 W
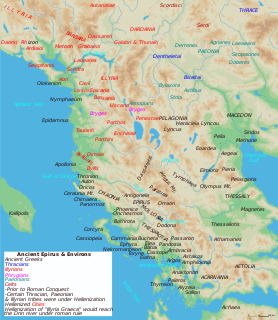
WAthamanians or Athamanes were an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited south-eastern Epirus and west Thessaly. Although regarded as "barbarians" by Strabo and Hecataeus of Miletus, the Athamanians self-identified as Greeks. The existence of myths about Athamas and Ino in Achaean Phthiotis suggests that the Athamanians were settled there before 1600 BC. They were an independent semi-barbarian tribe and were occasionally allies of the Aetolians. Amynander and Theodorus of Athamania are reported kings of the Athamanians.
 W
WEpirus was an ancient Greek state, located in the geographical region of Epirus in the western Balkans. The homeland of the ancient Epirotes was bordered by the Aetolian League to the south, Thessaly and Macedonia to the east, and Illyrian tribes to the north. For a brief period, the Epirote king Pyrrhus managed to make Epirus a powerful state in the Greek world, comparable to the likes of Macedon and Rome. His armies marched against Rome during an unsuccessful campaign in Italy.
 W
WLynkestis or Lyncus (Λύγκος) was a region, and in earlier times a Greek kingdom of Upper Macedonia, located on the southern borders of Illyria and Paeonia. The inhabitants of Lynkestis were known as Lyncestae or Lynkestai (Λυγκῆσται), a northwestern Greek tribe that belonged to the Molossian tribal state, or koinon, of Epirus. The main city was Heraclea Lyncestis.
 W
WMacedonia, also called Macedon, was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.
 W
WMacedonia, also called Macedon, was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.
 W
WThe Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, flourishing from c. 3000 BC to c. 1450 BC until a late period of decline, finally ending around 1100 BC. It represents the first advanced civilization in Europe, leaving behind massive building complexes, tools, artwork, writing systems, and a massive network of trade. The civilization was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. The name "Minoan" derives from the mythical King Minos and was coined by Evans, who identified the site at Knossos with the labyrinth and the Minotaur. The Minoan civilization has been described as the earliest of its kind in Europe, and historian Will Durant called the Minoans "the first link in the European chain".
 W
WMycenaean Greece was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1600–1100 BC. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system. The most prominent site was Mycenae, in the Argolid, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, Athens in Central Greece and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean and Mycenaean-influenced settlements also appeared in Epirus, Macedonia, on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the coast of Asia Minor, the Levant, Cyprus and Italy.
 W
WOrestis was a region of Upper Macedonia, corresponding roughly to the modern Kastoria regional unit located in West Macedonia, Greece. Its inhabitants were the Orestae, an ancient Greek tribe that was part of the Molossian tribal state or koinon.
 W
WThe ten city-kingdoms of ancient Cyprus were the Greek, Graeco-Phoenician or Graeco-Eteocypriot, states listed in an inscription of the Assyrian king Esarhaddon in 673-672 BC:Paphos, Πάφος (Greek) Salamis, Σαλαμίς (Greek) Soloi, Σόλοι (Greek) Kourion, Κούριον (Greek) Chytroi, Χῦτροι (Greek) Kition, Κίτιον (Graeco-Phoenician) Amathus, Ἀμαθούς (Graeco-Eteocypriot) Idalion, Ἰδάλιον (Greek) Ledrai, Λῆδραι (Greek) Tamassos, Ταμασσός (Greek)