 W
WA referendum on the policies of Ion Antonescu was held in Romania on 15 November 1941. The referendum, the second that year on Antonescu's policies, were held after the extension of working hours on 2 October had been met with riots. The vote was carried out orally, with a silence taken as a "yes" vote, and was approved with 99.99% in favour and only 68 people voting against.
 W
WThe Anti-Comintern Pact, officially the Agreement against the Communist International, was an anti-Communist pact concluded between Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan on 25 November 1936, and was directed against the Communist International (Comintern). It was signed by German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop and Japanese ambassador to Germany Kintomo Mushakoji. Italy, Spain and other countries joined it until November 1941.
 W
WThe Iași pogrom was a series of pogroms launched by governmental forces under Marshal Ion Antonescu in the Romanian city of Iași against its Jewish community, which lasted from 29 June to 6 July 1941. According to Romanian authorities, over 13,266 people, or one third of the Jewish population, were massacred in the pogrom itself or in its aftermath, and many were deported.
 W
WThe Legionnaires' rebellion and the Bucharest pogrom occurred in Bucharest, Romania, between 21–23 January 1941. As the privileges of the Iron Guard paramilitary organization were being cut off gradually by the Conducător Ion Antonescu, its members, also known as the Legionnaires, revolted. During the rebellion and pogrom the Iron Guard killed 125 Jews, and 30 soldiers died in the confrontation with the rebels. Following this, the Iron Guard movement was banned and 9,000 of its members were imprisoned.
 W
WOperation München was the Romanian codename of a joint German-Romanian offensive during the German invasion of the Soviet Union in World War II, with the primary objective of recapturing Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina and the Hertza region, ceded by Romania to the Soviet Union a year before. The operation concluded successfully after 24 days of fighting. Axis formations involved included the Romanian Third and the Fourth Armies and the German Eleventh Army. The invasion was followed by a genocide against the Jewish population of Bessarabia.
 W
WThe Raid on Constanța was an attack by the Soviet Black Sea Fleet on the Romanian port of Constanța on 26 June 1941, shortly after the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union, and resulted in the only encounter between major warships in the Black Sea during World War II. The attack was intended to be a coordinated effort between the fleet's ships and aircraft to split the attention of the defenders, but the bombers did not attack at the designated times.
 W
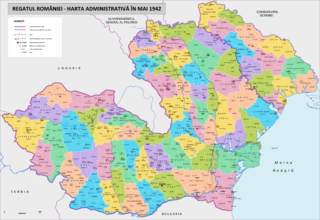
WThe Tighina Agreement was an agreement between Germany and Romania about administration, economy and security issues of the Transnistria Governorate that entered into force on 30 August 1941. It was signed during World War II, while the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union was taking place. The Tiraspol Agreement in which Romania received the region had entered in force shortly before, on 19 August.
 W
WThe Tiraspol Agreement was an agreement between Germany and Romania signed on 19 August 1941 in the city of Tiraspol regarding the Romanian administration of the region of Transnistria, which became the Transnistria Governorate. It fell under the rule of Gheorghe Alexianu, under immediate subordination of Ion Antonescu, the Conducător (leader) of Romania. It was signed during World War II, while the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union was taking place. The Tighina Agreement in which specific issues of the region were discussed entered in force shortly after, on 30 August. The agreement allowed full Romanian control over the territory between the Dniester and Southern Bug rivers, with the exception of the city of Odessa. The latter was ceded to Romania in the Tighina Agreement with some privileges for Germany.