 W
WThe Battle of the Natividad took place on November 16, 1846, in the Salinas Valley, in present-day Monterey County, California, United States, during the California Campaign of the Mexican–American War, between United States organized California militia and loyalist Mexican militia.
 W
WThe Battle of Olómpali was fought on June 24, 1846, in present-day Marin County, California. It was the only battle of the Bear Flag Revolt. The site is now a part of the Olompali State Historic Park.
 W
WThe Battle of Palo Alto was the first major battle of the Mexican–American War and was fought on May 8, 1846, on disputed ground five miles (8 km) from the modern-day city of Brownsville, Texas. A force of some 3,700 Mexican troops – most of the Army of The North – led by General Mariano Arista engaged a force of approximately 2,300 United States troops – the Army of Occupation led by General Zachary Taylor.
 W
WThe Capture of Tucson was an uncontested United States entry into the Mexican city of Tucson, Sonora, now the present day Tucson, Arizona. The would-be combatants were provisional Mexican Army troops and the American Army's "Mormon Battalion". Tucson temporarily 'fell' in December 1846 without resistance but was immediately reoccupied two days later by the Mexican forces once the US troops moved on.
 W
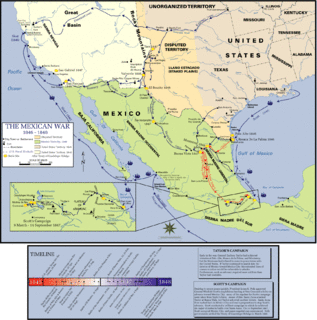
WThe California Campaign (1846–1847), colloquially the Conquest of California or Conquest of Alta California by the United States, was an early military campaign of the Mexican–American War that took place in the western part of Mexico's Alta California Department, in the present-day state of California. The California Campaign was marked by a series of small battles throughout 1846 and early 1847.
 W
WThe Battle of Dominguez Rancho or The Battle of the Old Woman's Gun or The Battle of Dominguez Hills was a military engagement of the Mexican–American War. The skirmish took place within Manuel Dominguez's 75,000-acre (300 km2) Rancho San Pedro.
 W
WThe Battle of Monterey, at Monterey, California, occurred on 7 July 1846, during the Mexican–American War. The United States captured the town unopposed.
 W
WThe Pacific Coast Campaign refers to United States naval operations against targets along Mexico's Pacific Coast during the Mexican–American War. It excludes engagements of the California Campaign in areas of The Californias north of the Baja California Peninsula. The objective of the campaign was to secure the Baja Peninsula of Mexico, and to blockade/capture west-coast ports of Mexico—especially Mazatlan, a major port-of-entry for imported supplies. The resistance of Mexican forces to the north in the Los Angeles area and the lack of ships, soldiers and logistical support prevented an early occupation of the peninsula and the west-coast Mexican seaports. The U.S. Navy attempted blockades of the ports three times before being able to successfully blockade and/or occupy them.
 W
WThe Battle of Resaca de la Palma was one of the early engagements of the Mexican–American War, where the United States Army under General Zachary Taylor engaged the retreating forces of the Mexican Ejército del Norte under General Mariano Arista on May 9, 1846. The United States emerged victorious and forced the Mexicans out of Texas.
 W
WThe Battle of San Pasqual, also spelled San Pascual, was a military encounter that occurred during the Mexican–American War in what is now the San Pasqual Valley community of the city of San Diego, California. The series of military skirmishes ended with both sides claiming victory, and the victor of the battle is still debated. On December 6 and December 7, 1846, General Stephen W. Kearny's US Army of the West, along with a small detachment of the California Battalion led by a Marine Lieutenant, engaged a small contingent of Californios and their Presidial Lancers Los Galgos, led by Major Andrés Pico. After U.S. reinforcements arrived, Kearny's troops were able to reach San Diego.
 W
WThe Siege of Los Angeles was a military response by armed Mexican civilians to the occupation, which had begun August 13, 1846, by the United States Marines of the Pueblo de Los Angeles during the Mexican–American War. It is also known as the Battle of Los Angeles.
 W
WThe Texas Campaign was the first front in the Mexican–American War, fought between the United States and Mexico. The front started with a Mexican assault near Brownsville. US forces were forced to surrender after hours of resisting, which lead President James K. Polk to declare war on Mexico. After the United States defeated a larger Mexican Army at Palo Alto and Resaca de la Palma, Mexican Forces led by Mariano Arista retreated out of Texas.