 miles (90.53 km), in 130 days. The mine promptly shut down, leaving the road without a purpose. In 1915 the road was purchased by Stephen T. Mather, the independently wealthy first director of the National Park Service, who donated it to the Park Service. The Park Service opened the road to the public, calling it the Tioga Road. Designated California State Route 120, the road traverses the park from its west to east entrances.
 W
WThe Jefferson Davis Highway, also known as the Jefferson Davis Memorial Highway, was a planned transcontinental highway in the United States in the 1910s and 1920s that began in Arlington, Virginia, and extended south and west to San Diego, California; it was named for Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States, United States senator, and Secretary of War. Because of unintended conflict between the National Auto Trail movement and the federal government, it is unclear whether it ever really existed in the complete form that its United Daughters of the Confederacy (UDC) founders originally intended.
 W
WThe Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail is a 1,210-mile (1,950 km) National Park Service unit in the United States National Historic Trail and National Millennium Trail programs. The trail route extends from Nogales on the U.S.-Mexico border in Arizona, through the California desert and coastal areas in Southern California and the Central Coast region to San Francisco.
 W
WThe La Playa Trail was a historic bayside trail in San Diego, connecting the settled inland areas to the commercial anchorage at Old La Playa on San Diego Bay. The La Playa Trail has been recognized as the oldest commercial trail in the Western United States. The trail was used during the Pre-Hispanic, Spanish, Mexican and American periods of San Diego history. Much of the length of the original trail corresponds to the current Rosecrans Street in the San Diego neighborhood of Point Loma. There are eight registered National Historic Districts and 70 identified historic sites along the trail, according to the La Playa Trail Association, which was formed in 2005 to recognize the historic nature of the trail and to honor the many different peoples who traveled along it.
 W
WThe Lincoln Highway is one of the earliest transcontinental highway routes for automobiles across the United States of America. Conceived in 1912 by Indiana entrepreneur Carl G. Fisher, and formally dedicated October 31, 1913, the Lincoln Highway ran coast-to-coast from Times Square in New York City west to Lincoln Park in San Francisco, originally through 13 states: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Nebraska, Colorado, Wyoming, Utah, Nevada, and California. In 1915, the "Colorado Loop" was removed, and in 1928, a realignment relocated the Lincoln Highway through the northern tip of West Virginia. Thus, there are a total of 14 states, 128 counties, and more than 700 cities, towns and villages through which the highway passed at some time in its history.
 W
WFor the trail's section in West Virginia see: The Midland Trail in West Virginia.
 W
WThe Mohave Trail was a Native American trade route between Mohave Indian villages on the Colorado River and settlements in coastal Southern California.
 W
WThe Mojave Road, also known as Old Government Road, is a historic route and present day dirt road across what is now the Mojave National Preserve in the Mojave Desert in the United States. This rough road stretched 147 miles (237 km) from Beale's Crossing, to Fork of the Road location along the north bank of the Mojave River where the old Mojave Road split off from the route of the Old Spanish Trail/Mormon Road.
 W
WThe Mojave Road Los Angeles was designated a California Historic Landmark on March 19, 1985. It runs from Drum Barracks in Los Angeles County to the Colorado River in San Bernardino County, California
 W
WNational Old Trails Road, also known as the Ocean-to-Ocean Highway, was established in 1912, and became part of the National Auto Trail system in the United States. It was 3,096 miles (4,983 km) long and stretched from Baltimore, Maryland, to California. Much of the route follows the old National Road and the Santa Fe Trail.
 W
WNewhall Pass is a low mountain pass in Los Angeles County, California. Historically called Fremont Pass and San Fernando Pass, with Beale's Cut, it separates the Santa Susana Mountains from the San Gabriel Mountains. Although the pass was originally discovered in August 1769 by Catalan explorer Gaspar de Portolà, it eventually was named for Henry Newhall, a significant businessman in the area during the 19th century.
 W
WThe Nobles Emigrant Trail, also known as the Fort Kearney, South Pass and Honey Lake Wagon Road, is a trail in California that was used by emigrant parties from the east as a shortened route to northern California. It was pioneered in 1851 by William Nobles, who discovered an easy shortcut between the Applegate Trail in Nevada and the Lassen Trail in California. The trail was extensively used until the 1870s, when it was superseded by railroads.
 W
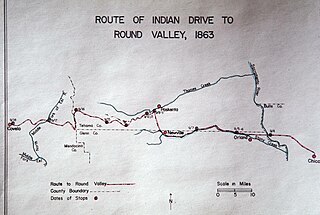
WThe Nome Cult Trail is a northern Californian historic trail located in present-day Mendocino National Forest which goes along Round Valley Road and through Rocky Ridge and the Sacramento Valley. It is also known as the Konkow Trail of Tears. On 28 August 1863 all Konkow Maidu were to be at the Bidwell Ranch in Chico to be taken to the Round Valley Reservation at Covelo in Mendocino County. Any Indians remaining in the area were to be shot. 435 Maidu were rounded up and marched under guard west out of the Sacramento Valley and through to the Coastal Range. 461 Native Americans started the trek, 277 finished. They reached Round Valley on 18 September 1863.
 W
WThe Old Plank Road is a plank road in Imperial County, California, that was built in 1915 as an east–west route over the Algodones Dunes. It effectively connected the extreme lower section of Southern California to Arizona and provided the last link in a commercial route between San Diego and Yuma.
 W
WThe Old Santa Susana Stage Road, or Santa Susana Wagon Road, is a route taken by early travelers between the San Fernando Valley and Simi Valley near Chatsworth, California, via the Santa Susana Pass. The main route climbs through what is now the Santa Susana Pass State Historic Park, with a branch in Chatsworth Park South.
 W
WThe Old Spanish Trail is a historical trade route that connected the northern New Mexico settlements of Santa Fe, New Mexico with those of Los Angeles, California and southern California. Approximately 700 mi (1,100 km) long, the trail ran through areas of high mountains, arid deserts, and deep canyons. It is considered one of the most arduous of all trade routes ever established in the United States. Explored, in part, by Spanish explorers as early as the late 16th century, the trail saw extensive use by pack trains from about 1830 until the mid-1850s.
 W
WThe Pony Express was a mail service delivering messages, newspapers, and mail using relays of horse-mounted riders that operated from April 3, 1860, to October 26, 1861, between Missouri and California in the United States of America.
 W
WPony Express National Historic Trail in the United States is the historic route of The Pony Express where men on horseback once carried the nation's mail across the country between 1860 and 1861. The horse-and-rider system became the United States' most direct and practical means of east-west communications before the telegraph, delivering mail in the unprecedented time of ten days.
 W
WNewhall Pass is a low mountain pass in Los Angeles County, California. Historically called Fremont Pass and San Fernando Pass, with Beale's Cut, it separates the Santa Susana Mountains from the San Gabriel Mountains. Although the pass was originally discovered in August 1769 by Catalan explorer Gaspar de Portolà, it eventually was named for Henry Newhall, a significant businessman in the area during the 19th century.
 W
WThe Santa Susana Pass, originally Simi Pass, is a low mountain pass in the Simi Hills of Southern California, connecting the San Fernando Valley and Los Angeles neighborhood of Chatsworth, to the city of Simi Valley and eponymous valley.
 W
WThe Siskiyou Trail stretched from California's Central Valley to Oregon's Willamette Valley; modern-day Interstate 5 follows this pioneer path. Originally based on existing Native American foot trails winding their way through river valleys, the Siskiyou Trail provided the shortest practical travel path between early settlements in California and Oregon.
 W
WSouthern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the California Gold Rush. Unlike the more northern routes, pioneer wagons could travel year round, mountain passes not being blocked by snows, however it had the disadvantage of summer heat and lack of water in the desert regions through which it passed in New Mexico Territory and the Colorado Desert of California. Subsequently, it was a route of travel and commerce between the eastern United States and California. Many herds of cattle and sheep were driven along this route and it was followed by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in 1857-1858 and then the Butterfield Overland Mail from 1858 - 1861.
 W
WTehachapi Pass is a mountain pass crossing the Tehachapi Mountains in Kern County, California. Traditionally, the pass marks the northeast end of the Tehachapis and the south end of the Sierra Nevada range.
 W
WThe Old Tejon Pass is a mountain pass in the Tehachapi Mountains linking Southern and Central California.
 W
WU.S. Route 6 (US 6) is a transcontinental United States Numbered Highway, stretching from Bishop, California, in the west to Provincetown, Massachusetts, in the east. The California portion of US 6 lies in the eastern portion of the state from Bishop in the Owens Valley north to the Nevada state line in Mineral County. Prior to a 1964 Highway renumbering project US 6 extended to the Pacific Ocean in Long Beach, California, as part of the historic auto trail named the Grand Army of the Republic Highway.
 W
WU.S. Route 66 is a part of a former United States Numbered Highway in the state of California that ran from the west in Santa Monica on the Pacific Ocean through Los Angeles and San Bernardino to Needles at the Arizona state line. It was truncated during the 1964 renumbering and its signage removed in 1974. The highway is now mostly replaced with several streets in Los Angeles, State Route 2 (SR 2), SR 110, SR 66, San Bernardino County Route 66 (CR 66), Interstate 15 (I-15), and I-40.
 W
WThe Victory Highway was an auto trail across the United States between New York City and San Francisco, roughly equivalent to the present U.S. Route 40. It was created by the Victory Highway Association, which was organized in 1921 to locate and mark a transcontinental highway to be dedicated to American forces who died in World War I. A series of Victory Eagle sculptures would mark the route, although only six were completed.
 W
WWalker Pass is a mountain pass by Lake Isabella in the southern Sierra Nevada. It is located in northeastern Kern County, approximately 53 mi (85 km) ENE of Bakersfield and 10 mi (16 km) WNW of Ridgecrest. The pass provides a route between the Kern River Valley and San Joaquin Valley on the west, and the Mojave Desert on the east.
 W
WYuma Crossing is a site in Arizona and California that is significant for its association with transportation and communication across the Colorado River. It connected New Spain and Las Californias in the Spanish Colonial period in and also during the Western expansion of the United States. Features of the Arizona side include the Yuma Quartermaster Depot and Yuma Territorial Prison. Features on the California Side include Fort Yuma, which protected the area from 1850 to 1885.