 W
WThe Action of 1 March 1968 refers to a co-ordinated attempt by four North Vietnamese trawlers to resupply the Viet Cong and the efforts of Operation Market Time elements to stop them during the Vietnam War. On 28 February 1968, United States Navy SP-2H Neptune aircraft on routine patrol detected a North Vietnamese SL class naval trawler heading towards the South Vietnamese coast from north of the DMZ. By the next morning, three more trawlers were discovered and units of Operation Market Time were deployed for a surprise interception. The suspect trawlers did not fly flags so it was not until the start of the engagement that their origin was discovered. The trawlers were steel-hulled vessels, 100 feet long and armed with 57-millimeter recoilless rifles and machine guns. All four vessels were loaded with weapons and ammunition intended to be delivered to the Viet Cong. American and South Vietnamese forces that engaged in action included the United States Coast Guard cutters Androscoggin, Point Grey, Point Welcome, Winona, Point Grace, Point Hudson, Point Marone, the swift boats USS PCF-18, USS PCF-20, USS PCF-42, USS PCF-43, USS PCF-46, USS PCF-47 and USS PCF-48, two South Vietnamese navy junks and one patrol boat. Two U.S. Army helicopter gunships also participated in combat as well as aircraft used to fire flares.
 W
WOperation Allen Brook was a US Marine Corps operation that took place south of Da Nang, lasting from 4 May to 24 August 1968.
 W
WDuring Operation Arc Light from 1965 to 1973, the United States deployed B-52F Stratofortresses from bases in the US to Guam to provide Battlefield air interdiction or BAI, including strikes at enemy bases, supply routes and behind the lines troop concentrations, as well as occasionally providing close air support (CAS) directly to ground combat operations in Vietnam. The conventional bombing campaign was supported by ground-control-radar detachments of the 1st Combat Evaluation Group (1CEVG) in Operation Combat Skyspot. Arc Light operations usually targeted enemy base camps, troops concentrations, and supply lines.
 W
WOperation Auburn was a US Marine Corps operation that took place south of Danang, lasting from 28 December 1967 to 3 January 1968.
 W
WThe First Battle of Saigon, fought during the Tet Offensive of the Vietnam War, was the coordinated attack by communist forces, including both the North Vietnamese Army and the Viet Cong (VC), against Saigon, the capital of South Vietnam.
 W
WThe Battle of South Saigon took place from 7-12 May 1968 during the Vietcong (VC) May Offensive of the Vietnam War. 4 VC battalions attempted to advance over a series of bridges into south Saigon, but were blocked by US Army units and eventually forced to retreat with heavy losses.
 W
WThe Battle of West Saigon took place from 5–12 May 1968 during the May Offensive of the Vietnam War as South Vietnamese and United States forces countered the main thrust of the offensive against the western suburbs of Saigon.
 W
WOperation Bolling was a search and destroy and security operation conducted during the Vietnam War by the U.S. 503rd Infantry Regiment in Phú Yên Province, South Vietnam from 19 September 1967 to 31 January 1969.
 W
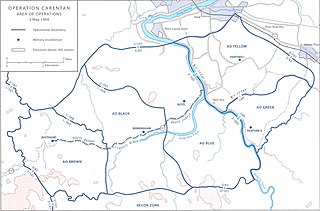
WOperation Carentan and Operation Carentan II were security operations conducted during the Vietnam War by the U.S. 1st and 2nd Brigades, 101st Airborne Division and the 3rd Brigade, 82nd Airborne Division in Thừa Thiên Province, South Vietnam from 18 March to 17 May 1968.
 W
WOperation Coburg was an Australian and New Zealand military action during the Vietnam War. The operation saw heavy fighting between the 1st Australian Task Force and North Vietnamese Army and Viet Cong during the wider fighting around Long Binh and Bien Hoa. American and South Vietnamese intelligence reports had indicated that an imminent communist offensive during the Tet New Year festival was likely, and in response the Australians and New Zealanders were deployed away from their base in Phuoc Tuy Province to bolster American and South Vietnamese forces defending the Long Binh–Bien Hoa complex north-east of Saigon. 1 ATF deliberately established fire support bases astride the communist lines of communication in the vicinity of the village of Trang Bom, expecting that they would attempt to destroy them. The Australians subsequently clashed with the Viet Cong during early patrols in Area of Operations (AO) Columbus, while later Fire Support Base (FSB) Andersen was repeatedly subjected to major ground assaults.
 W
WThe Battle of Coral–Balmoral was a series of actions fought during the Vietnam War between the 1st Australian Task Force and the North Vietnamese 7th Division and Viet Cong Main Force units, 40 kilometres (25 mi) north-east of Saigon. Following the defeat of the communist Tet offensive in January and February, in late April two Australian infantry battalions—the 1st and 3rd Battalions of the Royal Australian Regiment (RAR)—with supporting arms, were again deployed from their base at Nui Dat in Phước Tuy Province to positions astride infiltration routes leading to Saigon to interdict renewed movement against the capital. Part of the wider allied Operation Toan Thang I, it was launched in response to intelligence reports of another impending communist offensive, yet the Australians experienced little fighting during this period. Meanwhile, the Viet Cong successfully penetrated the capital on 5 May, plunging Saigon into chaos during the May Offensive in an attempt to influence the upcoming Paris peace talks scheduled to begin on the 13th. During three days of intense fighting the attacks were repelled by US and South Vietnamese forces, and although another attack was launched by the Viet Cong several days later, the offensive was again defeated with significant losses on both sides, causing extensive damage to Saigon and many civilian casualties. By 12 May the fighting was over, and the North Vietnamese and Viet Cong were forced to withdraw having suffered heavy casualties. US casualties were also heavy and it proved to be their most costly week of the war.
 W
WOperation Coronado XI was the eleventh of the Operation Coronado series of riverine military operations conducted by the U.S. Mobile Riverine Force (MRF) and units of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), designed to secure Cần Thơ in the aftermath of the Tet Offensive. It ran from 12 February to 3 March 1968.
 W
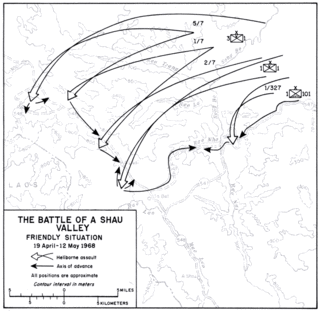
WOperation Delaware/Operation Lam Son 216 was a joint military operation launched during the Vietnam War. It began on 19 April 1968, with troops from the United States and the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) moving into the A Sầu Valley. The A Sầu Valley was a vital corridor for moving military supplies coming from the Ho Chi Minh Trail and was used by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) as a staging area for numerous attacks in northern I Corps. Other than small, special operations reconnaissance patrols, American and South Vietnamese forces had not been present in the region since the Battle of A Shau in March 1966, when a U.S. Special Forces camp located there was overrun.
 W
WDong Re Lao Mountain is located at 16.3038°N 107.2479°E in the A Shau Valley, Vietnam, near the Laotian border. It is densely forested and rises to 4,879 feet (1,487 m), just north of A Luoi, a former French airfield.
 W
WThe Hà My Massacre was a massacre purportedly conducted by the South Korean Marines on 25 February 1968 of unarmed citizens in Hà My village, Điện Dương commune, Điện Bàn District, Quảng Nam Province in South Vietnam.
 W
WThe Battle of Hat Dich was a series of military actions fought between an allied contingent, including the 1st Australian Task Force and the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and Viet Cong (VC) during the Vietnam War. Under the codename Operation Goodwood, two battalions from 1 ATF deployed away from their base in Phuoc Tuy Province, operating against suspected PAVN/VC bases in the Hat Dich area, in western Phuoc Tuy, south-eastern Bien Hoa and south-western Long Khanh Provinces as part of a large allied sweep known as Operation Toan Thang II. The Australians and New Zealanders conducted sustained patrolling throughout the Hat Dich and extensively ambushed tracks and river systems in the Rung Sat Special Zone, occupying a series of fire support bases as operations expanded. Meanwhile, American, South Vietnamese and Thai forces also operated in direct support of the Australians as part of the division-sized action.
 W
WThe Battle of Huế, also called the Siege of Huế, was a major military engagement in the Tết Offensive launched by North Vietnam and the Việt Cộng during the Vietnam War. After initially losing control of most of Huế and its surroundings, the combined South Vietnamese and American forces gradually recaptured the city over one month of intense fighting. The battle was one of the longest and bloodiest of the war, and the battle negatively affected American public perception of the war.
 W
WThe attack on the Joint General Staff (JGS) Compound, the headquarters of the Republic of Vietnam Military Forces, occurred during the early hours of 31 January 1968. The JGS was located east of Tan Son Nhut Air Base. The attack by Vietcong (VC) forces was one of several major attacks on Saigon in the first days of the Tet Offensive. The attack was repulsed with the VC suffering heavy losses; no material damage was done to the compound.
 W
WIn the Vietnam War, after the assassinations of Ngo Dinh Diem and John F. Kennedy in late 1963 and the Gulf of Tonkin incident in 1964 and the continuing political instability in the South, the United States made a policy commitment to begin joint warfare in South Vietnam, a period of gradual escalation and Americanization, involving the commitment of large-scale combat forces from the United States and allied countries. It was no longer assumed the Republic of Vietnam could create a desirable situation without major external assistance. This phase of the war lasted until the election of Richard Nixon, and the change of U.S. policy to Vietnamization, or giving the main combat role back to the South Vietnamese military.
 W
WThe 1968 Kham Duc C-130 shootdown was the aircraft shootdown of a United States Air Force Lockheed C-130B Hercules aircraft during the Battle of Kham Duc on May 12, 1968. All 155 people on board were killed. At the time, it was the deadliest aircraft crash in history, to date is the deadliest aviation accident/incident on Vietnamese soil, and remained the deadliest accident involving a U.S. military aircraft until Arrow Air Flight 1285 in 1985.
 W
WThe Battle of Kham Duc was a major battle of the Vietnam War. The event occurred in Khâm Đức, now district capital of Khâm Đức District, then in Quảng Tín Province, from 10–12 May 1968. During the Tet Offensive of 1968, the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) 2nd Division tried to capture Đà Nẵng, but they were defeated in the Battle of Lo Giang by elements of the U.S. 1st Marine Division and the 23rd Infantry Division (Americal). PAVN General Chu Huy Mân disengaged from the fight on the outskirts of the city, and pulled the 2nd Division into the mountains where it could rest, rebuild, and prepare for the next major operation. Khâm Đức, a small district in the north of Quảng Tín, was chosen as the next target for the 2nd Division. Following their defeat at Đà Nẵng, U.S. military intelligence agencies in I Corps Tactical Zone were confused by the movements of the 2nd Division, because they could not track down the unit.
 W
WThe Battle of Khe Sanh was conducted in the Khe Sanh area of northwestern Quảng Trị Province, Republic of Vietnam, during the Vietnam War. The main US forces defending Khe Sanh Combat Base (KSCB) were two regiments of the United States Marine Corps supported by elements from the United States Army and the United States Air Force (USAF), as well as a small number of Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) troops. These were pitted against two to three divisional-size elements of the North Vietnamese People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN).
 W
WOperation Lancaster was a U.S. Marine Corps operation that took place in northern Quảng Trị Province from November 1967 to January 20, 1968.
 W
WThe Battle of Lang Vei began on the evening of 6 February 1968 and concluded during the early hours of 7 February, in Quảng Trị Province, South Vietnam. Towards the end of 1967 the 198th Tank Battalion, People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) 202nd Armored Regiment, received instructions from the North Vietnamese Ministry of Defense to reinforce the 304th Division as part of the "Route 9-Khe Sanh Campaign". After an arduous journey down the Ho Chi Minh trail in January 1968, the 198th Tank Battalion linked up with the 304th Division for an offensive along Highway 9, which stretched from the Laotian border through to Quảng Trị Province. On 23 January, the 24th Regiment attacked the small Laotian outpost at Bane Houei Sane, under the control of the Royal Laos Army BV-33 "Elephant" Battalion.
 W
WThe Battle of Lima Site 85, also called Battle of Phou Pha Thi, was fought as part of a military campaign waged during the Vietnam War and Laotian Civil War by the North Vietnamese People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and the Pathet Lao, against airmen of the United States Air Force (USAF)'s 1st Combat Evaluation Group, elements of the Royal Lao Army, Royal Thai Border Patrol Police, and the Central Intelligence Agency-led Hmong Clandestine Army. The battle was fought on Phou Pha Thi mountain in Houaphanh Province, Laos, on 10 March 1968, and derives its name from the mountaintop where it was fought or from the designation of a 700 feet (210 m) landing strip in the valley below, and was the largest single ground combat loss of United States Air Force members during the Vietnam War.
 W
WOperation Mameluke Thrust was a US Marine Corps operation that took place in Happy Valley southwest of Danang, lasting from 19 May to 23 October 1968.
 W
WOperation Maui Peak was a US Marine Corps operation that took place near the Thường Ðức Camp southwest of Danang, lasting from 1 to 19 October 1968.
 W
WPHASE II of the Tet Offensive of 1968 was launched by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and Viet Cong (VC) against targets throughout South Vietnam, including Saigon from 29 April to 30 May 1968. The May Offensive was considered much bloodier than the initial phase of the Tet Offensive. US casualties across South Vietnam were 2,169 killed for the entire month of May making it the deadliest month of the entire Vietnam War for U.S. forces, while South Vietnamese losses were 2,054 killed. PAVN/VC losses exceeded 24,000 killed and over 2,000 captured. The May Offensive was a costly defeat for the PAVN/VC.
 W
WOperation Meade River was a US Marine Corps cordon and search operation that took place south of Danang, lasting from 20 November to 9 December 1968.
 W
WThe New Year's Day battle of 1968 was a military engagement during the Vietnam War that began on the evening of 1 January 1968. It involved units assigned to the U.S. 25th Infantry Division and two regiments of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN).
 W
WNguyễn Văn Lém, often referred to as Bảy Lốp, was a member of the Viet Cong. He was summarily executed in Saigon during the Tet Offensive in the Vietnam War, when Viet Cong and North Vietnamese forces launched a massive surprise attack. Lém was alleged to have murdered a general and 7 members of his family before being captured.
 W
WOperation Niagara was a U.S. Seventh Air Force close air support campaign carried out from January through March 1968, during the Vietnam War. Its purpose was to serve as an aerial umbrella for the defense of the U.S. Marine Corps Khe Sanh Combat Base on the Khe Sanh Plateau, in western Quang Tri Province of the Republic of Vietnam. The base was under siege by an estimated three-divisional force of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN).
 W
WOperation Sealords was a military operation that took place during the Vietnam War.
 W
WOperation Shed Light was a crash development project in aerial warfare, initiated in 1966 by the United States Air Force to increase the ability to accurately strike at night or in adverse weather. During the 1960s the United States military worked hard to interdict the movement of men and materiel along the Ho Chi Minh trail. The North Vietnamese were experts in the use of weather and darkness to conceal their movement, and understanding the superiority of American air power put their skills immediately to good use. US forces seeking to impede the steady flow of supplies attempted to locate largely static targets during the day with poor results.
 W
WOperation Ranch Hand was a U.S. military operation during the Vietnam War, lasting from 1962 until 1971. Largely inspired by the British use of 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D during the Malayan Emergency in the 1950s, it was part of the overall chemical warfare program during the war called "Operation Trail Dust". Ranch Hand involved spraying an estimated 20 million U.S. gallons (76,000 m3) of defoliants and herbicides over rural areas of South Vietnam in an attempt to deprive the Viet Cong of food and vegetation cover. Areas of Laos and Cambodia were also sprayed to a lesser extent. Nearly 20,000 sorties were flown between 1961 and 1971.
 W
WOperation Santa Fe was a security operation conducted during the Vietnam War by the U.S. 1st Brigade, 9th Infantry Division, the 1st Australian Task Force and the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) 18th Division against the May Tao Secret Zone, South Vietnam from 3 November 1967 to 5 January 1968.
 W
WOperation Somerset Plain was a joint military operation conducted by the United States and the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) in the A Sầu Valley from 4-20 August 1968.
 W
WOperation Speedy Express was a controversial U.S. Army 9th U.S. Infantry Division operation of the Vietnam War conducted in the Mekong Delta provinces Kiến Hòa and Vĩnh Bình. The operation, led by Major General Julian J. Ewell, was part of US military "pacification" efforts against the Viet Cong (VC). The US military sought to interdict lines of VC communication and deny them the use of base areas. At least 5,000 to 7,000 casualties were reported to have been civilians.
 W
WOperation Steel Tiger was a covert U.S. 2nd Air Division, later Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 aerial interdiction effort targeted against the infiltration of People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) men and material moving south from the Democratic Republic of Vietnam through southeastern Laos to support their military effort in the Republic of Vietnam during the Vietnam War.
 W
WThe Battle of Tam Kỳ took place during the Vietnam War from 3–6 March 1968. After a night-time rocket attack on their base camp by the People’s Army of Vietnam (PAVN) 3rd Regiment, 3rd Division, the 1st Squadron, 1st Cavalry Regiment and Company A, 3rd Battalion, 23rd Infantry Regiment engaged the PAVN killing 436.
 W
WThe attack on Tan Son Nhut Air Base, headquarters of the Republic of Vietnam Air Force (RVNAF) and the United States Air Force (USAF) 7th Air Force, occurred during the early hours of 31 January 1968. Tan Son Nhut Air Base was one of the major air bases used for offensive air operations within South Vietnam and for the support of United States Army and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) ground operations. The attack by Vietcong (VC) and People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) forces was one of several major attacks on Saigon in the first days of the Tet Offensive. The attack was repulsed with the VC/PAVN suffering heavy losses; only superficial damage was done to the base.
 W
WOperation Taylor Common was a search and destroy operation conducted by Task Force Yankee, a task force of the 1st Marine Division supported by the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), southwest of Hội An from 6 December 1968 to 8 March 1969.
 W
WOperation Tiger Hound was a covert U.S. 2nd Air Division, later Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 aerial interdiction campaign conducted in southeastern Laos from 5 December 1965 till 11 November 1968, during the Vietnam War. The purpose of the operation was to interdict the flow of People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) supplies on the Ho Chi Minh Trail from the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, through southeastern Laos, and into the northern provinces of the Republic of Vietnam. The missions were originally controlled by the 2d Air Division until that headquarters was superseded by the Seventh Air Force on 1 April 1966.
 W
WOperation Toan Thang I was a U.S. Army, Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), 1st Australian Task Force and Royal Thai Volunteer Regiment operation conducted between 8 April and 31 May 1968 in the Vietnam War. The operation was part of a reaction to the Tet Offensive designed to put pressure on Vietcong (VC) and People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) forces in III Corps.
 W
WOperation Toan Thang II was a U.S. Army and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) operation conducted between 1 June 1968 and 16 February 1969 in the Vietnam War. The operation was designed to keep pressure on Vietcong (VC) and People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) forces in III Corps.
 W
WOperation Truong Cong Dinh, was a United States and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) security operation to reestablish South Vietnamese control over the northern Mekong Delta in the aftermath of the Tet Offensive. The operation aimed to root out Viet Cong (VC) forces in the area, and to stop them from attacking traffic on the nearby Highway 4. The operation started on 7 March 1968 and lasted until August 1968, involving the 1st and 2nd brigades of the US 9th Infantry Division and the ARVN 7th Division backed by South Vietnamese Regional Forces. Operations were supported by an American artillery battalion, which established a fire support base on the north bank of the Mỹ Tho River and the Mobile Riverine Force (MRF) which conducted a series of riverine and airmobile operations.
 W
WThe Tet Offensive attack on the US Embassy took place on the early morning of 31 January 1968 when a 19-man Vietcong (VC) sapper team attempted to seize the US Embassy in Saigon at the start of the VC's Tet Offensive. While the VC successfully penetrated the embassy compound, they were unable to enter the chancery building and were pinned down by security forces, with the lone survivor eventually surrendering to US forces. Notwithstanding the attack's failure it had a profound political and psychological impact in the United States.
 W
WThe Republic of Vietnam competed as Vietnam at the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City, Mexico. Nine competitors, seven men and two women, took part in seven events in five sports.
 W
WThe year 1968 saw major developments in the Vietnam War. The military operations started with an attack on a US base by the North Vietnamese People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and the Viet Cong (VC) on January 1, ending a truce declared by the Pope and agreed upon by all sides. At the end of January, the PAVN and VC launched the Tet Offensive.
 W
WOperation Yellowstone was an operation conducted by the 1st and 3rd Brigades, 25th Infantry Division in northeast Tây Ninh Province, lasting from 8 December 1967 to 24 February 1968.