 W
WAncient Egyptian cattle were of four principal different types: long-horned, short-horned, polled and zebuine.
 W
WThe Eye of Horus, also known as wadjet, wedjat or udjat, is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, royal power, and good health. The Eye of Horus is similar to the Eye of Ra, which belongs to a different god, Ra, but represents many of the same concepts.
 W
WHomosexuality in ancient Egypt is a disputed subject within Egyptology: historians and egyptologists alike debate what kind of view the ancient Egyptians' society fostered about homosexuality. Only a handful of direct hints still survive and many possible indications are only vague and offer plenty of room for speculation.
 W
WThe term máchimoi commonly refers to a broad category of ancient Egyptian low-ranked soldiers which rose during the Late Period of Egypt and, more prominently, during the Ptolemaic dynasty.
 W
WThe medicine of the ancient Egyptians is some of the oldest documented. From the beginnings of the civilization in the late fourth millennium BC until the Persian invasion of 525 BC, Egyptian medical practice went largely unchanged but was highly advanced for its time, including simple non-invasive surgery, setting of bones, dentistry, and an extensive set of pharmacopoeia. Egyptian medical thought influenced later traditions, including the Greeks.
 W
WThe Merimde culture was a Neolithic culture in the West Nile Delta in Lower Egypt, which corresponds in its later phase to the Faiyum A culture and the Badari culture in Predynastic Egypt. It is estimated that the culture evolved between 4800 and 4300 BC. Merimde also refers to the archaeological site of the same name.
 W
WSlavery in ancient Egypt existed at least since the New Kingdom. Discussions of slavery in Pharaonic Egypt are complicated by terminology used by the Egyptians to refer to different classes of servitude over the course of dynastic history. Interpretation of the textual evidence of classes of slaves in ancient Egypt has been difficult to differentiate by word usage alone. There were three types of enslavement in Ancient Egypt: chattel slavery, bonded labor, and forced labor. But even these types of slavery are susceptible to individual interpretation based on evidence and research. Egypt's labor culture is represented by many men and women, and it is difficult to claim their social status into one category.
 W
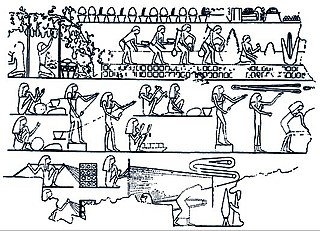
WAncient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam of ships. Egyptian paper, made from papyrus, and pottery were mass-produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean Basin. The wheel was used for a number of purposes, but chariots only came into use after the Second Intermediate Period. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology including ships and lighthouses.