 W
WThe Articles of Capitulation of Montreal were agreed upon between the Governor General of New France, Pierre François de Rigaud, Marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnal, and Major-General Jeffery Amherst on behalf of the French and British crowns. They were signed on 8 September 1760 in the British camp before the city of Montreal, during the French and Indian War after a two month campaign which led to the fall of the city.
 W
WThe Articles of Capitulation of Quebec were agreed upon between Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Roch de Ramezay, King's Lieutenant, Admiral Sir Charles Saunders, and General George Townshend on behalf of the French and British crowns during the Seven Years' War. They were signed on 18 September 1759, shortly after the Battle of the Plains of Abraham.
 W
WThe Bay of Fundy Campaign occurred during the French and Indian War when the British ordered the Expulsion of the Acadians from Acadia after the Battle of Fort Beauséjour (1755). The Campaign started at Chignecto and then quickly moved to Grand-Pré, Rivière-aux-Canards, Pisiguit, Cobequid, and finally Annapolis Royal. Approximately 7,000 Acadians were deported to the New England colonies.
 W
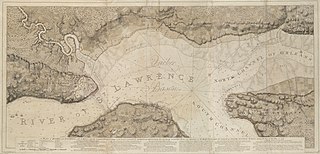
WThe Battle of Beauport, also known as the Battle of Montmorency, fought on 31 July 1759, was an important confrontation between the British and French Armed Forces during the Seven Years' War of the French province of Canada. The attack conducted by the British against the French defense line of Beauport, some 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) east of Quebec was checked, and the British soldiers of General James Wolfe retreated with 443 casualties and losses.
 W
WThe Battle of Bloody Creek was fought on December 8, 1757, during the French and Indian War. An Acadian and Mi'kmaq militia defeated a detachment of British soldiers of the 43rd Regiment at Bloody Creek, which empties into the Annapolis River at present day Carleton Corner, Nova Scotia, Canada. The battle occurred at the same site as a battle in 1711 during Queen Anne's War.
 W
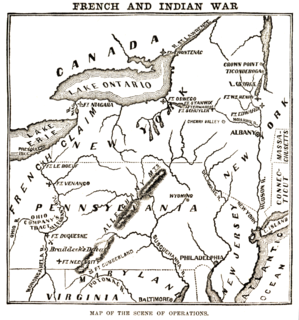
WThe Braddock expedition, also called Braddock's campaign or Braddock's Defeat, was a failed British military expedition which attempted to capture the French Fort Duquesne in the summer of 1755, during the French and Indian War. It was defeated at the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, and the survivors retreated. The expedition takes its name from General Edward Braddock, who led the British forces and died in the effort. Braddock's defeat was a major setback for the British in the early stages of the war with France and has been described as one of the most disastrous defeats for the British in the 18th century.
 W
WThe Cape Sable Campaign occurred in the fall of 1758 during the French and Indian War. The British sought to neutralize Acadian support for the French by deporting them. Colonel Roger Morris led a force of 325 British soldiers, aided by Captain Joseph Gorham with 60 rangers and Rogers' Rangers, to destroy the Acadian settlements in present-day Shelburne County and Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia, Canada.
 W
WThe Battle of Carillon, also known as the 1758 Battle of Ticonderoga, was fought on July 8, 1758, during the French and Indian War. It was fought near Fort Carillon on the shore of Lake Champlain in the frontier area between the British colony of New York and the French colony of New France.
 W
WThe Forbes Expedition was a British military expedition led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Beauséjour was fought on the Isthmus of Chignecto and marked the end of Father Le Loutre's War and the opening of a British offensive in the Acadia/Nova Scotia theatre of the Seven Years' War, which would eventually lead to the end of the French Empire in North America. The battle also reshaped the settlement patterns of the Atlantic region, and laid the groundwork for the modern province of New Brunswick.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Bull was a French attack on the British-held Fort Bull on 27 March 1756, early in the French and Indian War. The fort was built to defend a portion of the waterway connecting Albany, New York to Lake Ontario via the Mohawk River.
 W
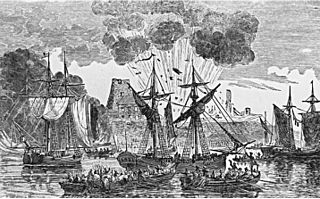
WThe Battle of Fort Duquesne was British assault on the eponymous French fort that was repulsed with heavy losses on 14 September 1758, during the French and Indian War.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Frontenac took place on August 26–28, 1758 during the Seven Years' War between France and Great Britain. The location of the battle was Fort Frontenac, a French fort and trading post which is located at the site of present-day Kingston, Ontario, at the eastern end of Lake Ontario where it drains into the St. Lawrence River.
 W
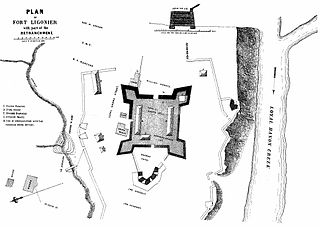
WThe Battle of Fort Ligonier was a battle of the French and Indian War. On 12 October 1758, French and Indian forces directed from nearby Fort Duquesne were repulsed in an attack on the British outpost of Fort Ligonier, then still under construction.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Necessity took place on July 3, 1754, in what is now Farmington in Fayette County, Pennsylvania. The engagement, along with the May 28 skirmish known as the Battle of Jumonville Glen, was George Washington's first military experience and the only surrender of his military career. The Battle of Fort Necessity began the French and Indian War, which later spiraled into the global conflict known as the Seven Years' War.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Niagara was a siege late in the French and Indian War, the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War. The British siege of Fort Niagara in July 1759 was part of a campaign to remove French control of the Great Lakes and Ohio Valley regions, making possible a western invasion of the French province of Canada in conjunction with General James Wolfe's invasion to the east.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Oswego was one in a series of early French victories in the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War won in spite of New France's military vulnerability. During the week of August 10, 1756, a force of regulars and Canadian militia under General Montcalm captured and occupied the British fortifications at Fort Oswego, located at the site of present-day Oswego, New York.
 W
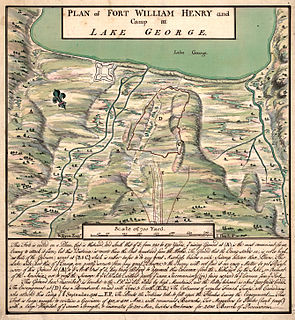
WThe Siege of Fort William Henry was conducted in August 1757 by French General Louis-Joseph de Montcalm against the British-held Fort William Henry. The fort, located at the southern end of Lake George, on the frontier between the British Province of New York and the French Province of Canada, was garrisoned by a poorly supported force of British regulars and provincial militia led by Lieutenant Colonel George Monro. After several days of bombardment, Monro surrendered to Montcalm, whose force included nearly 2,000 Indians from various tribes. The terms of surrender included the withdrawal of the garrison to Fort Edward, with specific terms that the French military protect the British from the Indians as they withdrew from the area.
 W
WThe Gulf of St. Lawrence Campaign occurred during the French and Indian War when British forces raided villages along present-day New Brunswick and the Gaspé Peninsula coast of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. Sir Charles Hardy and Brigadier-General James Wolfe were in command of the naval and military forces respectively. After the Siege of Louisbourg, Wolfe and Hardy led a force of 1,500 troops in nine vessels to the Gaspé Bay arriving there on September 5. From there they dispatched troops to Miramichi Bay, Grande-Rivière, Quebec and Pabos, and Mont-Louis, Quebec. Over the following weeks, Sir Charles Hardy took 4 sloops or schooners, destroyed about 200 fishing vessels and took about two hundred prisoners.
 W
WThe Ile Saint-Jean Campaign was a series of military operations in fall 1758, during the Seven Years' War, to deport the Acadians who either lived on Ile Saint-Jean or had taken refuge there from earlier deportation operations. Lieutenant-Colonel Andrew Rollo led a force of 500 British troops to take possession of Ile Saint-Jean.
 W
WThe Battle of Jumonville Glen, also known as the Jumonville affair, was the opening battle of the French and Indian War, fought on May 28, 1754, near present-day Hopwood and Uniontown in Fayette County, Pennsylvania. A company of colonial militia from Virginia under the command of Lieutenant Colonel George Washington, and a small number of Mingo warriors led by Tanacharison, ambushed a force of 35 Canadiens under the command of Joseph Coulon de Villiers de Jumonville.
 W
WThe Battle of Lake George was fought on 8 September 1755, in the north of the Province of New York. The battle was part of a campaign by the British to expel the French from North America, in the French and Indian War.
 W
WThe Louisbourg Expedition (1757) was a failed British attempt to capture the French Fortress of Louisbourg on Île Royale during the Seven Years' War.
 W
WThe Siege of Louisbourg was a pivotal operation of the Seven Years' War in 1758 that ended the French colonial era in Atlantic Canada and led to the subsequent British campaign to capture Quebec in 1759 and the remainder of French North America the following year.
 W
WThe Raid on Lunenburg occurred during the French and Indian War when Mi'kmaw and Maliseet fighters attacked a British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on May 8, 1756. The native militia raided two islands on the northern outskirts of the fortified Township of Lunenburg, [John] Rous Island and Payzant Island. According to French reports, the Raiding party killed twenty settlers and took five prisoners. This raid was the first of nine the Natives and Acadians would conduct against the peninsula over a three-year period during the war. The Wabanaki Confederacy took John Payzant and Lewis Payzant prisoner, both of whom left written account of their experiences.
 W
WThe Lunenburg Campaign was executed by the Mi'kmaq militia and Acadian militia against the Foreign Protestants who the British had settled on the Lunenburg Peninsula during the French and Indian War. The British deployed Joseph Gorham and his Rangers along with Captain Rudolf Faesch and regular troops of the 60th Regiment of Foot to defend Lunenburg. The Campaign was so successful, by November 1758, the members of the House of Assembly for Lunenburg stated "they received no benefit from His Majesty's Troops or Rangers" and required more protection.
 W
WThe Battle of the Monongahela took place on 9 July 1755, at the beginning of the French and Indian War, at Braddock's Field in what is now Braddock, Pennsylvania, 10 miles (16 km) east of Pittsburgh. A British force under General Edward Braddock, moving to take Fort Duquesne, was defeated by a force of French and Canadian troops under Captain Daniel Liénard de Beaujeu with its American Indian allies.
 W
WThe Montreal Campaign, also known as the Fall of Montreal, was a British three-pronged offensive against Montreal which took place from July 2 to 9 September 1760 during the French and Indian War as part of the global Seven Years' War. The campaign, pitted against an outnumbered and outsupplied French army, led to the capitulation and occupation of Montreal, the largest remaining city in French Canada.
 W
WThe Battle of Neuville, or Pointe-aux-Trembles, was a naval and land engagement that took place on 16 May 1760 during the French and Indian War on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River, near the village of Neuville, in New France, during the French siege of Quebec. A relief force of the Royal Navy, having forced a passage down the Saint Lawrence, managed to destroy the French ships led by Jean Vauquelin assisting in the siege. The British victory forced the French under Chevalier de Lévis to raise the siege and to withdraw attempts to retake Quebec City.
 W
WThe Petitcodiac River Campaign was a series of British military operations from June to November 1758, during the French and Indian War, to deport the Acadians that either lived along the Petitcodiac River or had taken refuge there from earlier deportation operations, such as the Ile Saint-Jean Campaign. Under the command of George Scott, William Stark's company of Rogers Rangers, Benoni Danks and Gorham's Rangers carried out the operation.
 W
WThe Battle of the Plains of Abraham, also known as the Battle of Quebec, was a pivotal battle in the Seven Years' War. The battle, which began on 13 September 1759, was fought on a plateau by the British Army and Royal Navy against the French Army, just outside the walls of Quebec City on land that was originally owned by a farmer named Abraham Martin, hence the name of the battle. The battle involved fewer than 10,000 troops in total, but proved to be a deciding moment in the conflict between France and Britain over the fate of New France, influencing the later creation of Canada.
 W
WThe Siege of Quebec, also known as the Second Siege of Quebec, was an unsuccessful French attempt to retake Quebec City in New France which had been captured by Britain the previous year. The siege lasted from 29 April until 15 May when British ships arrived to relieve the city which compelled the French commander Francis de Gaston, Chevalier de Lévis to break off the siege and retreat.
 W
WThe Battle of Restigouche was a naval battle fought in 1760 during the Seven Years' War on the Restigouche River between the British Royal Navy and the small flotilla of vessels of the French Navy, Acadian militia and Mi'kmaq militias. The loss of the French vessels, which had been sent to support and resupply the troops in New France after the fall of Quebec, marked the end of any serious attempt by France to keep hold of their colonies in North America. The battle was the last major engagement of the Mi'kmaq and Acadian militias before the Burying of the Hatchet Ceremony between the Mi'kmaq and the British.
 W
WThe Battle of Sabbath Day Point took place on 23 July 1757 just off the shore of Sabbath Day Point, Lake George, New York and ended in a French victory. The battle, pitched approximately 450 French and allied Indian forces under the leadership of Ensign de Corbiere of the Troupes de la Marine against 350 New Jersey Blues under the command of Colonel John Parker. Ensign de Corbiere, aware of Colonel Parker's plan, ambushed and surrounded Parker's forces as they approached the shore in bateaux. In the ensuing rout Colonel Parker lost approximately 250 men with nearly 160 men killed or drowned and the rest taken prisoner. The French reported only one man slightly wounded.
 W
WThe Battle of Sainte-Foy, sometimes called the Battle of Quebec, was fought on April 28, 1760 near the British-held town of Quebec in the French province of Canada during the Seven Years' War. It was a victory for the French under the Chevalier de Lévis over the British army under General Murray. The battle was notably bloodier than the Battle of the Plains of Abraham of the previous September, with 833 French casualties to 1,124 British casualties. It was the last French victory in North America.
 W
WThe Sainte-Thérèse Raid was a military raid on the town of Sainte-Thérèse in French Canada conducted by British elite forces known as Rogers' Rangers that took place during the French and Indian War from 3 to 18 June 1760. Led by Robert Rogers the raid was a pre-emptive strike ordered by Major General Jeffery Amherst as a prelude to his three pronged attack on Montreal the following month.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort Loudoun was an engagement during the Anglo-Cherokee War fought from February 1760 to August 1760 between the warriors of the Cherokee led by Ostenaco and the garrison of Fort Loudoun composed of British and colonial soldiers commanded by Captain Paul Demeré.
 W
WThe Battle of Signal Hill was fought on September 15, 1762, and was the last battle of the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War. A British force under Lieutenant Colonel William Amherst recaptured St. John's, after the French had seized earlier that year in a surprise attack.
 W
WThe 1757 Battle on Snowshoes was a skirmish fought between Rogers' Rangers and French and Indian troops during the French and Indian War on January 21, 1757. The battle was given this name because the British combatants were wearing snowshoes.
 W
WThe 1758 Battle on Snowshoes occurred on March 13, 1758, during the French and Indian War. It was fought by members of British Ranger companies led by Robert Rogers against French troops and Indians allied to France. The battle took place near Lake George, now in northern New York, but then in the frontier area between the British province of New York and the French province of Canada. The battle was given its name because the British combatants were wearing snowshoes.
 W
WThe St. Francis Raid was an attack in the French and Indian War by Robert Rogers on St. Francis, near the southern shore of the Saint Lawrence River in what was then the French province of Canada, on October 4, 1759. Rogers and about 140 men entered the village, which was reportedly occupied primarily by women, children, and the elderly, early that morning, slaughtered many of the inhabitants where they lay, shot down many who attempted to flee, and then burned the village. Rogers reported killing as many as 300 people, while French reports placed the number closer to thirty, mainly women and children. One of Rogers' men was killed, and seven were wounded.
 W
WThe St. John River Campaign occurred during the French and Indian War when Colonel Robert Monckton led a force of 1150 British soldiers to destroy the Acadian settlements along the banks of the Saint John River until they reached the largest village of Sainte-Anne des Pays-Bas in February 1759. Monckton was accompanied by Captain George Scott as well as New England Rangers led by Joseph Goreham, Captain Benoni Danks, as well as William Stark and Moses Hazen, both of Rogers' Rangers.
 W
WThe Battle of the Thousand Islands was an engagement fought on 16–24 August 1760, in the upper St. Lawrence River, among the Thousand Islands, along the present day Canada–United States border, by British and French forces during the closing phases of the Seven Years' War, as it is called in Canada and Europe, or the French and Indian War as it is referred to in the United States.
 W
WThe 1759 Battle of Ticonderoga was a minor confrontation at Fort Carillon on July 26 and 27, 1759, during the French and Indian War. A British military force of more than 11,000 men under the command of General Sir Jeffery Amherst moved artillery to high ground overlooking the fort, which was defended by a garrison of 400 Frenchmen under the command of Brigadier General François-Charles de Bourlamaque.
 W
WThe Battle of the Trough was a skirmish of the early French and Indian War (1754–63) fought between Native Americans and British settlers in the valley of the South Branch Potomac River in what is now northern Hardy County, West Virginia, USA.