 W
WSteelmaking is the process of producing steel from iron ore and/or scrap. In steelmaking, impurities such as nitrogen, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur and excess carbon are removed from the sourced iron, and alloying elements such as manganese, nickel, chromium, carbon and vanadium are added to produce different grades of steel. Limiting dissolved gases such as nitrogen and oxygen and entrained impurities in the steel is also important to ensure the quality of the products cast from the liquid steel.
 W
WAnthracite iron or Anthracite 'Pig Iron' is the substance created by the smelting together of anthracite coal and iron ore, that is using Anthracite coal instead of charcoal to smelt iron ores — and was an important historic advance in the late-1830s enabling great acceleration the industrial revolution in Europe and North America.
 W
WArgon oxygen decarburization (AOD) is a process primarily used in stainless steel making and other high grade alloys with oxidizable elements such as chromium and aluminum. After initial melting the metal is then transferred to an AOD vessel where it will be subjected to three steps of refining; decarburization, reduction, and desulfurization. AOD was invented in 1954 by the Lindé Division of The Union Carbide Corporation.
 W
WBasic oxygen steelmaking, also known as Linz–Donawitz-steelmaking or the oxygen converter process is a method of primary steelmaking in which carbon-rich molten pig iron is made into steel. Blowing oxygen through molten pig iron lowers the carbon content of the alloy and changes it into low-carbon steel. The process is known as basic because fluxes of burnt lime or dolomite, which are chemical bases, are added to promote the removal of impurities and protect the lining of the converter.
 W
WA beehive oven is a type of oven in use since the Middle Ages in Europe. It gets its name from its domed shape, which resembles that of a skep, an old-fashioned type of beehive.
 W
WThe Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten.
 W
WA blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. Blast refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric pressure.
 W
WA bloomery is a type of furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called a bloom. The mix of slag and iron in the bloom, termed sponge iron, is usually consolidated and further forged into wrought iron. Blast furnaces, which produce pig iron, have largely superseded bloomeries.
 W
WA blowing engine is a large stationary steam engine or internal combustion engine directly coupled to air pumping cylinders. They deliver a very large quantity of air at a pressure lower than an air compressor, but greater than a centrifugal fan.
 W
WBuštěhrad slag heap is a huge artificial hill between municipalities of Kladno-Vrapice, Buštěhrad and Stehelčeves near Kladno in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic that have arisen in the late 20th century as a dumping site for slag from the Kladno ironworks, and other industrial waste. This is one of the most massive heaps of Kladno area, which, particularly when viewed from the northeast, forms by far visible and noticeable part of the landscape in shape of a mesa.
 W
WCarburising, carburizing, or carburisation is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide. The intent is to make the metal harder. Depending on the amount of time and temperature, the affected area can vary in carbon content. Longer carburizing times and higher temperatures typically increase the depth of carbon diffusion. When the iron or steel is cooled rapidly by quenching, the higher carbon content on the outer surface becomes hard due to the transformation from austenite to martensite, while the core remains soft and tough as a ferritic and/or pearlite microstructure.
 W
WThe Cementation furnace in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England is a Grade II Listed Building and is the only example of this type of steel making furnace to survive intact in Great Britain. It is situated on Doncaster Street in the St Vincent's Quarter just 0.6 miles (1 km) north west of the city centre.
 W
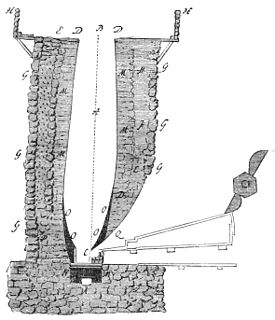
WThe cementation process is an obsolete technology for making steel by carburization of iron. Unlike modern steelmaking, it increased the amount of carbon in the iron. It was apparently developed before the 17th century. Derwentcote Steel Furnace, built in 1720, is the earliest surviving example of a cementation furnace. Another example in the UK is the cementation furnace in Doncaster Street, Sheffield.
 W
WCold blast, in ironmaking, refers to a furnace where air is not preheated before being blown into the furnace. This represents the earliest stage in the development of ironmaking. Until the 1820s, the use of cold air was thought to be preferable to hot air for the production of high-quality iron; this effect was due to the reduced moisture in cool winter air.
 W
WCrucible steel is steel made by melting pig iron, iron, and sometimes steel, often along with sand, glass, ashes, and other fluxes, in a crucible. In ancient times steel and iron were impossible to melt using charcoal or coal fires, which could not produce temperatures high enough. However, pig iron, having a higher carbon content thus a lower melting point, could be melted, and by soaking wrought iron or steel in the liquid pig-iron for a long time, the carbon content of the pig iron could be reduced as it slowly diffused into the iron. Crucible steel of this type was produced in South and Central Asia during the medieval era. This generally produced a very hard steel, but also a composite steel that was inhomogeneous, consisting of a very high-carbon steel and a lower-carbon steel. This often resulted in an intricate pattern when the steel was forged, filed or polished, with possibly the most well-known examples coming from the wootz steel used in Damascus swords. The steel was often much higher in carbon content and in quality in comparison with other methods of steel production of the time because of the use of fluxes.
 W
WDamascus steel was the forged steel of the blades of swords smithed in the Near East from ingots of Wootz steel either imported from Southern India or made in production centres in Merv or Khorasan. These swords are characterized by distinctive patterns of banding and mottling reminiscent of flowing water, sometimes in a "ladder" or "rose" pattern. Such blades were reputed to be tough, resistant to shattering, and capable of being honed to a sharp, resilient edge.
 W
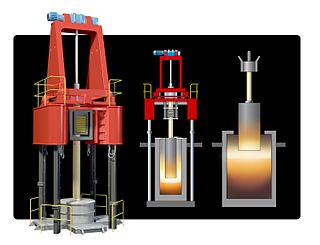
WAn electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats charged material by means of an electric arc.
 W
WElectroslag remelting (ESR), also known as electro-flux remelting, is a process of remelting and refining steel and other alloys for mission-critical applications in aircraft, thermal power stations, nuclear power plants, military technology, etc.
 W
WA finery forge is a forge used to produce wrought iron from pig iron by decarburization in a process called "fining" which involved liquifying cast iron in a fining hearth and removing carbon from the molten cast iron through oxidation. Finery forges were used as early as the 3rd century BC in China. The finery forge process was replaced by the puddling process and the roller mill, both developed by Henry Cort in 1783–4, but not becoming widespread until after 1800.
 W
WThe Flodin process is a direct reduction process for manufacturing modern iron, developed by Gustaf Henning Flodin from Sweden and patented in 1924.
 W
WThe Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten.
 W
WA heat number is an identification coupon number that is stamped on a material plate after it is removed from the ladle and rolled at a steel mill.
 W
WFerrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and alloys. It began far back in prehistory. The earliest surviving iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ores began, but by the end of the 2nd millennium BC iron was being produced from iron ores from at least Greece to India, and more controversially Sub-Saharan Africa. The use of wrought iron was known by the 1st millennium BC, and its spread marked the Iron Age. During the medieval period, means were found in Europe of producing wrought iron from cast iron using finery forges. For all these processes, charcoal was required as fuel.
 W
WHot blast refers to the preheating of air blown into a blast furnace or other metallurgical process. As this considerably reduced the fuel consumed, hot blast was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution. Hot blast also allowed higher furnace temperatures, which increased the capacity of furnaces.
 W
WThe Hulett was an ore unloader that was widely used on the Great Lakes of North America. It was unsuited to tidewater ports because it could not adjust for rising and falling tides, although one was used in New York City.
 W
WIn metallurgy, a ladle is a vessel used to transport and pour out molten metals. Ladles are often used in foundries and range in size from small hand carried vessels that resemble a kitchen ladle and hold 20 kilograms (44 lb) to large steelmill ladles that hold up to 300 tonnes. Many non-ferrous foundries also use ceramic crucibles for transporting and pouring molten metal and will also refer to these as ladles.
 W
WMelt is the working material in the steelmaking process, in making glass, and when forming thermoplastics. In thermoplastics, melt is the plastic in its forming temperature, which can vary depending on how it is being used. For steelmaking, it refers to steel in liquid form.
 W
WMill scale, often shortened to just scale, is the flaky surface of hot rolled steel, consisting of the mixed iron oxides iron(II) oxide (FeO), iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3), and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4, magnetite).
 W
WOpen hearth furnaces are one of a number of kinds of furnace where excess carbon and other impurities are burnt out of pig iron to produce steel. Since steel is difficult to manufacture due to its high melting point, normal fuels and furnaces were insufficient and the open hearth furnace was developed to overcome this difficulty. Compared to Bessemer steel, which it displaced, its main advantages were that it did not expose the steel to excessive nitrogen, was easier to control, and it permitted the melting and refining of large amounts of scrap iron and steel.
 W
WPattern welding is the practice in sword and knife making of forming a blade of several metal pieces of differing composition that are forge-welded together and twisted and manipulated to form a pattern. Often mistakenly called Damascus steel, blades forged in this manner often display bands of slightly different patterning along their entire length. These bands can be highlighted for cosmetic purposes by proper polishing or acid etching. Pattern welding was an outgrowth of laminated or piled steel, a similar technique used to combine steels of different carbon contents, providing a desired mix of hardness and toughness. Although modern steelmaking processes negate the need to blend different steels, pattern welded steel is still used by custom knifemakers for the cosmetic effects it produces.
 W
WPig iron is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel, also known as crude iron, which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a very high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silica and other constituents of dross, which makes it very brittle and not useful directly as a material except for limited applications.
 W
WPuddling is a step in the manufacture of high-grade iron in a crucible or furnace. It was invented in Great Britain during the Industrial Revolution. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in a oxidizing environment, resulting in wrought iron. It was one of the most important processes of making the first appreciable volumes of valuable and useful bar iron without the use of charcoal. Eventually, the furnace would be used to make small quantities of specialty steels.
 W
WA reja ("grille") is a decorative screen of iron.
 W
WA salamander in the metallurgy dialect means all liquid and solidified materials in the hearth of a blast furnace below the tap hole.
 W
WSlag is the glass-like by-product left over after a desired metal has been separated from its raw ore. Slag is usually a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. However, slags can contain metal sulfides and elemental metals. While slags are generally used to remove waste in metal smelting, they can also serve other purposes, such as assisting in the temperature control of the smelting, and minimizing any re-oxidation of the final liquid metal product before the molten metal is removed from the furnace and used to make solid metal. In some smelting processes, such as ilmenite smelting to produce titanium dioxide, the slag is the valuable product instead of the metal.
 W
WThe Stassano furnace is an electric arc furnace for the production of steel. Invented by Ernesto Stassano in 1898, it is the first electric furnace in history for ferrous metallurgy.
 W
WA steel mill or steelworks is an industrial plant for the manufacture of steel. It may be an integrated steel works carrying out all steps of steelmaking from smelting iron ore to rolled product, but may also be a plant where steel semi-finished casting products are made from molten pig iron or from scrap.
 W
Wsteeluniversity is a collection of free-to-use E-learning resources and interactive simulations covering major aspects of iron and steelmaking. It provides the underlying scientific, metallurgical and engineering principles and environmental aspects of the production, use and recycling of steel. These internet-delivered resources are aimed at undergraduate students of metallurgy, materials science and engineering subjects as well as graduate employees in the steel industry supply chain.
 W
WThe tatara (鑪) is the traditional Japanese furnace used for smelting iron and steel. The word later also came to mean the entire building housing the furnace. The traditional steel in Japan comes from ironsand processed in a special way, called tatara system.
 W
WTinning is the process of thinly coating sheets of wrought iron or steel with tin, and the resulting product is known as tinplate. The term is also widely used for the different process of coating a metal with solder before soldering.
 W
WA tank car is a type of railroad car or rolling stock designed to transport liquid and gaseous commodities.
 W
WA tuyere or tuyère is a tube, nozzle or pipe through which air is blown into a furnace or hearth.
 W
WA Walloon forge is a type of finery forge that decarbonizes pig iron into wrought iron.