 W
WFort Assumption was a French fortification constructed in 1739 on the fourth Chickasaw Bluff on the Mississippi River in Shelby County, present day Memphis, Tennessee. The fort was used as a base against the Chickasaw in the unsuccessful Indian-removal Campaign of 1739.
 W
WFort Beauharnois was a French fort built on the shores of Lake Pepin, a wide section of the upper Mississippi River, in 1727. The location chosen was on lowlands and the fort was rebuilt in 1730 on higher ground. It was the site of the first Roman Catholic chapel in Minnesota, which was dedicated to St. Michael the Archangel. The fort was named after the Governor of New France at the time, Charles de Beauharnois.
 W
WFort de Buade was a French fort in the present U.S. state of Michigan's Upper Peninsula across the Straits of Mackinac from the northern tip of lower Michigan's "mitten". It was garrisoned between 1683 and 1701. The city of St. Ignace developed at the site, which also had the historic St. Ignace Mission founded by Jesuits. The fort was named after New France's governor at the time, Louis de Buade de Frontenac.
 W
WFort Carillon, the precursor of Fort Ticonderoga, was constructed by Pierre de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, Governor of Canada, to protect Lake Champlain from a British invasion. Situated on the lake some 15 miles (24 km) south of Fort Saint Frédéric, it was built to prevent an attack on Canada and slow the advance of the enemy long enough for reinforcements to arrive.
 W
WFort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on June 22, 1564, as a new territorial claim in French Florida and a safe haven for Huguenots. The French colony came into conflict with the Spanish, who established St. Augustine in September 1565, and Fort Caroline was sacked by Spanish troops under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés on September 20. The Spanish continued to occupy the site as San Mateo until 1569.
 W
WFort de Cavagnial was a French fort and trading post located on the west cliffs of the Missouri River, somewhere north of Kansas City, Kansas, and Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, from 1744 until about 1764. While the ruins of the site were still visible when Meriwether Lewis and William Clark ventured in the area during their famed 1804 westward expedition, all traces of the fort were eventually lost by the mid-19th century. Today, the exact location of the fort is a mystery.
 W
WFort Charlotte, Mobile is a partially-reconstructed 18th-century fort in Mobile, Alabama.
 W
WFort de Chartres was a French fortification first built in 1720 on the east bank of the Mississippi River in present-day Illinois. It was used as an administrative center for the province. Due generally to river floods, the fort was rebuilt twice, the last time in limestone in the 1750s in the era of French colonial control over Louisiana and the Illinois Country.
 W
WFort Crevecoeur was the first public building erected by Europeans within the boundaries of the modern state of Illinois and the first fort built in the West by the French. It was founded on the east bank of the Illinois River, in the Illinois Country near the present site of Creve Coeur, a suburb of Peoria, Illinois, in January 1680. It was destroyed on 16 April of that same year by members of La Salle's expedition, who were fearful of being attacked by the Iroquois as the Beaver Wars extended into the area.
 W
WFort De La Boulaye Site, also known as Fort Mississippi, is the site of a fort built by the French in 1699–1700, to support their claim of the Mississippi River and valley. Native Americans forced the French to vacate the fort by 1707.
 W
WFort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit was a fort established on the west bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac in 1701. In the 18th century, French colonial settlements developed on both sides of the river, based on the fur trade, missions and farms.
 W
WFort Duquesne was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the English, and later Americans, and developed as Pittsburgh in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Fort Duquesne was destroyed by the French, prior to English conquest during the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War on the North American front. The latter replaced it, building Fort Pitt between 1759 and 1761. The site of both forts is now occupied by Point State Park, where the outlines of the two forts have been laid in brick.
 W
WFort Denonville was a French fort built in 1688 at the current site of Fort Niagara. It replaced Fort Conti which had been built on the site in 1679 and had burned later that year.
 W
WFort Duquesne is a historical French former fur trade post. It was built c. 1750 and was first discovered in 1983. The following year, on November 15, 1984, the site was added to the National Register of Historic Places. The site is about two miles north of Little Falls, on the west side of the Mississippi River. Since 2004, the site is part of the Charles A. Lindbergh State Park, as a result of a law passed by the Minnesota Legislature.
 W
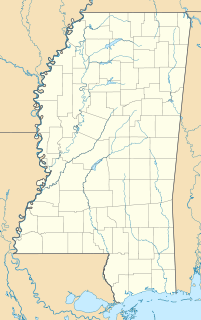
WFort St. Pierre was a colonial French fortified outpost on the Yazoo River in what is now Warren County, Mississippi. Also known as Fort St. Claude and the Yazoo Post, it was established in 1719 and served as the northernmost outpost of French Louisiana. It was destroyed in 1729 by Native Americans and was not rebuilt. Its location, north of Vicksburg on the east bank of the river, was discovered by archaeologists in the 1970s, and was given the Smithsonian trinomial 23-M-5. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 2000.
 W
WThe Spanish assault on French Florida began as part of imperial Spain's geopolitical strategy of developing colonies in the New World to protect its claimed territories against incursions by other European powers. From the early 16th century, the French had historic claims to some of the lands in the New World that the Spanish called La Florida. The French crown and the Huguenots led by Admiral Gaspard de Coligny believed that planting French settlers in Florida would help defuse religious conflicts in France and strengthen its own claim to a part of North America. The Crown wanted to discover and exploit valuable commodities, especially silver and gold, as the Spanish had done with the mines of Mexico and Central and South America. The political and religious enmities that existed between the Catholics and Huguenots of France resulted in the attempt by Jean Ribault in February 1562 to settle a colony at Charlesfort on Port Royal Sound, and the subsequent arrival of René Goulaine de Laudonnière at Fort Caroline, on the St. Johns River in June 1564.
 W
WFort L'Huillier was a short-lived fortification in New France located near the confluence of the Blue Earth and Le Sueur Rivers in what is now Minnesota.
 W
WThe Fort de La Présentation, a mission fort, was built in 1749 and so named by the French Sulpician priest, Abbé Picquet. It was also sometimes known as Fort La Galette. It was built at the confluence of the Oswegatchie River and the St Lawrence River in present-day New York. The French wanted to strengthen their alliance with the powerful Iroquois, as well as convert them to Catholicism. With increasing tensions with Great Britain, they were concerned about their thinly populated Canadian colony. By 1755 the settlement included 3,000 Iroquois residents loyal to France, in part because of the fur trade, as well as their hostility to encroachment by British colonists in their other territories. By comparison, Montréal had only 4,000 residents.
 W
WFort Le Boeuf was a fort established by the French during 1753 on a fork of French Creek, in present-day Waterford, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort was part of a line that included Fort Presque Isle, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne.
 W
WFort Lévis, a fortification on the St. Lawrence River, was built in 1759 by the French. They had decided that Fort de La Présentation was insufficient to defend their St. Lawrence River colonies against the British. Named for François Gaston de Lévis, Duc de Lévis, the fort was constructed on Isle Royale, 3 miles (4.8 km) downstream from the other fort. The fort surrendered after intense bombardment in August 1760 to the British and was renamed Fort William Augustus. The fort was abandoned in 1766. During the construction of the Saint Lawrence Seaway, the remains of the fort were destroyed and submerged beneath the waters of the river.
 W
WFort Machault was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, at present-day Franklin, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort was part of a line that included Fort Presque Isle, Fort Le Boeuf, and Fort Duquesne.
 W
WFort Massac was a French colonial and early National-era fort on the Ohio River in Massac County, Illinois, United States.
 W
WFort Maurepas, later known as Old Biloxi, was developed in colonial French Louisiana in April 1699 along the Gulf of Mexico. . Fort Maurepas was designated temporarily as the capital of Louisiana in 1719. The capital was moved from Mobile westward to Biloxi (present-day Mississippi} then to New Orleans in 1722 on the Mississippi River. Government buildings in the latter city were still under construction.
 W
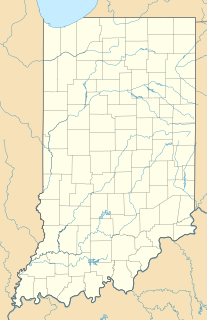
WFort Miami, originally called Fort St. Philippe or Fort des Miamis, was the name of a pair of French palisade forts built at Kekionga, a large Miami Indian village founded where the St. Joseph River and St. Marys River merge to form the Maumee River in northeastern Indiana, near the Ohio border.
 W
WFort Miami was a fort on the bank of the St. Joseph River at the site of the present-day city of St. Joseph, Michigan, in the United States.
 W
WFort Michilimackinac was an 18th-century French, and later British, fort and trading post at the Straits of Mackinac; it was built on the northern tip of the lower peninsula of the present-day state of Michigan in the United States. Built around 1715, and abandoned in 1783, it was located along the Straits, which connect Lake Huron and Lake Michigan of the Great Lakes of North America. Present-day Mackinaw City developed around the site of the fort, which has been designated as a National Historic Landmark. It is preserved as an open-air historical museum, with several reconstructed wooden buildings and palisade.
 W
WFort Niagara is a fortification originally built to protect the interests of New France in North America. It is located near Youngstown, New York, on the eastern bank of the Niagara River at its mouth, on Lake Ontario.
 W
WThe Old Mobile Site was the location of the French settlement La Mobile and the associated Fort Louis de La Louisiane, in the French colony of New France in North America, from 1702 until 1712. The site is located in Le Moyne, Alabama, on the Mobile River in the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta. The settlement served as the capital of French Louisiana from 1702 until 1711, when the capital was relocated to the site of present-day Mobile, Alabama. The settlement was founded and originally governed by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville. Upon the death of d'Iberville, the settlement was governed by his younger brother, Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville. The site can be considered a French colonial counterpart to the English settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. The settlement site and fort were listed on the National Register of Historic Places on May 6, 1976. The Old Mobile Site was determined eligible for designation as a National Historic Landmark on January 3, 2001.
 W
WFort Orleans was a French fort in colonial North America, the first fort built by any European forces on the Missouri River. It was built near the mouth of the Grand River near present-day Brunswick. Intended to be the linchpin in the vast New France empire stretching from Montreal to New Mexico, the fort was occupied from 1723–1726. It was the first multi-year European settlement in what is today the U.S. state of Missouri.
 W
WFort Ouiatenon, built in 1717, was the first fortified European settlement in what is now called Indiana. It was a palisade stockade with log blockhouse used as a French trading post on the Wabash River located approximately three miles southwest of modern-day West Lafayette. The name 'Ouiatenon' is a French rendering of the name in the Wea language, waayaahtanonki, meaning 'place of the whirlpool'. It was one of three French forts built during the 18th century in what was then New France, later the Northwest Territory and today the state of Indiana, the other two being Fort Miami and Fort Vincennes. A substantial French settlement grew up around the fort in the mid-18th century. It was ceded to the British and abandoned after the French and Indian war. Later, it passed into Indian hands and was destroyed in 1791 by American militia during the Northwest Indian War. It was never a U.S. fort. The original site was rediscovered in the 1960s and is now an archaeological site on the National Register of Historical Places.
 W
WFort Pentagouët was a French fort established in present-day Castine, Maine, which was the capital of Acadia (1670–1674). It is the oldest permanent settlement in New England.
 W
WPetit Fort was a structure located in northwestern Indiana, in or near the Indiana Dunes, near the mouth of Fort Creek, now known as Dunes Creek. It may have been a French military outpost, but was more likely a private residence, trading post, or at most a support station for larger forts in the area. The National Park Service refers to it as a "fur depot."
 W
WFort Presque Isle was a fort built by French soldiers in summer 1753 along Presque Isle Bay at present-day Erie, Pennsylvania, to protect the northern terminus of the Venango Path. It was the first of the French posts built in the Ohio Country, and was part of a line that included Fort Le Boeuf, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne.
 W
WFort Prudhomme, or Prud'homme, was a simple stockade fortification, constructed in late Feb. 1682 on one of the Chickasaw Bluffs of the Mississippi River in West Tennessee by Cavelier de La Salle's French canoe expedition of the Mississippi River Basin. The fortification was intended to provide shelter during the search for a member of the expedition who got lost at a stop while hunting, it was used by the expedition for only ten days. Fort Prudhomme was the first structure built by the French in Tennessee; its exact location is not known.
 W
WRedwood is an unincorporated community located southeast of Twin Lake in Warren County, Mississippi, United States. The town is located near the junction of U.S. Route 61 and Mississippi Highway 3, approximately 10 miles north of Vicksburg. Its zip code is 39156.
 W
WFort Rosalie was built by the French in 1716 within the territory of the Natchez Native Americans and it was part of the French colonial empire in the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi.
 W
WFort Saint Charles (1732) on Lake of the Woods was the second post built by La Vérendrye during his expansion of trade and exploration west of Lake Superior. It was located on Magnuson's Island on the Northwest Angle of Minnesota, 3.5 miles east of Angle Inlet, Minnesota and one mile southwest of Penasse, Minnesota, the most northerly point in that state. The site of the modern reconstruction may be somewhat different since the lake levels were raised by control structures on the Winnipeg River. For related forts, see Winnipeg River.
 W
WThe French colonization of Texas began with the establishment of a fort in present-day southeastern Texas. It was established in 1685 near Arenosa Creek and Matagorda Bay by explorer Robert Cavelier de La Salle. He intended to found the colony at the mouth of the Mississippi River, but inaccurate maps and navigational errors caused his ships to anchor instead 400 miles (640 km) to the west, off the coast of Texas. The colony survived until 1688. The present-day town of Inez is near the fort's site. The colony faced numerous difficulties during its brief existence, including Native American raids, epidemics, and harsh conditions. From that base, La Salle led several expeditions to find the Mississippi River. These did not succeed, but La Salle did explore much of the Rio Grande and parts of east Texas.
 W
WSpanish Fort, also known as Old Spanish Fort, Fort St. Jean, and Fort St. John, is a historic place in New Orleans, Louisiana, formerly the site of a fort and later an amusement park.
 W
WFort Saint-Frédéric was a French fort built on Lake Champlain to secure the region against British colonization and control the lake. It was located in modern New York State across the lake from modern Vermont at the town of Crown Point, New York. The fort, whose construction began in 1734, was never attacked, and was destroyed in 1759 before the advance of a large British army under General Jeffery Amherst.
 W
WFort St. Jean Baptiste State Historic Site, or Fort des Natchitoches, in Natchitoches, Louisiana, USA, is a replica of an early French fort based upon the original blueprints of 1716 by Sieur Charles Claude Dutisné and company. The settlement which became the town of Natchitoches was founded in 1714 by French Canadian Louis Antoine Juchereau de St. Denis as the first permanent European settlement in the lands later encompassed by the Louisiana Purchase. In 1722, Juchereau de St. Denis in 1722 became commandant of Fort St. Jean Baptiste des Natchitoches. The fort was devised as a trading and military outpost to counter any Spanish incursions into French territory. Soon it became a center of economic significance, particularly with neighboring Caddo tribes. After 1764, Fort St. Jean was abandoned, with the transfer of Louisiana to Spain. The exact location of the fort has since been lost. In 1979, the fort was reconstructed in the vicinity of where the fort is believed to have been located. Today, the fort is an attraction within the Cane River National Heritage Area. The site is also host to living history re-enactments of what life in the fort was like in the 1750s.
 W
WFort Saint Joseph was a fort established on land granted to the Jesuits by King Louis XIV; it was located on what is now the south side of the present-day town of Niles, Michigan. Père Claude-Jean Allouez established the Mission de Saint-Joseph in the 1680s. Allouez ministered to the local Native Americans, who were primarily Odawa and Ojibwe.
 W
WStarved Rock State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of Illinois, characterized by the many canyons within its 2,630 acres (1,064 ha). Located just southeast of the village of Utica, in Deer Park Township, LaSalle County, Illinois, along the south bank of the Illinois River, the park hosts over two million visitors annually, the most for any Illinois state park.
 W
WThe French colonization of Texas began with the establishment of a fort in present-day southeastern Texas. It was established in 1685 near Arenosa Creek and Matagorda Bay by explorer Robert Cavelier de La Salle. He intended to found the colony at the mouth of the Mississippi River, but inaccurate maps and navigational errors caused his ships to anchor instead 400 miles (640 km) to the west, off the coast of Texas. The colony survived until 1688. The present-day town of Inez is near the fort's site. The colony faced numerous difficulties during its brief existence, including Native American raids, epidemics, and harsh conditions. From that base, La Salle led several expeditions to find the Mississippi River. These did not succeed, but La Salle did explore much of the Rio Grande and parts of east Texas.
 W
WFort Ticonderoga, formerly Fort Carillon, is a large 18th-century star fort built by the French at a narrows near the south end of Lake Champlain, in northern New York, in the United States. It was constructed by Canadian-born French military engineer Michel Chartier de Lotbinière, Marquis de Lotbinière between October 1755 and 1757, during the action in the "North American theater" of the Seven Years' War, often referred to in the US as the French and Indian War. The fort was of strategic importance during the 18th-century colonial conflicts between Great Britain and France, and again played an important role during the Revolutionary War.
 W
WFort Tombecbe, also spelled Tombecbee and Tombeché, was a stockade fort located on the Tombigbee River near the border of French Louisiana, in what is now Sumter County, Alabama. It was constructed under the leadership of Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, Sieur de Bienville in 1736-37 as trading post about 270 miles (430 km) upriver from Mobile, on an 80-foot (24 m) limestone bluff. Fort Tombecbe was built in Choctaw lands and would play a major role in colonial France's efforts to stop British intrusions into the area. Bienville claimed that the new fort was to protect the Choctaw from the Chickasaw. Tombecbe was a major French outpost and trade depot among the Choctaw, the largest Native American group in the colony.
 W
WFort Toulouse, also called Fort des Alibamons and Fort Toulouse des Alibamons, is a historic fort near the city of Wetumpka, Alabama, United States, that is now maintained by the Alabama Historical Commission. The French founded the fort in 1717, naming it for Louis-Alexandre de Bourbon, comte de Toulouse. In order to counter the growing influence of the British colonies of Georgia and Carolina, the government of French Louisiana erected a fort on the eastern border of the Louisiana Colony in what is now the state of Alabama.
 W
WDuring the 18th and early 19th centuries, the French, British and U.S. forces built and occupied a number of forts at Vincennes, Indiana. These outposts commanded a strategic position on the Wabash River. The names of the installations were changed by the various ruling parties, and the forts were considered strategic in the French and Indian War, the American Revolutionary War, the Northwest Indian War and the War of 1812. The last fort was abandoned in 1816.
 W
WFort Wayne, situated on a portion of what is now Fort Wayne, Indiana, was a series of three successive military log stockades (forts) existing between 1794 and 1819 in the Miami Indian village of Kekionga on the portage between the St. Mary's and St. Joseph Rivers in northeastern Indiana near the Ohio border. The first fort with that name was built in 1794 by Captain Jean François Hamtramck under orders from General "Mad" Anthony Wayne as part of the campaign against the Miami Indians during the Northwest Indian War. It was named after General Wayne, who was victorious at the just prior Battle of Fallen Timbers. Wayne may have chosen the name himself—the fort was dedicated the day after he left it. The fort was officially occupied by the army on October 21, 1794. The fort was a basic stockade with few buildings, and was located near the present intersection of Berry and Clay streets.