 W
WAgathodaemon was an alchemist in late Roman Egypt, known only from fragments quoted in medieval alchemical treatises, chiefly the Anepigraphos, which refer to works of his believed to be from the 3rd century. He is primarily remembered for his various descriptions of elements and minerals, most particularly his descriptions of a method of producing silver, and of a substance he had created, which he called a 'fiery poison', and which, judging by his account, was arsenic trioxide, a highly toxic amphoteric oxide.
 W
WAmmon, Amun, Ammonas, Amoun (Ἀμοῦν), or Ammonius the Hermit was a 4th-century Christian ascetic and the founder of one of the most celebrated monastic communities in Egypt. He was subsequently declared a saint. He was one of the most venerated ascetics of the Nitrian Desert, and Saint Athanasius mentions him in his life of Saint Anthony. His name is the same as that of the ancient Egyptian god Amun.
 W
WAnthony or Antony the Great, was a Christian monk from Egypt, revered since his death as a saint. He is distinguished from other saints named Anthony such as Anthony of Padua, by various epithets of his own: Saint Anthony, Anthony of Egypt, Anthony the Abbot, Anthony of the Desert, Anthony the Anchorite, and Anthony of Thebes. For his importance among the Desert Fathers and to all later Christian monasticism, he is also known as the Father of All Monks. His feast day is celebrated on 17 January among the Orthodox and Catholic churches and on Tobi 22 in the Coptic calendar.
 W
WAthanasius of Alexandria, also called Athanasius the Great, Athanasius the Confessor or, primarily in the Coptic Orthodox Church, Athanasius the Apostolic, was the 20th bishop of Alexandria. His intermittent episcopacy spanned 45 years, of which over 17 encompassed five exiles, when he was replaced on the order of four different Roman emperors. Athanasius was a Christian theologian, a Church Father, the chief defender of Trinitarianism against Arianism, and a noted Egyptian leader of the fourth century.
 W
WCleopatra the Alchemist was a Greek alchemist, author, and philosopher. She experimented with practical alchemy but is also credited as one of the four female alchemists that could produce the Philosopher's stone. Some writers consider her to be the inventor of the alembic, a distillation apparatus.
 W
WPatapios of Thebes is the patron saint of dropsy. Saint Patapios’ memory is celebrated on 8 December and also at the Tuesday 2 days after the Sunday of Easter. His relic is kept at the female monastery of Saint Patapios at Loutraki, a spa town near Athens, Greece.
 W
WSaint Philemon was an actor at Antinoöpolis, Egypt, who was converted by saint Apollonius. They were martyred together under the persecutions of Diocletian.
 W
WSaint Rais, also known as Iris, Iraida, Irais, Herais or Rhais, is a martyr venerated by the Roman Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches. According to one account, she was the daughter of a Christian priest named Peter living in Alexandria, Roman Province of Egypt. At the age of twelve, she was sent to live in a women's monastery at Tamman. One day in 303 AD, during a time of widespread persecution of Christians during the reign of the Roman Emperor Diocletian, she went to a well to draw water with other nuns. On the way, they saw a ship with a group of nuns, monks, and other Christians in chains, who were being abused by Loukianos and his men. Rais berated the abusers and insisted that they kill her as well if they were killing Christians. They took her into custody. When the ship had reached Antinoöpolis, Rais was one of the first to die. When Loukianos yelled out, "I spit upon the Christian God," Rais objected, stepped up and spat into the tyrant's face. Loukianos then ordered the girl to be tortured and beheaded.
 W
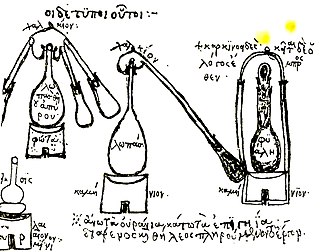
WZosimos of Panopolis was an Egyptian-born Greek alchemist and Gnostic mystic who lived at the end of the 3rd and beginning of the 4th century AD. He was born in Panopolis, and flourished ca. 300. He wrote the oldest known books on alchemy, which he called "Cheirokmeta," using the Greek word for "things made by hand." Pieces of this work survive in the original Greek language and in translations into Syriac or Arabic. He is one of about 40 authors represented in a compendium of alchemical writings that was probably put together in Constantinople in the 7th or 8th century AD, copies of which exist in manuscripts in Venice and Paris. Stephen of Alexandria is another.