 W
WThe Yemeni Crisis began with the 2011–12 revolution against President Ali Abdullah Saleh, who had led Yemen for more than three decades. After Saleh left office in early 2012 as part of a mediated agreement between the Yemeni government and opposition groups, the government led by Saleh's former vice president, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, struggled to unite the fractious political landscape of the country and fend off threats both from Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula and Houthi militants that had been waging a protracted insurgency in the north for years.
 W
WThe Aden unrest refers to initially ongoing conflict between Islamist factions, such as al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant's Yemen Branch, against the loyalists of president Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi and later to conflict between UAE-backed and Saudi-backed factions within the coalition. In 2017, fighting also broke out between factions aligned with different members of the Saudi-led coalition namely Saudi Arabia-backed Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and Al-Islah and UAE-backed separatist Southern Transitional Council and Southern Movement.
 W
WThe Battle of Aden was a conflict between the Southern Transitional Council (STC) and the Yemeni government around the headquarters in Aden.
 W
WThe Yemeni Revolution (intifada),or the Coffee Revolution, and also known as the Yemeni Revolution of Dignity followed the initial stages of the Tunisian Revolution and occurred simultaneously with the Egyptian Revolution of 2011 and other Arab Spring protests in the Middle East and North Africa. In its early phase, protests in Yemen were initially against unemployment, economic conditions and corruption, as well as against the government's proposals to modify Yemen's constitution. The protesters' demands then escalated to calls for the resignation of Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh. Mass defections from the military, as well as from Saleh's government, effectively rendered much of the country outside of the government's control, and protesters vowed to defy its authority.
 W
WPresidential elections were held in Yemen on 21 February 2012. Acting President Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi was the only candidate, and was subsequently sworn into office on 25 February 2012.
 W
WAn outbreak of cholera began in Yemen in October 2016, and is ongoing as of August 2020. In February and March 2017, the outbreak declined during a wave of cold weather, but the number of cholera cases resurged in April 2017. As of October 2018, there have been more than 1.2 million cases reported, and more than 2,500 people—58% children—have died in the Yemen cholera outbreak, which the United Nations deemed the worst humanitarian crisis in the world at that time.
 W
WThe Battle of Aden, also known as the Battle for Aden or the Aden Battles was a series of clashes in the city of Aden between the pro-Hadi government troops backed by Saudi Arabia and Southern Transitional Council forces backed by the United Arab Emirates.
 W
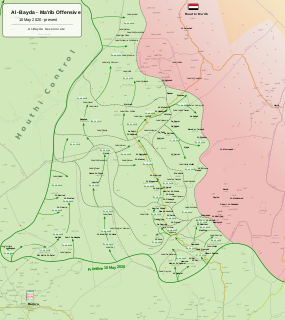
WThe Al Bayda offensive began in late July 2020 with the restart of military operations by Houthis forces in Al Bayda Governorate, during the Second Yemeni Civil War against forces of Al-Qaeda in Yemen, the Islamic State in Yemen and military forces loyal to the Government of Abd Rabbuh Mansur Al-Hadi.
 W
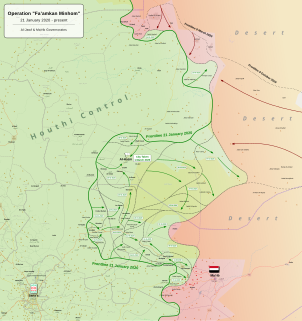
WThe Al Jawf offensive began in February 2020 with clashes in the Al Jawf Governorate and reached a decisive phase with the capture of the town of Al Hazm by the Houthi movement on 1 March 2020 from the Hadi government, during the Second Yemeni Civil War.
 W
WOn 14 September 2019, drones were used to attack the state-owned Saudi Aramco oil processing facilities at Abqaiq and Khurais in eastern Saudi Arabia. The Houthi movement in Yemen claimed responsibility, tying it to events surrounding the Saudi Arabian intervention in the Yemeni Civil War and stating they used ten drones in the attack launched from Yemen, south of the facilities. Saudi Arabian officials said that many more drones and cruise missiles were used for the attack and originated from the north and east, and that they were of Iranian manufacture. The United States and Saudi Arabia have stated that Iran was behind the attack while France, Germany, and the United Kingdom jointly stated Iran bears responsibility for it. Iran has denied any involvement. The situation has exacerbated the Persian Gulf crisis.
 W
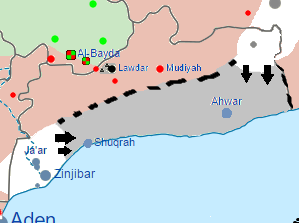
WThe Abyan campaign was a campaign for control of the Abyan Governorate of Yemen, between the Houthis and Yemen Army units loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and militiamen and Yemen Army units loyal to Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side, supported by jihadists of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. The Pro-Hadi Forces recaptured the Abyan Governorate on 11 August, after launching an offensive on pro-Houthi forces in early August.
 W
WThe Abyan conflict (2016–2018) was a series of clashes between forces of AQAP loyal to Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and forces loyal to Southern Movement for the control of Abyan.
 W
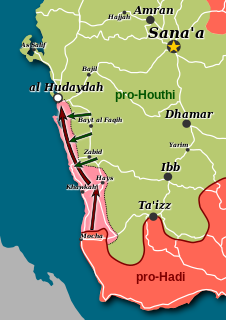
WAl Hudaydah offensive, also called western coast offensive, describes the offensive launched in December 2017 by pro-government forces against the Houthis in Al Hudaydah Governorate as part of Yemen's 2015 civil war. As of December 2018, the pro-government forces have captured the towns of Mocha, Al Khawkhah, Hays, Al Tahaya, and brokered a ceasefire in Al Hudaydah City.
 W
WAl-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, or AQAP, also known as Ansar al-Sharia in Yemen, is a militant Islamist group primarily active in Yemen and Saudi Arabia that is part of the al-Qaeda network. It is considered the most active of al-Qaeda's branches that emerged after the weakening of central leadership. The U.S. government believes AQAP to be the most dangerous al-Qaeda branch. The group established an emirate during the 2011 Yemeni Revolution, which waned in power after foreign interventions in the subsequent Yemeni Civil War.
 W
WA number of armed groups have involved themselves in the ongoing Yemeni Civil War.
 W
WThe Battle of Aden was a battle for the control of Aden, Yemen, between the Houthis and Yemen Army units and militias loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and Southern Movement militias, and Yemen Army units and militias loyal to Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side.
 W
WThe First Battle of Mukalla (2015) was a battle between al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, local tribesmen, and the Yemen Army for control of the coastal city of Mukalla, Yemen.
 W
WThe Battle of Sa'dah erupted in March 2011 between Houthi insurgents and tribal forces loyal to Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh in the northern city of Sa'dah. Following days of heavy clashes, the Houthis managed to capture the entire Sadah governorate including its provincial capital and establishes an independent administration, thereby marking the first such Yemeni governorate to fell out from central government control since the nationwide uprising began in 2011.
 W
WThe Battle of Sana'a in 2014 marked the advance of the Houthis into Sana'a, the capital of Yemen, and heralded the beginning of the armed takeover of the government that unfolded over the following months. Fighting began on 9 September 2014, when pro-Houthi protesters under the command of Abdul-Malik al-Houthi marched on the cabinet office and were fired upon by security forces, leaving seven dead. The clashes escalated on 18 September, when 40 were killed in an armed confrontation between the Houthis led by military commander Mohammed Ali al-Houthi and supporters of the Sunni hardliner Islah Party when the Houthis tried to seize Yemen TV, and 19 September, with more than 60 killed in clashes between Houthi fighters and the military and police in northern Sana'a. By 21 September, the Houthis captured the government headquarters, marking the fall of Sana'a.
 W
WThe Battle of Sanaa (2017) was fought between forces loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh and the Houthis in the Yemeni capital of Sana'a. Both sides were allied during the 2014–15 Houthi takeover of the government but the alliance ended when Saleh decided to break ranks with the Houthis and call for dialogue with Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, who are leading a military intervention in Yemen. Fighting then broke out between the Houthis and forces loyal to Saleh as the Saudi-led coalition began bombing Houthi areas, ultimately resulting in Saleh's death and a Houthi victory.
 W
WThe Battle of the Jabara Valley occurred between 26 and 29 August 2019, during the Second Yemeni Civil War. It was part of the Operation Victory from God, a major Houthi-led offensive along the Saudi-Yemeni border.
 W
WThe blockade of Yemen refers to a sea, land and air blockade on Yemen which started with the positioning of Saudi Arabian warships in Yemeni waters in 2015 with the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen. The United States joined the blockade in October 2016. In November 2017, after a Houthi missile heading towards King Khalid International Airport was intercepted, the Saudi-led military coalition stated it would close all sea land and air ports to Yemen, but shortly began reopening them after criticism from the United Nations (UN) and over 20 aid groups. The blockade of Yemen has resulted in widespread starvation, to the extent that the United Nations has raised concerns about the possibility of it becoming the deadliest famine in decades. The World Health Organization announced that the number of suspected persons with cholera in Yemen reached approximately 500,000 people.
 W
WThe Cabinet of Yemen refers to the governing body of the internationally recognized Yemen government led by President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi who replaced former President of Yemen Ali Abdullah Saleh on February 25, 2012 as the new President of Yemen. He then selected new cabinet members of the Yemeni Government.
 W
WThe Saudi Arabian–Yemeni border conflict is an ongoing armed conflict between the Royal Saudi Armed Forces and Yemeni Houthi forces that has been taking place in the Arabian Peninsula, including the southern Saudi regions of Asir, Jizan, and Najran, and northern Yemeni governorates of Saada, AL-Jawf, and Hajjah, since the onset of the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen in 2015.
 W
WThe Houthi insurgency in Yemen, also known as the Houthi rebellion, Sa'dah War, or Sa'dah conflict, was a military rebellion pitting Zaidi Shia Houthis against the Yemeni military that began in Northern Yemen and has since escalated into a full-scale civil war. The conflict was sparked in 2004 by the government's attempt to arrest Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, a Zaidi religious leader of the Houthis and a former parliamentarian on whose head the government had placed a $55,000 bounty. Initially, most of the fighting took place in Sa'dah Governorate in northwestern Yemen, but some of the fighting spread to neighbouring governorates Hajjah, 'Amran, al-Jawf and the Saudi province of Jizan. After the Houthi takeover of the capital city Sana'a in late 2014, the insurgency became a full-blown civil war with a major Saudi-led intervention in Yemen beginning in March 2015.
 W
WThe Houthi movement, officially called Ansar Allah and colloquially simply Houthis, is an Islamic political and armed movement that emerged from Sa'dah in northern Yemen in the 1990s. The movement was called Houthis because its founder is from the Houthi tribe. They are of the Zaidi school, though the movement also includes Sunnis. Under the leadership of Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, the group emerged as an opposition to former Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, whom they charged with massive financial corruption and criticized for being backed by Saudi Arabia and the United States at the expense of the Yemeni people and Yemen's sovereignty. Resisting Saleh's order for his arrest, Hussein was killed in Sa'dah in 2004 along with a number of his guards by the Yemeni army, sparking the Houthi insurgency in Yemen. Since then, except for a short intervening period, the movement has been led by his brother Abdul-Malik al-Houthi.
 W
WThe Houthi takeover in Yemen, also known as the September 21 Revolution, or 2014–15 coup d'état, was a gradual armed takeover of former Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh by the Houthis and their supporters that pushed the Yemeni government from power. It had origins in Houthi-led protests that began the previous month, and escalated when the Houthis stormed the Yemeni capital Sana'a on 21 September 2014, causing the resignation of Prime Minister Mohammed Basindawa, and later the resignation of President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and his ministers on 22 January 2015 after Houthi forces seized the presidential palace, residence, and key military installations, and the formation of a ruling council by Houthi militants on 6 February 2015.
 W
WThe Lahij insurgency was a guerrilla war waged by tribesmen loyal to Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi against the Houthis and Yemen Army units loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh, who controlled most of the Lahij Governorate of Yemen. In late July, Pro-Hadi forces had launched an offensive to recapture Al Anad Air Base and rest of Lahij Governorate. On 4 August, Pro-Hadi forces had retaken full control of the Lahij Governorate.
 W
WThe National Dialogue Conference (NDC) was a transitional dialogue process held at the Movenpick Hotel in Sana'a, Yemen from March 18, 2013 to January 24, 2014, as part of the Yemeni crisis reconciliation efforts.
 W
WThe Nihm Offensive was a military operation that began in mid-December 2015 in the District of Nihm, when government forces took control of "Mas camp" which borders the governorates of Al-Jawf, and Ma'rib. On 19-20 December, government forces coming from Ma'rib and al-Jawf, took control of the 312th Armored Brigade camp, and 334th Armored Brigade camp. Government forces faced fierce resistance that lasted until February 2016, when they were able to take control of the 312th Armored Corps camp.
 W
WOperation Raahat was an operation of the Indian Armed Forces to evacuate Indian citizens and foreign nationals from Yemen during the 2015 military intervention by Saudi Arabia and its allies in that country during the Yemeni Crisis. The evacuation by sea began on 1 April 2015 from the port of Aden. The air evacuation by the Indian Air Force and Air India commenced on 3 April 2015 from Sana'a. More than 4,640 Indian citizens in Yemen were evacuated along with 960 foreign nationals from 41 countries. The air evacuation ended on 9 April 2015 while the evacuation by sea ended on 11 April 2015.
 W
WOn 7 January 2015, a car bomb was detonated in front of a police academy in the Yemeni capital Sana'a, killing at least 38 people and injuring more than 60 others. This was the third major attack in the country in less than a month, after the deadliest attack in the country during 2014, as well as the second major bombing in less than a month, after the 2014 Rada' bombings and the 2014 Ibb bombing.
 W
WThe Saudi-led intervention in Yemen is an intervention launched by Saudi Arabia on 26 March 2015, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, in response to calls from the pro-Saudi president of Yemen Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after he was ousted by the Houthi movement due to economic and political grievances, and fled to Saudi Arabia.
 W
WThe Shabwah campaign was a campaign for control of the Shabwah Governorate of Yemen, between the Houthis and Yemen Army units loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and militiamen and Yemen Army units loyal to Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side. The offensive was also launched during a previously started AQAP offensive.
 W
WThe Shabwah Governorate offensive (2014–present) is an insurgent campaign by Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) forces to take control of Shabwah Governorate during the Yemeni Civil War.
 W
WThe Siege of Dammaj started in October 2011 when the Houthis, a Zaidi-led rebel group which control the Saada Governorate, accused Wahhabi loyal to the Yemeni government of smuggling weapons into their religious center in the town of Dammaj and demanded they hand over their weapons and military posts in the town. As the Salafis refused, Houthi rebels responded by imposing a siege on Dammaj, closing the main entrances leading to the town. The town is controlled by the Houthis and the fighting was mainly centered on Dar al-Hadith religious school, which is run by Salafis, although its founder rejected Osama bin Laden in the 1990s. The Salafis from Dammaj and the current imam of Dar al-Hadith, Sheikh Yahya Hajoori claims that they are totally against al-Qaeda and all that they stand for.
 W
WThe Sons of al Mahrah is a Yemeni protest movement that emerged from Al Mahrah Governorate in 2018. It is led by former governor, Sheikh Ali Salem Al-Harizi. The movement protests the "Saudi occupation policy" in the al-Mahrah Governorate and the UAE occupation of Socotra.
 W
WThe South Yemen insurgency was a series of protests and attacks on government forces in southern Yemen between 2009 and 2014. Although the violence was blamed on elements within the southern secessionist movement, leaders of the group maintained that their aims of independence were to be achieved through peaceful means, and claimed that attacks were from ordinary citizens in response to the government's provocative actions. The insurgency came amid the Shia insurgency in the country's north that was led by Houthi communities. Southern leaders led a brief, unsuccessful secession in 1994 following unification. Many of them were involved in the secession movement. Southern separatist insurgents were active mainly in the area of former South Yemen, but also in Ad Dali' Governorate, which was not a part of the independent southern state.
 W
WThe Southern Abyan Offensive refers to a 2016 offensive that AQAP launched in late February, which ended with a victory for AQAP as Yemeni tribal fighters loyal to president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi were driven out of the Abyan Governorate.
 W
WThe Southern Transitional Council is a secessionist organization in Yemen. The 26 members of the STC include the governors of five southern governorates and two government ministers. It was formed by a faction of the Southern Movement, also known as al-Hirak al-Janoubi. The Southern Movement was established in 2007, during the term of former president Ali Abdullah Saleh, and it has called for and worked toward the separation of southern Yemen from the rest of the nation.
 W
WThe Supreme Political Council is an unrecognised executive body formed by the Houthi movement and the General People's Congress (GPC) to rule Yemen. Formed on 28 July 2016, the presidential council consists of 10 members and was headed by Saleh Ali al-Sammad as president until his death from a drone air strike on 19 April 2018 with Qassem Labozah as vice-president. Its territory that it rules consists of the former North Yemen, which united with South Yemen in 1990.
 W
WThe Supreme Revolutionary Committee, sometimes referred to as the Revolutionary Council or the Revolutionary Committee, is an interim body in Yemen formed by the Zaidiyyah Shia group Ansar Allah. In their 6 February 2015 "constitutional declaration" after seizing control of the Yemeni capital and much of former North Yemen, and the failure of Thursday talks between the Houthis and Yemen’s many political parties that were aimed at forming a government to replace Hadi and his cabinet, the group declared the committee would act as Yemen's interim authority. The committee was given the task of forming a new 551-seat parliament, which would then select a five-member presidential council to rule the country for two years.
 W
WHSV-2 Swift is a hybrid catamaran. She was privately owned and operated by Sealift Inc., and was originally built under the JHSV program as a proof of concept. As part of this program, she was directly leased for evaluation from her builders by the United States Navy Military Sealift Command from 2003 to 2013, primarily as a mine countermeasures and sea basing test platform. Later during her official naval career she was mostly used for fleet support and humanitarian partnership missions.
 W
WThe Taiz campaign (2015–present) is a protracted military confrontation between opposing Yemeni forces in the city of Taiz for control of the city and surrounding area. The battle began one month after the start of the Yemeni Civil War.
 W
WOn 30 April 2018, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) deployed more than a hundred troops with artillery and armored vehicles to the Yemeni archipelago of Socotra in the Guardafui Channel without prior coordination with Yemen. The initial deployment consisted of UAE military aircraft carrying more than fifty UAE soldiers and two armored vehicles, followed by two more aircraft carrying more soldiers, tanks and other armored vehicles. Al Jazeera reported that shortly after landing, UAE forces dismissed Yemeni soldiers stationed at administrative installations such as Socotra Airport and seaports until further notice, and the flag of the United Arab Emirates was raised above official government buildings in Hadibu.
 W
WThe Yemeni Civil War is an ongoing multi-sided civil war that began in late 2014 mainly between the Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi-led Yemeni government and the Houthi armed movement, along with their supporters and allies. Both claim to constitute the official government of Yemen.
 W
WYemeni peace process refers to the proposals and negotiations to pacify the Yemeni Crisis by arranging a power transfer scheme within the country and later cease-fire attempts within the raging civil war. While initially unsuccessful, the reconciliation efforts resulted with presidential elections, held in Yemen in February 2012. The violence in Yemen, however, continued during the elections and after, culminating in Houthi successful grip of power and the ensuing civil war.