 W
WThe Song dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties to its north. It was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.
 W
WThe architecture of the Song dynasty (960–1279) was noted for its towering Buddhist pagodas, enormous stone and wooden bridges, lavish tombs, and extravagant palaces. Although literary works on architecture existed beforehand, architectural writing blossomed during the Song dynasty, maturing into a more professional form that described dimensions and working materials in a concise, organized manner. In addition to the examples still standing, depictions in Song artwork, architectural drawings, and illustrations in published books all aid modern historians in understanding the architecture of the period.
 W
WBingqian, or Bingxingqian, is a term, which translates into English as "biscuit coins", "pie coins", or "cake coins", used by Chinese and Taiwanese coin collectors to refer to cash coins with an extremely broad rim as, these cash coins can also be very thick. While the earliest versions of the Bingqian did not extraordinarily broad rims.
 W
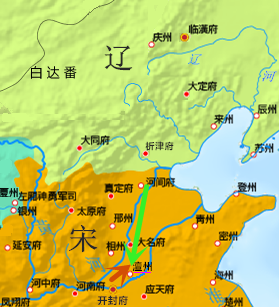
WThe Chanyuan Treaty in 1005 was the pivotal point in the relations between the Northern Song (960-1127) and the Liao Dynasties (916-1125). The ruling class of the Liao were a people of nomadic origin known as the Khitan who rose in the northeast around present-day Heilongjiang Province. The Song dynasty, also referred to as the Northern Song, ruled virtually all of China from the late tenth century when it eliminated the last of the kingdoms in the north and the south that stood against Chinese unification.
 W
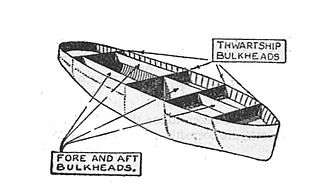
WA compartment is a portion of the space within a ship defined vertically between decks and horizontally between bulkheads. It is analogous to a room within a building, and may provide watertight subdivision of the ship's hull important in retaining buoyancy if the hull is damaged. Subdivision of a ship's hull into watertight compartments is called compartmentation.
 W
WThe Song dynasty was a culturally rich and sophisticated age for China. It saw great advancements in the visual arts, music, literature, and philosophy. Officials of the ruling bureaucracy, who underwent a strict and extensive examination process, reached new heights of education in Chinese society, while general Chinese culture was enhanced by widespread printing, growing literacy, and various arts.
 W
WThe Donglin Academy, also known as the Guishan Academy, was a former Chinese educational institution in Wuxi, China. It was originally built in 1111 during the Northern Song dynasty; the neo-Confucian scholar Yang Shi (楊時) taught there, but the academy later fell into disuse and disrepair. The name "Donglin" was inspired by the Donglin Temple at the base of Mount Lu, Jiangxi. Yang Shi visited the Donglin Temple and felt that it was a good place for teaching. When he finished his scholarship, he travelled to Wuxi and saw that the layout of the academy was similar to the Donglin Temple, so he taught at that site for 18 years. The academy was thus called "Donglin Academy".
 W
WThe Five Great Kilns, also known as Five Famous Kilns, is a generic term for ceramic kilns or wares which produced Chinese ceramics during the Song dynasty (960–1279) that were later held in particularly high esteem. The group were only so called by much later writers, and of the five, only two seem to have produced wares directly ordered by the Imperial court, though all can be of very high quality. All were imitated later, often with considerable success.
 W
WA flare, also sometimes called a fusee, is a type of pyrotechnic that produces a bright light or intense heat without an explosion. Flares are used for distress signaling, illumination, or defensive countermeasures in civilian and military applications. Flares may be ground pyrotechnics, projectile pyrotechnics, or parachute-suspended to provide maximum illumination time over a large area. Projectile pyrotechnics may be dropped from aircraft, fired from rocket or artillery, or deployed by flare guns or handheld percussive tubes.
 W
WIn an explosive, pyrotechnic device, or military munition, a fuse is the part of the device that initiates function. In common usage, the word fuse is used indiscriminately. However, when being specific, the term fuse describes a simple pyrotechnic initiating device, like the cord on a firecracker whereas the term fuze is sometimes used when referring to a more sophisticated ignition device incorporating mechanical and/or electronic components, such as a proximity fuze for an M107 artillery shell, magnetic or acoustic fuze on a sea mine, spring-loaded grenade fuze, pencil detonator, or anti-handling device.
 W
WThe Hanlin Academy was an academic and administrative institution founded in the eighth-century Tang China by Emperor Xuanzong in Chang'an.
 W
WThe headwear of Song dynasty officials consisted of a black hat with two wing-like flaps. The thin flaps are stiff and straight, and could extend up to almost a meter each.
 W
WChinese archaeology has been practiced since the Song dynasty (960-1279) with early practices of antiquarianism. Although native Chinese antiquarianism developed some rigorous methods of unearthing, studying, and cataloging ancient artifacts, the field of archaeology never developed into a branch of study outside of Chinese historiography. Native Chinese antiquarian studies waned after the Song period but were revived during the Qing dynasty (1644-1912).
 W
WThe Song dynasty of China was a ruling dynasty that controlled China proper and southern China from the middle of the 10th century into the last quarter of the 13th century. The dynasty was established by Emperor Taizu of Song with his usurpation of the throne of Later Zhou, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
 W
WThe military history of the Song dynasty covers the period of Chinese history from 960 AD to 1279 AD when China was conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty created by Kublai Khan after the Division of the Mongol Empire.
 W
WThis is a timeline of the Song dynasty (960–1279).
 W
WHuaguangjiao One is a Chinese merchant ship, built during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), that sank off the coast of the Paracel Islands in the South China Sea. The ship's name translates as "Magnificent China Reef Wreck #1". It was discovered in 1996 and is currently the oldest hull that China has discovered in the open seas.
 W
WThe Huizi, issued in the year 1160, was the official banknote of the Chinese Southern Song dynasty. It has the highest amount of issuance among various banknote types during the Song dynasty. Huizi notes came on three-colour printed paper and their usage was heavily promoted by the government of the Southern Song dynasty, the Huizi were backed by 280,000 guàn of copper cash coins.
 W
WThe transition from the Tang to the Song dynasty (960–1279) in China did not greatly interrupt the trends of Muslims established during the Tang.
 W
WThe term Jacob's staff, also known as cross-staff, a ballastella, a fore-staff, or a balestilha, is used to refer to several things. In its most basic form, a Jacob's staff is a stick or pole with length markings; most staffs are much more complicated than that, and usually contain a number of measurement and stabilization features. The two most frequent uses are:in astronomy and navigation for a simple device to measure angles, later replaced by the more precise sextants; in surveying for a vertical rod that penetrates or sits on the ground and supports a compass or other instrument.
 W
WThe keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event.
 W
WThis is a list of campaigns of Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty.
 W
WA lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself that rises and falls.
 W
WThe Longhua Temple is a Buddhist temple dedicated to the Maitreya Buddha in Shanghai. Although most of the present day buildings date from later reconstructions, the temple preserves the architectural design of a Song dynasty (960–1279) monastery of the Chan School. It is the largest, most authentic and complete ancient temple complex in the city of Shanghai.
 W
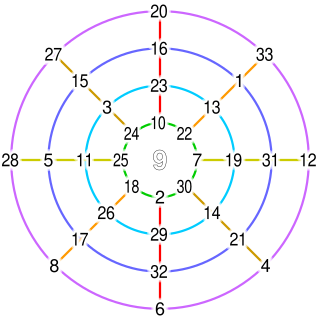
WMagic circles were invented by the Song dynasty (960–1279) Chinese mathematician Yang Hui. It is the arrangement of natural numbers on circles where the sum of the numbers on each circle and the sum of numbers on diameter are identical. One of his magic circles was constructed from 33 natural numbers from 1 to 33 arranged on four concentric circles, with 9 at the center.
 W
WThe Marco Polo Bridge or Lugou Bridge (卢沟桥) is a stone bridge located 15 km southwest of Beijing city center in the Fengtai District. It bridges the Yongding River, a major tributary of Hai River. Situated at the eastern end of the bridge is the Wanping Fortress, a historic 17th-century fortress, with the Museum of the War of Chinese People's Resistance Against Japanese Aggression inside.
 W
WA multiple rocket launcher (MRL) or multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) is a type of rocket artillery system that contains multiple launchers which assembled onto a same platform, and shoots its rocket ordnance in a fashion similar to a volley gun. Rockets are self-propelled in flight and have different capabilities than conventional artillery shells, such as longer effective range, lower recoil, typically considerably higher payload than a similarly sized artillery platform, or even carrying multiple warheads.
 W
WThe Nanhai One is a Chinese merchant ship, which sank into the South China Sea during the Southern Song dynasty between 1127 and 1279.
 W
WThe Northern Song is an era during the Song Dynasty. It came to an end when its capital city, the city of Kaifeng, was conquered by enemies from the north. Later, the provisional capital of the Northern Song Dynasty was founded in Ying Tian Fu. Historically, the Song Dynasty include both the Northern and the Southern Song. It is named "Northern" to distinguish from the "Southern", which resided mainly in Southern China. Emperor Taizu of Song elaborated a mutiny and usurped the throne of the Later Zhou, which marked the beginning of the Dynasty. In 1127, its capital city Kaifeng fell into the hand of the state of Jin, during which time the ruling Emperor Qinzong and his family all fell captive in an event known as the Jingkang Incident. The Northern Song came to its end the next year. It was ruled by nine emperors, and lasted for 127 years.
 W
WAn oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is transformed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas, jet fuel and fuel oils. Petrochemicals feed stock like ethylene and propylene can also be produced directly by cracking crude oil without the need of using refined products of crude oil such as naphtha. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.According to the Oil and Gas Journal in the world a total of 636 refineries were operated on the 31 December 2014 for a total capacity of 87.75 million barrels (13,951,000 m3).
 W
WThe Quanzhou Ship (泉州湾古船), or Quanzhou wreck, was a 13th-century Chinese seagoing sailing junk that sank near the city of Quanzhou in Fujian Province, and was discovered in 1973. It remains one of the most important marine archaeology finds in China, and is an important piece of physical evidence about the shipbuilding techniques of the Song China and the international maritime trade of the period.
 W
WSalt, salt production, and salt taxes played key roles in Chinese history, economic development, and relations between state and society. The lure of salt profits led to technological innovation and new ways to organize capital. Debate over government salt policies brought forth conflicting attitudes toward the nature of government, private wealth, the relation between the rich and the poor, while the administration of these salt policies was a practical test of a government's competence.
 W
WFloodability is the susceptibility of a ship's construction to flooding. It also refers to the ability to intentionally flood certain areas of the hull for damage control purposes, or to increase stability, which is particularly important in combat vessels, which often face the possibility of serious hull breach due to enemy action, and which rely on well-trained Damage Controlmen to equalize and then stop flooding of the hull.
 W
WChinese society during the Song dynasty (960–1279) was marked by political and legal reforms, a philosophical revival of Confucianism, and the development of cities beyond administrative purposes into centers of trade, industry, and maritime commerce. The inhabitants of rural areas were mostly farmers, although some were also hunters, fishers, or government employees working in mines or the salt marshes. Conversely, shopkeepers, artisans, city guards, entertainers, laborers, and wealthy merchants lived in the county and provincial centers along with the Chinese gentry—a small, elite community of educated scholars and scholar-officials.
 W
WThe Southern Song dynasty refers to an era of the Song dynasty after Kaifeng was captured by the Jurchen Jin dynasty in 1127. The government of the Song was forced to establish a new capital city at Lin'an which wasn't near any sources of copper so the quality of the cash coins produced under the Southern Song significantly deteriorated compared to the cast copper-alloy cash coins of the Northern Song dynasty. The Southern Song government preferred to invest in their defenses while trying to remain passive towards the Jin dynasty establishing a long peace until the Mongols eventually annexed the Jin before marching down to the Song establishing the Yuan dynasty.
 W
WSung Wong Toi is an important historic relic in Kowloon, Hong Kong. While its remaining portion is now located in the Sung Wong Toi Garden (宋皇臺花園) in Ma Tau Chung, it was originally a 45-metre-tall boulder standing on the top of Sacred Hill (聖山) in Ma Tau Chung above Kowloon Bay.
 W
WThe Song dynasty invented some technological advances in Chinese history, many of which came from talented statesmen drafted by the government through imperial examinations.
 W
WThis article elaborates on the historical relationship development between imperial China and Tibetan regime in Tang and Song dynasty. For detailed information of the history of Tibetan regime, see Tibetan regime.
 W
WA trebuchet is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder.
 W
WThe White Deer Grotto Academy is a former school at the foot of Wulou Peak in Lushan, now in Jiujiang, Jiangxi province. It was one of the Four Great Academies of China, and today it is maintained as an important landmark.
 W
WThe 1034 Yellow River flood was a natural disaster along China's Yellow River originating in a burst fascine following heavy rainfall at Henglong in the territory of the Northern Song. The flood divided the Yellow River from its previous course into three more northerly channels meeting the Chihe, You, and Jin.
 W
WThe Yuelu Academy is on the east side of Yuelu Mountain in Changsha, Hunan province, on the west bank of the Xiang River. As one of the four most prestigious academies over the last 1000 years in China, Yuelu Academy has been a famous institution of higher learning as well as a centre of academic activities and cultures since it was formally set up during the Northern Song dynasty. The academy was converted into Hunan Institute of Higher Learning in 1903. It was later renamed Hunan Normal College, Hunan Public Polytechnic School, and finally Hunan University in 1926. Yuelu Academy was once the center for the pursuit of Chinese ancient learning and idealism in China's feudalist era.
 W
WThe Yunjing is one of the two oldest existing examples of a Chinese rhyme table – a series of charts which arrange Chinese characters in large tables according to their tone and syllable structures to indicate their proper pronunciations. Current versions of the Yunjing date to AD 1161 and 1203 editions published by Zhang Linzhi (張麟之). The original author(s) and date of composition of the Yunjing are unknown. Some of its elements, such as certain choices in its ordering, reflect features particular to the Tang dynasty, but no conclusive proof of an actual date of composition has yet been found.
 W
WZhangpu County is a county of Zhangzhou prefecture-level city in far southern Fujian province, People's Republic of China. The county seat is located in the town of Sui'an (绥安镇).
 W
WThe Zhaona Xinbao is a special type of Southern Song dynasty cash coin developed as a propaganda and psychological warfare tool for recruiting defectors from the army of the Jurchen Jin dynasty around the year Shaoxing 1 under the reign of Emperor Gaozong. These special coins superficially resemble traditional Chinese cash coins but contain an inscription alluding to their intent, generally these Zhaona Xinbao tokens were made from bronze but in very rare cases they were also made from silver or gold.
 W
WZiqi was a kingdom established by the Wuman in southwestern China during the Song dynasty. The territory of Ziqi included parts of modern-day Guizhou, Guangxi and Yunnan provinces of China.