 W
WThe Haw Wars were fought against Chinese quasi-military forces invading parts of Tonkin and the Siam from 1865–1890. Forces invading Lao domains were ill-disciplined and freely plundered Buddhist temples. Not knowing these were remnants of the aftermath of the Taiping Rebellion led by Hong Xiuquan, a heterodox Christian convert, the invaders were confused with Chinese Muslims from Yunnan called Haw. Forces sent by King Rama V failed to suppress the various groups, the last of which eventually disbanded in 1890.
 W
WThe Invasion and rebellion of the Five Barbarians is a Chinese expression referring to a series of rebellions between 304 - 316 A.D. by four non-Chinese peoples living in North China against the Jin dynasty (265–420), which had recently been weakened by a series of civil wars. The uprisings helped topple Emperor Huai of Jin in Luoyang and ended the Western Jin dynasty in northern China.
 W
WThe Mongol conquest of Western Xia was a series of conflicts between the Mongol Empire and the Tangut Western Xia dynasty. Hoping to gain both plunder and a vassal state, Mongol leader Genghis Khan commanded some initial raids against Western Xia before launching a full-scale invasion in 1209. This marked both the first major invasion conducted by Genghis and the first major Mongol invasion of China.
 W
WThe Mongol invasions of Japan , which took place in 1274 and 1281, were major military efforts undertaken by Kublai Khan of the Yuan dynasty to conquer the Japanese archipelago after the submission of the Korean kingdom of Goryeo to vassaldom. Ultimately a failure, the invasion attempts are of macro-historical importance because they set a limit on Mongol expansion and rank as nation-defining events in the history of Japan. The invasions are referred to in many works of fiction and are the earliest events for which the word kamikaze is widely used, originating in reference to the two typhoons faced by the Mongol fleets.
 W
WThe Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty, also known as the Mongol–Jin War, was fought between the Mongol Empire and the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in Manchuria and north China. The war, which started in 1211, lasted over 23 years and ended with the complete conquest of the Jin dynasty by the Mongols in 1234.
 W
WQin's wars of unification were a series of military campaigns launched in the late 3rd century BC by the Qin state against the other six major Chinese states — Han, Zhao, Yan, Wei, Chu and Qi. During 247–221 BC, Qin emerged as one of the dominant powers of the very strong and powerful Seven Warring States.
 W
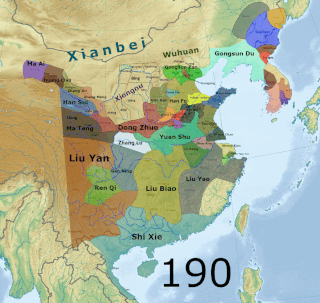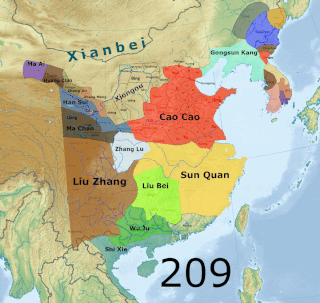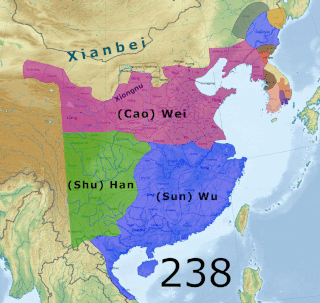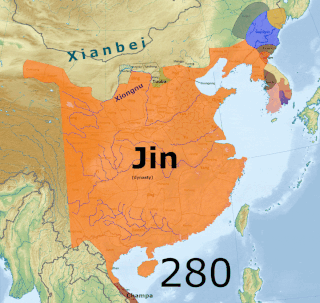
WThe Three Kingdoms from 220–280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the states of Wei, Shu, and Wu. The Three Kingdoms period started with the end of the Han dynasty and was followed by the Jin dynasty. The short-lived Yan kingdom in the Liaodong Peninsula, which lasted from 237 to 238, is sometimes considered as a "4th kingdom".