 W
WThe Sultanate of Bengal, was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. Its imperial capital was one of the world's largest cities. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states, including Odisha in the southwest, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. In the early 16th-century, the Bengal Sultanate reached the peak of its territorial growth with control over Kamrup and Kamata in the northeast and Jaunpur and Bihar in the west. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation and one of Asia's strongest states. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Suri Empire, followed by Mughal conquest and disintegration into petty kingdoms.
 W
WThe Adina Mosque is a historical largest mosque in India located in Malda District, West Bengal, India.
 W
WUlugh Khan Jahan Ali, was a Muslim saint and the Khan-i-Azam of Khalifatabad. It is believed that he built the great Mosque City of Bagerhat, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WGauḍa is a historic city of Bengal in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, and one of the most prominent capitals in classical and medieval Indian subcontinent. Located on the border between India and Bangladesh, with most of its ruins on the Indian side and a few structures on the Bangladeshi side, it was once one of the most populous cities in the world. The ruins of this former city now straddle the international border and are divided between the Malda district of West Bengal and Chapai Nawabganj District of Rajshahi Division. The Kotwali Gate, formerly part of the citadel, now marks the border checkpoint between the two countries.
 W
WGhiyathiyyah Madrasah, later known as Bangaliyyah Madrasah, refers to the madrasas constructed in Hejaz during the 14th-15th century by the Sultans of Bengal. Part of a history of interactions between the Bengal Sultanate and Sharifate of Mecca, an account of these can be found in the Tarikh Makkah.
 W
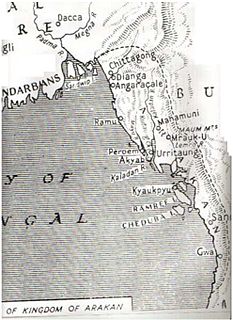
WArakan is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessible only by sea. The region now forms the Rakhine State in Myanmar.
 W
WThe Mosque City of Bagerhat is a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Bagerhat District, Bangladesh. It contains several mosques built during the Bengal Sultanate in the 15th-century, of which the Sixty Dome Mosque is the largest. Other mosques include the Singar Mosque, the Nine Dome Mosque, the Tomb of Khan Jahan, the Bibi Begni Mosque and the Ronvijoypur Mosque. The mosques were built during the governorship of Ulugh Khan Jahan, a Turkic military officer appointed as governor in the Sundarbans by Sultan Mahmud Shah of Bengal.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Mrauk-U was an independent coastal kingdom of Arakan which existed for over 350 years. It was based in the city of Mrauk-U, near the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal. The kingdom from 1429 to 1785 ruled over what is now Rakhine State, Myanmar and Chittagong Division, Bangladesh. From 1429 to 1531 it was a protectorate of the Bengal Sultanate at different time periods. After gaining independence from Bengal, it prospered with help from the Portuguese settlement in Chittagong. In 1666, it lost control of Chittagong after a war with the Mughal Empire. Its reign continued until the 18th century, when it fell to the invasion of the Burmese Empire.
 W
WPandua is a historic city of the Indian subcontinent. It was the first capital city of the Bengal Sultanate for 114 years between the mid 14th and mid 15th centuries. It continued to be a "mint town" until the 16th-century. The capital later shifted to Gaur. Pandua was described by travelers as a cosmopolitan administrative, commercial and military base, with a population of natives, royalty, aristocrats and foreigners from across Eurasia.