 W
WHuman history in California began when indigenous Americans first arrived some 13,000 years ago. Coastal exploration by Europeans began in the 16th century, and settlement by Europeans along the coast and in the inland valleys began in the 18th century. California was ceded to the United States under the terms of the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo following the defeat of Mexico in the Mexican–American War. American westward expansion intensified with the California Gold Rush, beginning in 1848. California joined the Union as a free state in 1850, due to the Compromise of 1850. By the end of the 19th century, California was still largely rural and agricultural, but had a population of about 1.4 million.
 W
WThe indigenous peoples of California are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. With over forty groups seeking to be federally recognized tribes, California has the second largest Native American population in the United States. The California cultural area does not conform exactly to the state of California's boundaries. Many tribes on the eastern border with Nevada are classified as Great Basin tribes, and some tribes on the Oregon border are classified as Plateau tribes. Tribes in Baja California who do not cross into California are classified as indigenous peoples of Mexico.
 W
WAn Act for the Admission of the State of California into the Union is the federal legislation that admitted California to the United States of America as the thirty-first state. California is one of only a few states which became a state without first being an organized territory.
 W
WThe history of California can be divided into: the Native American period, the European exploration period (1542–1769), the Spanish colonial period (1769–1821), the Mexican period (1821–1848), and United States statehood. California was one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse areas in pre-Columbian North America. After contact with Spanish explorers, most of the Native Americans died out from European diseases.
 W
WBelow is a list of the Governors of early California (1769–1850), before its admission as the 31st U.S. state. First explored by Gaspar de Portolá, with colonies established at San Diego and Monterey, California was a remote, sparsely-settled Spanish province of New Spain. In 1822, following Mexican independence, California became part of Mexico.
 W
WJuan Bautista de Anza was born in the Spanish province of New Navarre in Viceroyalty of New Spain. Of Basque descent, he served as an expeditionary leader, military officer, and politician primarily in California and New Mexico under the Spanish Empire. He is credited as one of the founding fathers of Spanish California and served as an official within New Spain as Governor of the Province of New Mexico.
 W
WThe California Republic, or Bear Flag Republic, was an unrecognized breakaway state from Mexico, that for 25 days in 1846 militarily controlled an area north of San Francisco, in and around what is now Sonoma County in California.
 W
WThe California Republic, or Bear Flag Republic, was an unrecognized breakaway state from Mexico, that for 25 days in 1846 militarily controlled an area north of San Francisco, in and around what is now Sonoma County in California.
 W
WThe Blythe Intaglios or Blythe Geoglyphs are a group of gigantic figures incised on the ground near Blythe, California, in the Colorado Desert. The ground drawings or geoglyphs were created by humans for an, as yet, unknown reason.
 W
WBrushy Peak Regional Preserve is a regional park that is part of the East Bay Regional Parks (EBRPD) and the Livermore Area Recreation and Park District (LARPD) systems. It is located in unincorporated land in Alameda County, just north of Livermore, California.
 W
WJuan Rodríguez Cabrillo was an Iberian maritime explorer best known for investigations of the West Coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the first European to explore present-day California, navigating along the coast of California in 1542–1543.
 W
WThe California Constitutional Conventions were two separate constitutional conventions that took place in California during the nineteenth century which led to the creation of the modern Constitution of California. The first, known as the Monterey Convention, held in September and October 1849 in advance of California attaining U.S. statehood the following year, adopted the state's original constitution. This document maintains jurisdiction along with the current constitution which was ratified on May 7, 1879, following the Sacramento Convention. Article 3 Section 2 of the current Constitution references the original boundaries as stated in the 1849 Constitution at Article 7. The result of Progressive mistrust of elected officials, this later constitution took a full year to finalize and is today the third longest in the world, and has been described as "the perfect example of what a constitution ought not to be". Multiple calls for a third state constitutional convention have been raised during the past quarter-century, but none has thus far gained widespread political momentum.
 W
WThe California Dream is the psychological motivation to gain fast wealth or fame in a new land. As a result of the California Gold Rush after 1849, California's name became indelibly connected with the Gold Rush, and fast success in a new world became known as the "California Dream". California was perceived as a place of new beginnings, where great wealth could reward hard work and good luck. The notion inspired the idea of an American Dream. California was seen as a lucky place, a land of opportunity and good fortune. It was a powerful belief, underlying many of the accomplishments of the state, and equally potent when threatened.
 W
WThe California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the United States and abroad. The sudden influx of gold into the money supply reinvigorated the American economy, and the sudden population increase allowed California to go rapidly to statehood, in the Compromise of 1850. The Gold Rush had severe effects on Native Californians and accelerated the Native American population's decline from disease, starvation and the California Genocide. By the time it ended, California had gone from a thinly populated ex-Mexican territory, to having one of its first two U.S. Senators, John C. Frémont, selected to be the first presidential nominee for the new Republican Party, in 1856.
 W
WWomen in the California Gold Rush, which began in Northern California in 1848, initially included Spanish descendants, or Californios, who already lived in California, Native American women, and rapidly arriving immigrant women from all over the world. At first, the numbers of immigrant women were scarce, but they contributed to their community nonetheless. Some of the first people in the mining fields were wives and families who were already in California. A few settler women and kids and the few men who didn't leave their family worked right alongside the men but most men who arrived left their wives and families home. The number of women in California changed very quickly as the rich gold strikes and lack of women created strong pressures in the new Gold Rush communities to restore sex balance. As travel arrangements improved and were made easier and more predictable the number of women coming to California rapidly increased. Most women probably came by way of Panama as this was one of the fastest trips and one of the most reliable—although expensive in 1850--$400–$600/person one-way. Passage via Panama became much more predictable after the paddle wheel steam ship lines were up and running by late 1849. In Ireland, the Great Famine was a period of mass starvation, disease and emigration between 1845 and 1852 that drove many desperate women to the United States and on to California. It was very depressing and very discouraging.
 W
WThe California hide trade was a trading system of various products based in cities along the California coastline, operating from the early 1820s to the mid-1840s.
 W
WA California interim government existed from mid-1846 until September, 1850. United States military occupation of territory comprising today's U.S. state of California came soon after the outbreak of the Mexican–American War in 1846. Occupation replaced the previous system of government under Mexico with a "Law of war" system centralizing and combining military command and civil governance under a series of military commanders/governors. Existing local government structure, however, was largely left in place.
 W
WThe California Republic, or Bear Flag Republic, was an unrecognized breakaway state from Mexico, that for 25 days in 1846 militarily controlled an area north of San Francisco, in and around what is now Sonoma County in California.
 W
WThe California Trail was an emigrant trail of about 3,000 mi (4,800 km) across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail followed the same corridor of networked river valley trails as the Oregon Trail and the Mormon Trail, namely the valleys of the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater rivers to Wyoming. In the present states of Wyoming, Idaho, and Utah, the California and Oregon trails split into several different trails or cutoffs.
 W
WThe Californian was the first California newspaper.
 W
WThe Californias, occasionally known as the Three Californias or Two Californias, are a region of North America spanning the United States and Mexico, consisting of the U.S. state of California and the Mexican states of Baja California and Baja California Sur. Historically, the term Californias was used to define the vast northwestern region of Spanish America, as the Province of the Californias, and later as a collective term for Alta California and the Baja California Peninsula.
 W
WJose Castro House, now known as the Castro-Breen Adobe, in San Juan Bautista, California, USA, is a historic Monterey Colonial adobe home built by José Antonio Castro in 1840. Castro was Commandant General of Alta California. In 1848 Castro sold the house to Patrick Breen, survivor of the ill-fated Donner party of 1846, and the Breen family lived in the house until 1935. They sold it to the State of California who adapted it as a museum and incorporated it into the San Juan Bautista Plaza Historic District.
 W
WThe Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–American War. It also set Texas's western and northern borders and included provisions addressing fugitive slaves and the slave trade. The compromise was brokered by Whig senator Henry Clay and Democratic senator Stephen Douglas with the support of President Millard Fillmore.
 W
WThe California Campaign (1846–1847), colloquially the Conquest of California or Conquest of Alta California by the United States, was an early military campaign of the Mexican–American War that took place in the western part of Mexico's Alta California Department, in the present-day state of California. The California Campaign was marked by a series of small battles throughout 1846 and early 1847.
 W
WThe Constitution of California is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of California, describing the duties, powers, structures and functions of the government of California. California's original constitution was drafted in both English and Spanish by American pioneers, European settlers, and Californios and adopted at the 1849 Constitutional Convention of Monterey, following the American Conquest of California and the Mexican-American War and in advance of California's Admission to the Union in 1850. The constitution was amended and ratified on 7 May 1879, following the Sacramento Convention of 1878-79.
 W
WThe Curse of Capistrano is a 1919 serialized five-part prose story by Johnston McCulley and the first work to feature the fictional Californio character Diego Vega, the masked hero also called Zorro. The story was adapted into the silent film The Mark of Zorro in 1920, leading to new popularity. The full five-part story was then published as a book in 1924, also using the title The Mark of Zorro.
 W
WThe Alta California or Daily Alta California was a 19th-century San Francisco newspaper.
 W
WThe Donner Party was a group of American pioneers who migrated to California in a wagon train from the Midwest. Delayed by a series of mishaps, they spent the winter of 1846–1847 snowbound in the Sierra Nevada mountain range. Some of the migrants resorted to cannibalism to survive, eating the bodies of those who had succumbed to starvation and sickness.
 W
WThe Eagle Borax Works in Death Valley, California was established near Bennetts Well in 1882 by Isidore Daunet, J.M. McDonald, M. Harmon and C.C. Blanch to mine the borate deposits that Daunet discovered there in 1880. The partnership established the first borax works in the valley. Partly refined borax was hauled to Daggett, California through the Panamint Valley using 12-mule teams hauling two wagons. The extraction business operated until 1884 when problems mounted and Daunet took his own life. The property eventually passed to the U.S. Borax Company, which kept it as a mining reserve, then to Borax Consolidated, Ltd. in 1922. The property was sold to the Death Valley Hotel Company in 1956, and finally to the National Park Service.
 W
WEl Camino Real, sometimes associated with Calle Real, usually refers to the 600-mile (965-kilometer) road connecting the 21 Spanish missions in California, along with a number of sub-missions, four presidios, and three pueblos, stretching at its southern end from the San Diego area Mission San Diego de Alcalá, all of the way up to the trail's northern terminus at Mission San Francisco Solano in Sonoma, just north of San Francisco Bay.
 W
WThe Emeryville Shellmound, in Emeryville, California, is a sacred burial site of the Ohlone people, a once-massive archaeological shell midden deposit. It was one of a complex of five or six mounds along the mouth of the perennial Temescal Creek, on the east shore of San Francisco Bay between Oakland and Berkeley. It was the largest of the over 425 shellmounds that surrounded San Francisco Bay. The site of the Shellmound is now a California Historical Landmark (#335).
 W
WEmigrant Gap is a gap in a ridge on the California Trail as it crosses the Sierra Nevada, to the west of what is now known as Donner Pass. Here the cliffs are so steep that, back in the 1840s, the pioneers on their way to California had to lower their wagons on ropes in order to continue.
 W
WGlen Helen Regional Park is a county park located in San Bernardino, California, United States adjacent to the Cajon Pass. It was the site of both US Festivals of the early 1980s. It is also home to the Glen Helen Amphitheater, the largest outdoor amphitheater in the United States. The park also hosts several off-road races since 1985.
 W
WThe Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, officially titled the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits and Settlement between the United States of America and the Mexican Republic, is the peace treaty signed on February 2, 1848, in the Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo between the United States and Mexico that ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The treaty was ratified by the United States on March 10 and by Mexico on May 19. The ratifications were exchanged on May 30, and the treaty was proclaimed on July 4, 1848.
 W
WThe Harmony Borax Works is located in Death Valley at Furnace Creek Springs, then called Greenland. It is now located within Death Valley National Park in Inyo County, California. It is on the National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WThe history of San Jose, California, the third largest city in the state, and the largest of all cities in the San Francisco Bay Area and Northern California, with a population of 1,021,795:
 W
WThe history of Santa Barbara, California, begins approximately 13,000 years ago with the arrival of the first Native Americans. The Spanish came in the 18th century to occupy and Christianize the area, which became part of Mexico following the Mexican War of Independence. In 1848, the expanding United States acquired the town along with the rest of California as a result of defeating Mexico in the Mexican–American War. Santa Barbara transformed then from a small cluster of adobes into successively a rowdy, lawless Gold Rush era town; a Victorian-era health resort; a center of silent film production; an oil boom town; a town supporting a military base and hospital during World War II; and finally it became the economically diverse resort destination it remains in the present day. Twice destroyed by earthquakes, in 1812 and 1925, it was rebuilt in a Spanish Colonial style.
 W
WKanakas were workers from various Pacific Islands employed in British colonies, such as British Columbia (Canada), Fiji, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and Queensland (Australia) in the 19th and early 20th centuries. They also worked in California and Chile.
 W
WThe Legend of Zorro is a 2005 American Western swashbuckler film directed by Martin Campbell, produced by Walter F. Parkes, Laurie MacDonald and Lloyd Phillips, with music by James Horner, and written by Roberto Orci and Alex Kurtzman. It is the sequel to 1998's The Mask of Zorro; Antonio Banderas and Catherine Zeta-Jones reprise their roles as the titular hero and his spouse, Elena, and Rufus Sewell stars as the villain, Count Armand. The film takes place in San Mateo County, California and was shot in San Luis Potosí, Mexico, with second-unit photography in Wellington, New Zealand. The film was theatrically released on October 28, 2005, by Columbia Pictures, and earned $142.4 million on a $75 million budget.
 W
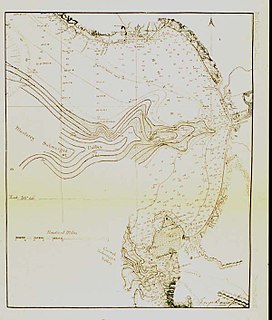
WCalifornia is a unique place that has not always been well understood. For hundreds of years there persisted a European misconception that California was an island and many maps were made depicting it as such. Eventually, by the 18th century, enough information about California reached the outside world to dispel that myth. As California became increasingly populated, comprehensive surveying and mapping of its territory seemingly expanded slowly. When gold was discovered in 1848 and it joined the United States as the thirty first state in 1851 interest in plotting California's landscapes boomed.
 W
WThe maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exchange for tea, silks, porcelain, and other Chinese goods, which were then sold in Europe and the United States. The maritime fur trade was pioneered by Russians, working east from Kamchatka along the Aleutian Islands to the southern coast of Alaska. British and Americans entered during the 1780s, focusing on what is now the coast of British Columbia. The trade boomed around the beginning of the 19th century. A long period of decline began in the 1810s. As the sea otter population was depleted, the maritime fur trade diversified and transformed, tapping new markets and commodities, while continuing to focus on the Northwest Coast and China. It lasted until the middle to late 19th century.
 W
WMarsh Creek State Historic Park is a California state park in east Contra Costa County, California, United States. It was named as the newest California State Park on January 27, 2012. The newly named park contains 3,659 acres and is about 3.3 miles (5.3 km) south of downtown Brentwood. It is not open to the public as of January 2015. No opening date has been announced.
 W
WThe Mask of Zorro is a 1998 American swashbuckler film based on the character of the masked vigilante Zorro created by Johnston McCulley. It was directed by Martin Campbell and stars Antonio Banderas, Anthony Hopkins, Catherine Zeta-Jones, and Stuart Wilson. The film features the original Zorro, Don Diego de la Vega (Hopkins), escaping from prison to find his long-lost daughter (Zeta-Jones) and avenge the death of his wife at the hands of the corrupt governor Rafael Montero (Wilson). He is aided by his successor (Banderas), who is pursuing his own vendetta against the governor's right-hand man while falling in love with de la Vega's daughter.
 W
WThe Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the Intervención Estadounidense en México, was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1845 U.S. annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered Mexican territory since the government did not recognize the Velasco treaty signed by Mexican General Antonio López de Santa Anna when he was a prisoner of the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was de facto an independent country, but most of its citizens wished to be annexed by the United States. Domestic sectional politics in the U.S. were preventing annexation since Texas would have been a slave state, upsetting the balance of power between northern free states and southern slave states. In the 1844 United States presidential election, Democrat James K. Polk was elected on a platform of expanding U.S. territory in Oregon and Texas. Polk advocated expansion by either peaceful means or by armed force, with the 1845 annexation of Texas as furthering that goal. For Mexico, this was a provocation, but Polk went further, sending U.S. Army troops to the area; he also sent a diplomatic mission to Mexico to try to negotiate the sale of territory. U.S. troops' presence was provocative and designed to lure Mexico into starting the conflict, putting the onus on Mexico and allowing Polk to argue to Congress that a declaration of war should be issued. Mexican forces attacked U.S. forces, and the United States Congress declared war.
 W
WMission grapes are a variety of Vitis vinifera introduced from Spain to the western coasts of North and South America by Catholic New World missionaries for use in making sacramental, table, and fortified wines. It is grown in South America, particularly in Chile and Peru, under then names Criolla and Pais. During the 19th century, the grape was known by several other names, including the Los Angeles grape, and the California grape.
 W
WThe Mohave Trail was a Native American trade route between Mohave Indian villages on the Colorado River and settlements in coastal Southern California.
 W
WNew Albion, also known as Nova Albion, was the name of the continental area north of Mexico claimed by Sir Francis Drake for England when he landed on the North American west coast in 1579. This claim became the justification for English charters across America to the Atlantic coast and soon influenced further national expansion projects on the continent. Today, Drake's landing site is known as Point Reyes, California, a marine environment which is the setting of several small towns, ranches, and Point Reyes National Seashore.
 W
WThe Old Tejon Pass is a mountain pass in the Tehachapi Mountains linking Southern and Central California.
 W
WPacheco Pass, elevation 1,368 ft (417 m), is a low mountain pass located in the Diablo Range in southeastern Santa Clara County, California. It is the main route through the hills separating the Santa Clara Valley and the Central Valley.
 W
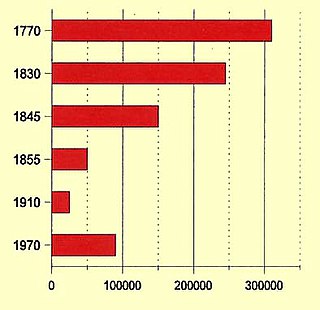
WThe Population of Native California refers to the population of Indigenous peoples of California. Estimates prior to and after European contact have varied substantially. Pre-contact estimates range from 133,000 to 705,000 with some recent scholars concluding that these estimates are low.
 W
WThe Portolá expedition was a Spanish voyage of exploration in 1769–1770 that was the first recorded European land entry and exploration of the interior of the present-day U.S. state of California. It was led by Gaspar de Portolá, governor of Las Californias, the Spanish colonial province that included California, Baja California, and other parts of present-day Mexico and the United States. The expedition led to the founding of Alta California and contributed to the solidification of Spanish territorial claims in the disputed and unexplored regions along the Pacific coast of North America.
 W
WPoso Creek or Posey Creek is an 87.9-mile (141.5 km) intermittent stream in Kern County, California.
 W
WRussian America was the name of the Russian colonial possessions in North America from 1733 to 1867. Its capital was Novo-Arkhangelsk, which is now Sitka, Alaska, United States. Settlements spanned parts of what are now the U.S. states of California, Alaska and three forts in Hawaii. Formal incorporation of the possessions by Russia did not take place until the Ukase of 1799 which established a monopoly for the Russian–American Company and also granted the Russian Orthodox Church certain rights in the new possessions. Many of its possessions were abandoned in the 19th century. In 1867, Russia sold its last remaining possessions to the United States of America for $7.2 million.
 W
WThe Russian colonization of the Americas covers the period from 1732 to 1867, when the Russian Empire laid claim to northern Pacific Coast territories in the Americas. Russian colonial possessions in the Americas are collectively known as Russian America. Russian expansion eastward began in 1552, and in 1639 Russian explorers reached the Pacific Ocean. In 1725, Emperor Peter the Great ordered navigator Vitus Bering to explore the North Pacific for potential colonization. The Russians were primarily interested in the abundance of fur-bearing mammals on Alaska's coast, as stocks had been depleted by over hunting in Siberia. Bering's first voyage was foiled by thick fog and ice, but in 1741 a second voyage by Bering and Aleksei Chirikov made sight of the North American mainland.
 W
WThe Siskiyou Trail stretched from California's Central Valley to Oregon's Willamette Valley; modern-day Interstate 5 follows this pioneer path. Originally based on existing Native American foot trails winding their way through river valleys, the Siskiyou Trail provided the shortest practical travel path between early settlements in California and Oregon.
 W
WEstablished in 1850, the Society of California Pioneers is dedicated to the study and enjoyment of California art, history, and culture. Founded by individuals arriving in California before 1850 and thriving under the leadership of several generations of their direct descendants, The Society has continuously served its members, the academic community, and the public. As the oldest organization West of The Mississippi, The Society opened the first library in California, as well as a grand hall for meetings, lectures, and social events. Today The Society operates a public museum and a research library, both housed in one of the iconic Montgomery Barracks Buildings on The Presidio of San Francisco's historic Main Post.
 W
WThe Stone House of John Marsh is a historic stone house in Contra Costa County, California, built in 1855–56. It is now included in the newly-designated Marsh Creek State Park. It has not been officially opened to the public because of safety concerns, but restoration began in 2006 and is continuing as of October 2017.
 W
WRobert Gray was an American merchant sea captain who is known for his achievements in connection with two trading voyages to the northern Pacific coast of North America, between 1790 and 1793, which pioneered the American maritime fur trade in that region. In the course of those voyages, Gray explored portions of that coast and, in 1790, completed the first American circumnavigation of the world. He was noted for coming upon and naming the Columbia River in 1792, while on his second voyage.
 W
WZorro is a fictional character created in 1919 by American pulp writer Johnston McCulley, and appearing in works set in the Pueblo of Los Angeles during the era of Spanish California (1769–1821). He is typically portrayed as a dashing masked vigilante who defends the commoners and indigenous peoples of California against corrupt and tyrannical officials and other villains. His signature all-black costume includes a cape, a hat known as a sombrero cordobés, and a mask covering the upper half of his face.