 W
WAnthony or Antony the Great, was a Christian monk from Egypt, revered since his death as a saint. He is distinguished from other saints named Anthony such as Anthony of Padua, by various epithets of his own: Saint Anthony, Anthony of Egypt, Anthony the Abbot, Anthony of the Desert, Anthony the Anchorite, and Anthony of Thebes. For his importance among the Desert Fathers and to all later Christian monasticism, he is also known as the Father of All Monks. His feast day is celebrated on 17 January among the Orthodox and Catholic churches and on Tobi 22 in the Coptic calendar.
 W
WCleopatra the Alchemist was a Greek alchemist, author, and philosopher. She experimented with practical alchemy but is also credited as one of the four female alchemists that could produce the Philosopher's stone. Some writers consider her to be the inventor of the alembic, a distillation apparatus.
 W
WDiophantus of Alexandria was an Alexandrian mathematician, who was the author of a series of books called Arithmetica, many of which are now lost. His texts deal with solving algebraic equations. While reading Claude Gaspard Bachet de Méziriac's edition of Diophantus' Arithmetica, Pierre de Fermat concluded that a certain equation considered by Diophantus had no solutions, and noted in the margin without elaboration that he had found "a truly marvelous proof of this proposition," now referred to as Fermat's Last Theorem. This led to tremendous advances in number theory, and the study of Diophantine equations and of Diophantine approximations remain important areas of mathematical research. Diophantus coined the term παρισότης (parisotes) to refer to an approximate equality. This term was rendered as adaequalitas in Latin, and became the technique of adequality developed by Pierre de Fermat to find maxima for functions and tangent lines to curves. Diophantus was the first Greek mathematician who recognized fractions as numbers; thus he allowed positive rational numbers for the coefficients and solutions. In modern use, Diophantine equations are usually algebraic equations with integer coefficients, for which integer solutions are sought.
 W
WLucius Domitius Domitianus was a Roman usurper against Diocletian, who seized power for a short time in Aegyptus.
 W
WOrigen of Alexandria, also known as Origen Adamantius, was an early Christian scholar, ascetic, and theologian who was born and spent the first half of his career in Alexandria. He was a prolific writer who wrote roughly 2,000 treatises in multiple branches of theology, including textual criticism, biblical exegesis and hermeneutics, homiletics, and spirituality. He was one of the most influential figures in early Christian theology, apologetics, and asceticism. He has been described as "the greatest genius the early church ever produced".
 W
WPlotinus was a major Hellenistic philosopher who lived in Roman Egypt. In his philosophy, described in the Enneads, there are three principles: the One, the Intellect, and the Soul. His teacher was Ammonius Saccas, who was of the Platonic tradition. Historians of the 19th century invented the term Neoplatonism and applied it to Plotinus and his philosophy, which was influential during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Much of the biographical information about Plotinus comes from Porphyry's preface to his edition of Plotinus' Enneads. His metaphysical writings have inspired centuries of Pagan, Jewish, Christian, Gnostic, and Islamic metaphysicians and mystics, including developing precepts that influence mainstream theological concepts within religions, such as his work on duality of the One in two metaphysical states.
 W
WSaint Rais, also known as Iris, Iraida, Irais, Herais or Rhais, is a martyr venerated by the Roman Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches. According to one account, she was the daughter of a Christian priest named Peter living in Alexandria, Roman Province of Egypt. At the age of twelve, she was sent to live in a women's monastery at Tamman. One day in 303 AD, during a time of widespread persecution of Christians during the reign of the Roman Emperor Diocletian, she went to a well to draw water with other nuns. On the way, they saw a ship with a group of nuns, monks, and other Christians in chains, who were being abused by Loukianos and his men. Rais berated the abusers and insisted that they kill her as well if they were killing Christians. They took her into custody. When the ship had reached Antinoöpolis, Rais was one of the first to die. When Loukianos yelled out, "I spit upon the Christian God," Rais objected, stepped up and spat into the tyrant's face. Loukianos then ordered the girl to be tortured and beheaded.
 W
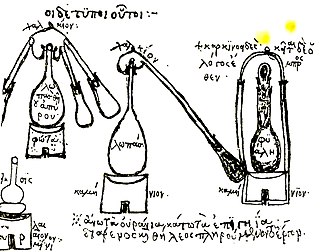
WZosimos of Panopolis was an Egyptian-born Greek alchemist and Gnostic mystic who lived at the end of the 3rd and beginning of the 4th century AD. He was born in Panopolis, and flourished ca. 300. He wrote the oldest known books on alchemy, which he called "Cheirokmeta," using the Greek word for "things made by hand." Pieces of this work survive in the original Greek language and in translations into Syriac or Arabic. He is one of about 40 authors represented in a compendium of alchemical writings that was probably put together in Constantinople in the 7th or 8th century AD, copies of which exist in manuscripts in Venice and Paris. Stephen of Alexandria is another.