 W
WThe King–Crane Commission, officially called the 1919 Inter-Allied Commission on Mandates in Turkey, was a commission of inquiry concerning the disposition of areas within the former Ottoman Empire.
 W
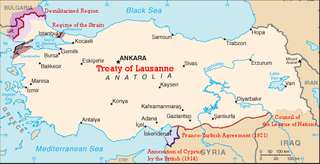
WThe Treaty of Lausanne was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. It officially settled the conflict that had originally existed between the Ottoman Empire and the Allied French Republic, British Empire, Kingdom of Italy, Empire of Japan, Kingdom of Greece, and the Kingdom of Romania since the onset of World War I. The original text of the treaty is in French. It was the result of a second attempt at peace after the failed Treaty of Sèvres. The earlier treaty had been signed in 1920, but later rejected by the Turkish national movement who fought against its terms. The Treaty of Lausanne ended the conflict and defined the borders of the modern Turkish Republic. In the treaty, Turkey gave up all claims to the remainder of the Ottoman Empire and in return the Allies recognized Turkish sovereignty within its new borders. It provided for the Greek-Turkish population exchange and allowed unrestricted civilian passage through the Turkish Straits.
 W
WThe Menemen Massacre occurred on June 16–17, 1919 in the town of Menemen, shortly after the Greek forces landed in nearby Smyrna, as part of the post World War I Greek occupation of Turkey.
 W
WOttoman casualties of World War I covers the civilian and military casualties of the Ottoman Empire. Ottoman Empire's casualties were enormous regardless of the method used in the calculations. The military casualties were published in the book Ordered to Die: A History of the Ottoman Army in the First World War, but the post-war partitioning of the Ottoman Empire made the estimation of the total civilian casualties harder. Also, it was not a novelty in world history to see from time to time people forced to move from one region to another, be it in the form of refugees, of population transfer, or of search for political asylum, but World War I and its aftermath caused migrations at unprecedented large scales, including the Ottoman Empire citizens.
 W
WThe Future of Palestine, also known as the Samuel memorandum, was a memorandum circulated by Herbert Samuel to the British Cabinet in January and March 1915, two months after the British declaration of war on the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WThe partition of the Ottoman Empire was a geopolitical event that occurred after World War I and the occupation of Constantinople by British, French and Italian troops in November 1918. The partitioning was planned in several agreements made by the Allied Powers early in the course of World War I, notably the Sykes-Picot Agreement, after the Ottoman Empire had joined the Ottoman–German Alliance. The huge conglomeration of territories and peoples that formerly comprised the Ottoman Empire was divided into several new states. The Ottoman Empire had been the leading Islamic state in geopolitical, cultural and ideological terms. The partitioning of the Ottoman Empire after the war led to the domination of the Middle East by Western powers such as Britain and France, and saw the creation of the modern Arab world and the Republic of Turkey. Resistance to the influence of these powers came from the Turkish National Movement but did not become widespread in the other post-Ottoman states until the period of rapid decolonisation after World War II.
 W
WThe Treaty of Sèvres was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy and created large occupation zones within the Ottoman Empire. It was one of a series of treaties that the Central Powers signed with the Allied Powers after their defeat in World War I. Hostilities had already ended with the Armistice of Mudros.
 W
WTurkish courts-martial of 1919–20 were courts-martial of the Ottoman Empire that occurred soon after the Armistice of Mudros, in the aftermath of World War I. The leadership of the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) and selected former officials were charged with several charges including subversion of the constitution, wartime profiteering, and the massacres of both Armenians and Greeks. The court reached a verdict which sentenced the organizers of the massacres – Talat, Enver, and Cemal – and others to death.