 W
WThe 551 Beirut earthquake occurred on 9 July with an estimated magnitude of about 7.5 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a devastating tsunami which affected the coastal towns of Byzantine Phoenicia, causing great destruction and sinking many ships. Overall large numbers of people were reported killed, with one estimate of 30,000 by the Anonymous pilgrim of Piacenza for Beirut alone.
 W
WThe 557 Constantinople earthquake took place on the night of December 14. This earthquake, described in the works of Agathias, John Malalas, and Theophanes the Confessor, caused great damage to Constantinople, then capital of the Byzantine Empire in a region frequently afflicted with earthquakes. More minor quakes had preceded the large event, including two in April and October respectively. The main quake in December was of unparalleled ferocity, and "almost completely razed" the city. It caused damage to the Hagia Sophia which contributed to the collapse of its dome the next year, as well as damaging the walls of Constantinople to the extent that Hun invaders were able to penetrate it with ease the following season.
 W
WThe Anastasian Wall Battle or Battle at the Anastasian Wall, which took place at the end of winter – beginning of the spring in 559, was a crucial combat between Byzantine army commanded by Dux Sergius and target to Constantinople detachment of the Kutrigurs Bulgarian armies commanded by Zabergan in the Kutrigurs large champagne against the Empire in 558-559 AD. The battle took place at the east side of the Anastasian Wall, about 40 km of Constantinople after Kutrigurs pass the Wall in their raid to the Empire capital.
 W
WAt the Battle of Taginae in June/July 552, the forces of the Byzantine Empire under Narses broke the power of the Ostrogoths in Italy, and paved the way for the temporary Byzantine reconquest of the Italian Peninsula.
 W
WThe Second Council of Constantinople is the fifth of the first seven ecumenical councils recognized by both the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. It is also recognized by the Old Catholics and others. Protestant opinions and recognition of it are varied. Some Protestants, such as Calvinists, recognize the first four councils, whereas most Anglo-Catholics and Lutherans accept all seven. Constantinople II was convoked by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I under the presidency of Patriarch Eutychius of Constantinople. It was held from 5 May to 2 June 553. Participants were overwhelmingly Eastern bishops—only sixteen Western bishops were present, including nine from Illyricum and seven from Africa, but none from Italy—out of the 152 total.
 W
WThe Battle of Mons Lactarius took place in 552 or 553 during the Gothic War waged on behalf of Justinian I against the Ostrogoths in Italy.
 W
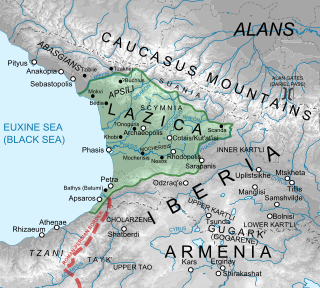
WThe Siege of Phasis took place in 555–556 during the Lazic War between the Byzantine and Sasanian Empires. Expecting an easy victory, the Persians besieged the town of Phasis in Lazica, held by the Byzantines, but were defeated in the ensuing irregular battle. The main source for the siege is the 6th-century historian Agathias.
 W
WThe city of Rome was besieged in AD 549–550 by the Ostrogoths, led by Totila, during a campaign to recapture Italy from the Byzantine Empire. After Totila imposed a blockade, soldiers from the city's garrison opened the gates to him. Many of the male inhabitants were killed in the city or while attempting to flee. The city was afterwards repopulated and rebuilt.