 W
WThe Battle of Yinkou was a land battle of the First Sino-Japanese War between the forces of Meiji Japan and Qing China, fought outside the treaty port town of Yingkou, Manchuria. It is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Niuzhuang or Newchwang.
 W
WThe Dungan revolt (1895–96) was a rebellion of various Chinese Muslim ethnic groups in Qinghai and Gansu against the Qing dynasty, that originated because of a violent dispute between two Sufi orders of the same sect. The Wahhabi inspired Yihewani organization then joined in and encouraged the revolt, which was crushed by loyalist Muslims.
 W
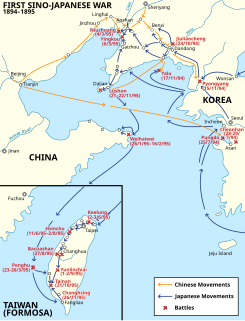
WThe First Sino-Japanese War was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895.
 W
WThe Japanese invasion of Taiwan was a conflict between the Empire of Japan and the armed forces of the short-lived Republic of Formosa following the Qing Dynasty's cession of Taiwan to Japan in April 1895 at the end of the First Sino-Japanese War. The Japanese sought to take control of their new possession, while the Republican forces fought to resist Japanese occupation. The Japanese landed near Keelung on the northern coast of Taiwan on 29 May 1895, and in a five-month campaign swept southwards to Tainan. Although their advance was slowed by guerrilla activity, the Japanese defeated the Formosan forces whenever they attempted to make a stand. The Japanese victory at Baguashan on 27 August, the largest battle ever fought on Taiwanese soil, doomed the Formosan resistance to an early defeat. The fall of Tainan on 21 October ended organised resistance to Japanese occupation, and inaugurated five decades of Japanese rule in Taiwan.
 W
WThe Kucheng massacre was a massacre of Western Christians that took place at Gutian Fujian, China on August 1, 1895. At dawn of that day, a fasting folk religious group attacked British missionaries who were then taking summer holidays at Gutian Huashan, killing eleven people and destroying two houses. The Kucheng Massacre is considered one of the worst attacks against foreigners in China prior to the Boxer Movement in 1899–1901, the only comparable event in China's missionary history being the Tianjin Massacre in 1870.
 W
WThe Pescadores campaign was the last military operation of the First Sino-Japanese War and an essential preliminary to the Japanese conquest of Taiwan.
 W
WThe Treaty of Shimonoseki , also known as Treaty of Bakan in China, was a treaty signed at the Shunpanrō hotel, Shimonoseki, Japan on 17 April 1895, between the Empire of Japan and Qing China, ending the First Sino-Japanese War. The peace conference took place from 20 March to 17 April 1895. This treaty followed and superseded the Sino-Japanese Friendship and Trade Treaty of 1871.
 W
WThe Tripartite Intervention or Triple Intervention was a diplomatic intervention by Russia, Germany, and France on 23 April 1895 over the harsh terms of the Treaty of Shimonoseki imposed by Japan on Qing dynasty China that ended the First Sino-Japanese War. The goal was to stop Japanese expansion in China. The Japanese reaction against the Triple Intervention was one of the causes of the subsequent Russo-Japanese War.
 W
WThe Battle of Weihaiwei (Japanese: Ikaiei-no-tatakai was a battle of the First Sino-Japanese War. It took place between 20 January and 12 February 1895 in Weihai, Shandong Province, China between the forces of the Japan and Qing China. In early January 1895, the Japanese landed forces in eastern Shandong positioning forces behind the Chinese naval base at Weihaiwei.