 W
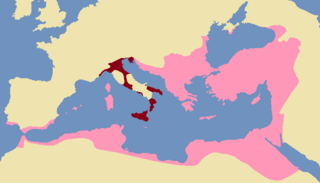
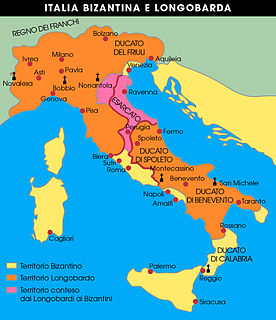
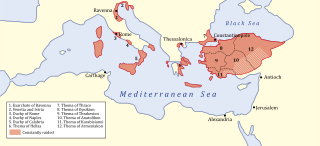
WThe Exarchate of Ravenna or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the Lombards. It was one of two exarchates established following the western reconquests under Emperor Justinian to more effectively administer the territories, along with the Exarchate of Africa.
 W
WThe Byzantine–Lombard wars were a protracted series of conflicts which occurred from AD 568 to 750 between the Byzantine Empire and a Germanic tribe known as the Lombards. The wars began primarily because of the imperialistic inclinations of the Lombard king Alboin, as he sought to take possession of Northern Italy. The conflicts ended in a Byzantine defeat, as the Lombards were able to secure large parts of Northern Italy at first, eventually conquering the Exarchate of Ravenna in 750.
 W
WThe Duchy of Perugia was a duchy in the Italian part of the Byzantine Empire. Its civil and military administration was overseen by a duke (dux) appointed by and under the authority originally of the Praetorian Prefect of Italy (554–584) and later of the Exarch of Ravenna (584–751). Its chief city and namesake was Perugia (Perusia), located at its centre. It was a band of territory connecting the Duchy of the Pentapolis to its northeast with the Duchy of Rome to its southwest, and separating the duchies of Tuscia and Spoleto, both parts of the Lombard Kingdom of Italy. It was of great strategic significance to the Byzantines since it provided communication between Rome, the city of the Popes, and Ravenna, the capital of the Exarchate. Since it cut off the Duke of Spoleto from his nominal overlord, the king ruling from Pavia, it also disturbed the Lombard kingdom, which was a constant thorn in the Byzantines' side. This strategic importance meant that many Lombard and Byzantine armies passed through it.
 W
WThe Duchy of Rome was a state within the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna. Like other Byzantine states in Italy, it was ruled by an imperial functionary with the title dux. The duchy often came into conflict with the Papacy over supremacy within Rome. The duchy was founded by the conquest of Emperor Justinian I in 533 AD. After the founding of the Papal States in 751, the title of Duke of Rome fell into disuse.
 W
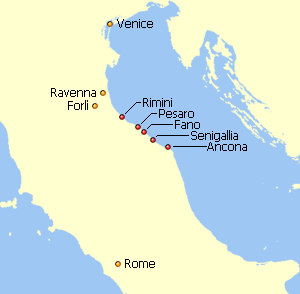
WIn the Byzantine Empire, the Duchy of the Pentapolis was a duchy, a territory ruled by a duke (dux) appointed by and under the authority of the Praetorian Prefect of Italy (554–584) and then the Exarch of Ravenna (584–751). The Pentapolis consisted of the cities of Ancona, Fano, Pesaro, Rimini and Sinigaglia. It lay along the Adriatic coast between the rivers Marecchia and Misco immediately south of the core territory of the exarchate ruled directly by the exarch, east of the Duchy of Perugia, another Byzantine territory, and north of the Duchy of Spoleto, which was part of the Lombard Kingdom of Italy. The duchy probably extended inland as far as the Apennine Mountains, perhaps beyond, and its southernmost town was Humana (Numera) on the northern bank of the Misco. The capital of the Pentapolis was Rimini and the duke was both the civil and military authority in the duchy.
 W
WThe Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic, traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and maritime republic in parts of present-day Italy which existed from 697 AD until 1797 AD. Centered on the lagoon communities of the prosperous city of Venice, it incorporated numerous overseas possessions in modern Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Greece, Albania and Cyprus. The republic grew into a trading power during the Middle Ages and strengthened this position in the Renaissance. Citizens spoke the still-surviving Venetian language, although publishing in (Florentine) Italian became the norm during the Renaissance.
 W
WMaritime Venice or Byzantine Venice refers to a territory of the Byzantine Empire framed in the Exarchate of Italy and corresponding to the coastal belt of ancient Venetia, on the coast of present-day Veneto and Friuli-Venezia Giulia. This is distinct from the hinterland of the Euganean Venice which passed from the end of the sixth century under the control of the Lombards.
 W
WTiberius Petasius was a Byzantine usurper in Italy c.730/731.