 W
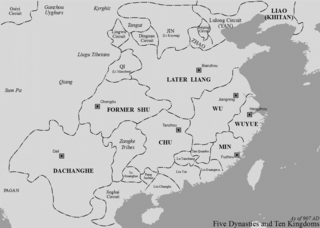
WChu, often referred to as Ma Chu (马楚) or Southern Chu (南楚) to distinguish it from other historical states called Chu, was a kingdom in south China during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960). It existed from 907 to 951.
 W
WDachanghe or possibly Da Changhe was a kingdom from 902 to 928 in modern Yunnan, China. Founded by Zheng Maisi (鄭買嗣), it was the successor state of the Kingdom of Nanzhao (738–902), whose ruling Meng (蒙) family was mass-murdered in a bloody coup by Zheng. The Zheng family suffered a similar fate 26 years later at the hands of Yang Ganzhen (楊干貞), who helped found a state named Datianxing (大天興) (928–929).
 W
WThe Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State, was a kingdom situated in modern Yunnan province, China from 937 until 1253 when it was conquered by the Mongols. Its kings continued to administer the area as Mongol vassals until the Ming conquest of Yunnan. Today the former capital of the Dali Kingdom is still called Dali in modern Yunnan Province.
 W
WThe Dule Temple is a Buddhist temple located in Jizhou District of suburban Tianjin, China. The temple is of historical as well as architectural significance. Its oldest surviving buildings are two timber-frame structures, the front gate and the central hall (pavilion) that houses a colossal clay statue of the goddess Guanyin (Avalokiteśvara). Both structures date back to the Liao dynasty and are among the oldest surviving wooden buildings in China.
 W
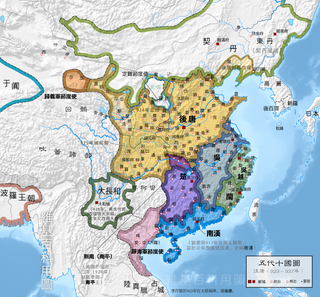
WThe Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–979) was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was the last prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history.
 W
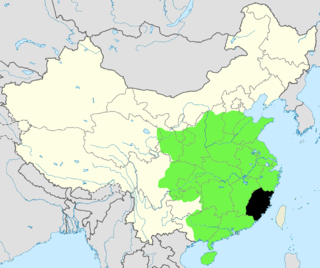
WFujian Circuit, also translated as Fujian Province, was one of the major circuits during the Tang and Song dynasties of imperial China. Its administrative area corresponds to roughly the modern Chinese province of Fujian.
 W
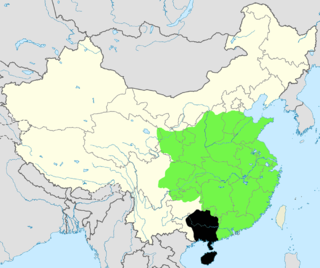
WGuangnan East Circuit or Guangnan East Province was one of the major circuits during the Song dynasty. Its administrative area corresponds to roughly the modern Chinese province of Guangdong.
 W
WGuangnan West Circuit or Guangnan West Province was one of the major circuits during the Song dynasty. Its administrative area corresponds to roughly the modern provinces of Guangxi and Hainan, as well as the western part of Guangdong.
 W
WHaimen is a district of Nantong, Jiangsu province, with a population of approximately 1 million. It is located at the opposite side of the Yangtze River to Shanghai and is directly north of Chongming Island except for a small portion that forms Haimen City's Haiyong Township. Haimen is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Haimen. Haimen is located in the poorer north Jiangsu region and together with Qidong City, traditionally has one of the highest rates of liver cancer in China and in the world, with upwards of 1 out of every 10 adults in the rural areas dying from liver cancer.
 W
WThe Later Han was founded in 947. It was the fourth of the Five Dynasties, and the third consecutive sinicized Shatuo ethnicity state, however, other sources indicate that the Later Han emperors claimed patrilineal Han Chinese ancestry. It was among the shortest-lived of all Chinese regimes, lasting for slightly under four years before it was overcome by a rebellion that resulted in the founding of the Later Zhou.
 W
WThe Northern Han was a dynastic state of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Liu Min (劉旻), formerly known as Liu Chong (劉崇), and lasted from 951 to 979.
 W
WSouthern Han, originally Yue, was one of the ten kingdoms that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located on China's southern coast, controlling modern Guangdong and Guangxi. The kingdom greatly expanded its capital Xingwang Fu. It attempted but failed to annex the independent polity of Jinghai which was controlled by the Vietnamese.
 W
WThe Hoi Tong Monastery, also known by many other names, is a Buddhist temple and monastery on Henan Island in Guangzhou, China. It shares its grounds with the city's Haichuang Park.
 W
WHuazhou or Hua Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China in modern southwestern Guangdong, China. It existed from 980 to 1912.
 W
WHualin Temple is a Buddhist temple located in Gulou District, Fuzhou, Fujian. After the introduction of Chan Buddhism from China to Japan in the Song dynasty (960–1279), the architectural style of Song dynasty have a profound influence on Japan traditional cultural and folk customs. The oldest things in the temple is the Main Hall, which was built in the early Song dynasty (960–1279).
 W
WThe Iron Lion of Cangzhou, also known as the "Sea Guard Howler", is a cast iron sculpture located in Cangzhou City, in Hebei Province, China, about 180 km (110 mi) southwest of Beijing. Cast in the Later Zhou dynasty in 953, the iron lion is the largest known and oldest surviving iron-cast artwork in China.
 W
WJin, also known as Hedong (河東) and Former Jin (前晉) in historiography, was an early state of the imperial Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period until 923 when it became the Later Tang dynasty (923–937). Its rulers were the Shatuo warlords Li Keyong and Li Cunxu. Although the Five Dynasties period began only in 907, Li Keyong's territory which centered around modern Shanxi can be referred to as Jin as early as 896, when he was officially created the Prince of Jin by the failing and powerless Tang dynasty court, or even as early as 883, when he was created the jiedushi of Hedong Circuit, which controlled more or less the same territory.
 W
WThe Later Jìn, also called Shi Jin (石晉), was one of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in China. It was founded by Shi Jingtang and became a vassal of the Khitan-led Liao dynasty, its protector. After Jin's second ruler, Shi Chonggui, fell out with the Liao, the Liao invaded in 946 and 947, destroying and annexing the Later Jin.
 W
WJinghu North Circuit or Jinghu North Province was one of the circuits during the Song dynasty. Its administrative area corresponds to roughly the modern province of Hunan.
 W
WJinghu South Circuit or Jinghu South Province was one of the circuits during the Song dynasty. Its administrative area corresponds roughly to the modern province of Hunan.
 W
WJingnan, also known as Nanping and Northern Chu (北楚) in historiography, was one of the Ten Kingdoms in south-central China created in 924, marking the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960).
 W
WLeifeng Pagoda is a five story tall tower with eight sides, located on Sunset Hill south of the West Lake in Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China. Originally constructed in the year AD 975, it collapsed in 1924 but was rebuilt in 2002. Since then, it has become a popular tourist attraction.
 W
WThe Later Liang, also known as Zhu Liang, was one of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in China. It was founded by Zhu Wen, posthumously known as Taizu of Later Liang, after he forced the last emperor of the Tang dynasty to abdicate in his favour. The Later Liang would last until 923 when it was destroyed by Later Tang.
 W
WLiangzhe Circuit (997–1160s) was one of the major circuits during the Song dynasty (960–1279). Its administrative area corresponds roughly to modern Zhejiang, Shanghai, and southern Jiangsu. The fertile Yangtze River Delta lay within Liangzhe Circuit, as did Lake Tai. Liangzhe was the wealthiest circuit in Song.
 W
WThe Liao dynasty, also known as the Liao Empire, officially the Great Liao, or the Khitan (Qidan) State, was an empire and imperial dynasty in East Asia that ruled from 916 to 1125 over present-day Northern and Northeast China, Mongolia and portions of the Russian Far East and North Korea. The empire was founded by Yelü Abaoji, Khagan of the Khitans around the time of the collapse of the Tang dynasty, and was the first state to control all of Manchuria. Being ruled by the Khitan Yelü clan, the Liao dynasty is considered by historians to be a conquest dynasty of China.
 W
WLiuhe Pagoda, literally Six Harmonies Pagoda, is a multi-story Chinese pagoda in southern Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, China. It is located at the foot of Yuelun Hill, facing the Qiantang River. It was originally constructed in 970 by the Wuyue Kingdom, destroyed in 1121, and reconstructed fully by 1165, during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279).
 W
WMin was one of the Ten Kingdoms which was in existence between the years of 909 and 945. It existed in a mountainous region of modern-day Fujian province of China and had a history of quasi-independent rule. Its capital was Fuzhou. It was founded by Wang Shenzhi.
 W
WNanjing was the name for modern Beijing during the Liao dynasty, when Khitan rulers made the city the southern capital. To distinguish Nanjing, which literally means "Southern Capital" in Chinese, from modern Nanjing in Jiangsu Province and Beijing Damingfu, the Northern Song Dynasty name for modern Daming County in Hebei Province, Chinese historians sometimes refer to Beijing during the Liao dynasty as Liao Nanjing. The Khitan rulers of the Liao acquired the city, then known as Youzhou, in the cession of the Sixteen Prefectures in 938 from the Later Jìn, one of the five shortlived dynasties that ruled northern China following the end of the Tang Dynasty. The city was officially renamed Nanjing, Youdu Fu (南京幽都府). In 1012, the city was renamed Nanjing, Xijin Fu (南京析津府). The city was also colloquially referred to at the time as Yanjing. In 1122, the city was captured by the Jurchen Jin dynasty and was officially renamed Yanjing, ending the use of Nanjing for what is today modern Beijing.
 W
WThe Niujie Mosque(simplified Chinese: 牛街礼拜寺; traditional Chinese: 牛街禮拜寺; pinyin: Niú Jiē Lǐ Bài Sì; Wade–Giles: Niu-chieh Li-pai-ssu "Oxen Street House of Worship" or Chinese: 牛街清真寺; pinyin: Niú Jiē Qīng Zhēn Sì; Wade–Giles: Niu-chieh Ch'ing-chen-ssu "Oxen Street Mosque") is the oldest mosque in Beijing, China. It was first built in 996 during the Liao Dynasty and was reconstructed as well as enlarged under the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing Dynasty.
 W
WPuji Temple is a Buddhist temple located on the island of Putuoshan in Zhoushan, Zhejiang, China.
 W
WShanghai is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China. It is under the direct administration of the State Council of China. The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. With a population of 24.28 million as of 2019, it is the most populous urban area in China and the second most populous city proper in the world. Shanghai is a global center for finance, research, technology, manufacturing, and transportation, and the Port of Shanghai is the world's busiest container port.
 W
WGreat Shu called in retrospect Former Shu or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was one of the Ten Kingdoms formed during the chaotic period between the rules of the Tang dynasty and the Song dynasty. It existed in 907–925 CE. It was the third state named "Shu" on the same territory, the second one having been Shu Han.
 W
WShu, also known as Meng Shu, was one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in China. It was located in present-day Sichuan with its capital in Chengdu and lasted from 934 to 965. It was the fourth and latest state of this name on the same territory.
 W
WThe Song dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties to its north. It was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.
 W
WTang, known in history as Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty that lasted from 923 to 937 during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in the history of China.
 W
WSouthern Tang, later known as Jiangnan (江南), was an empire in Southern China and one of the so-called Ten Kingdoms between the fall of the Tang in 907 and the start of the Song dynasty in 960. Southern Tang replaced the Wu empire when Li Bian deposed the emperor Yang Pu.
 W
WThe Yongling Mausoleum, commonly known as the tomb of Wang Jian, is the burial place of Wang Jian (847–918), the founding emperor of Former Shu. It is located at 10 Yongling Road, Jinniu District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
 W
WWu (吳), also referred to as Huainan (淮南), Hongnong (弘農), Southern Wu (南吳), or Yang Wu (楊吳), was one of the Ten Kingdoms in eastern China which was in existence from 907 to 937. Its capital was Jiangdu Municipality (江都).
 W
WWuyue, 907–978, was an independent coastal kingdom founded during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960) of Chinese history. It was ruled by the Qian family, whose family name remains widespread in the kingdom's former territory.
 W
WYan, sometimes known in historiography as Jie Yan (桀燕), was a very short-lived kingdom in the vicinity of present-day Beijing at the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, which is traditionally dated as being from 907 to 960. Yan, established by Liu Shouguang in 911, only lasted for two years before destroyed by Li Cunxu the prominent leader of Later Tang.
 W
WYanfu Temple or Yanfu Chan Temple is a Buddhist temple located in Wuyi County, Zhejiang, China. The Mahavira Hall is the earliest Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) architecture and one of the three Yuan dynasty wooden architecture in Jiangnan.
 W
WThe Yuelu Academy is on the east side of Yuelu Mountain in Changsha, Hunan province, on the west bank of the Xiang River. As one of the four most prestigious academies over the last 1000 years in China, Yuelu Academy has been a famous institution of higher learning as well as a centre of academic activities and cultures since it was formally set up during the Northern Song dynasty. The academy was converted into Hunan Institute of Higher Learning in 1903. It was later renamed Hunan Normal College, Hunan Public Polytechnic School, and finally Hunan University in 1926. Yuelu Academy was once the center for the pursuit of Chinese ancient learning and idealism in China's feudalist era.
 W
WYuxi is a prefecture-level city in the central part of Yunnan province of the People's Republic of China. The administrative center of Yuxi is Hongta District. Yuxi is approximately 90 kilometres (56 mi) south of Kunming.
 W
WZhao was a state early in the Five Dynasties period of the history of China in what is now central Hebei. The ancestors of Zhao's only prince, Wang Rong, had long governed the region as military governors (Jiedushi) of the Tang dynasty's Chengde Circuit, and after the collapse of the Tang in 907, the succeeding Later Liang's founding emperor ("Taizu"), Zhu Wen made Wang, then his vassal, the Prince of Zhao. In 910, when the Emperor tried to directly take over the territory of Zhao and its neighboring Yiwu Circuit, Wang Rong and Yiwu's military governor Wang Chuzhi turned against the Later Liang, aligning themselves with Later Liang's archenemy, Jin's prince, Li Cunxu, instead. In 921, Wang Rong's soldiers assassinated him, slaughtered the Wang clan, and supported his adoptive son Zhang Wenli to succeed him instead. Li Cunxu soon defeated Zhang Wenli's son and successor Zhang Chujin and incorporated Zhao into Jin territory.
 W
WThe Later Zhou was the last in a succession of five dynasties that controlled most of northern China during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, which lasted from 907 to 960 and bridged the gap between the Tang Dynasty and the Song Dynasty.