 W
WAfter the defeat of Germany in World War II, the country was divided between the two global blocs in the East and West, a period known as the division of Germany. Germany was stripped of its war gains and lost territories in the east to Poland and the Soviet Union. At the end of the war, there were some eight million foreign displaced persons in Germany; mainly forced laborers and prisoners; including around 400,000 from the concentration camp system, survivors from a much larger number who had died from starvation, harsh conditions, murder, or being worked to death. Over 10 million German-speaking refugees arrived in Germany from other countries in Central and Eastern Europe. Some 9 million Germans were POWs, many of whom were kept as forced laborers for several years to provide restitution to the countries Germany had devastated in the war, and some industrial equipment was removed as reparations.
 W
WNazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich until 1943 and Greater German Reich in 1943–45, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country which they transformed into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazis' conceit that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe.
 W
WOperation Bolívar was the codename for the German espionage in Latin America during World War II. It was under the operational control of Department VID 4 of Germany's Security Service, and was primarily concerned with the collection and transmission of clandestine information from Latin America to Europe. Overall, the Germans were successful in establishing a secret radio communications network from their control station in Argentina, as well as a courier system involving the use of Spanish merchant vessels for the shipment of paper-form intelligence.
 W
WThe evacuation of children in Germany during the World War II was designed to save children in Nazi Germany from the risks associated with the aerial bombing of cities, by moving them to areas thought to be less at risk. The German term used for this was Kinderlandverschickung (KLV), a short form of Verschickung der Kinder auf das Land.
 W
WAmerican food policy in occupied Germany refers to the food supply policies enacted by the U.S., and to some extent its dependent Allies, in the western occupation zones of Germany in the first two years of the ten-year postwar occupation of Western Germany following World War II.
 W
WIn the years following World War II, large numbers of German civilians and captured soldiers were forced into labor by the Allied forces. The topic of using Germans as forced labor for reparations was first broached at the Tehran conference in 1943, where Soviet premier Joseph Stalin demanded 4,000,000 German workers.
 W
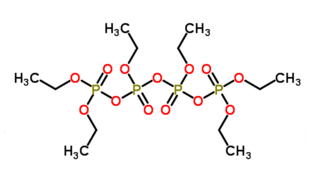
WHexaethyl tetraphosphate (also known as HET) is the organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula [(C2H5O)3P2O3]2O. The compound has not been isolated in pure form but appears to be a colorless liquid at room temperature. Commercial samples appear brown due to impurities. It is a constituent of the insecticide Bladan. In the 1940s, it was about as significant an insecticide as DDT and was referred to as "another of DDT's rivals for fame" in a 1948 book.
 W
WThe Monnet plan was proposed by French civil servant Jean Monnet after the end of World War II. It was a reconstruction plan for France that proposed giving France control over the German coal and steel areas of the Ruhr area and Saar and using these resources to bring France to 150% of pre-war industrial production. The plan was adopted by Charles de Gaulle in early 1946. The plan would permanently limit German economic capacity, and greatly increase French power.
 W
WThe Morgenthau Plan was a proposal to eliminate Germany's ability to wage war following World War II by eliminating its arms industry and removing or destroying other key industries basic to military strength. This included the removal or destruction of all industrial plants and equipment in the Ruhr. It was first proposed by United States Secretary of the Treasury Henry Morgenthau Jr. in a 1944 memorandum entitled Suggested Post-Surrender Program for Germany.