 W
WThe May 1958 crisis was a political crisis in France during the turmoil of the Algerian War of Independence (1954–62) which led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic and its replacement by the Fifth Republic led by Charles de Gaulle who returned to power after a twelve-year absence. It started as a political uprising in Algiers on 13 May 1958 and then became a military coup d'état led by a coalition headed by Algiers deputy and reserve airborne officer Pierre Lagaillarde, French Generals Raoul Salan, Edmond Jouhaud, Jean Gracieux, and Jacques Massu, and by Admiral Philippe Auboyneau, commander of the Mediterranean fleet. The coup was supported by former Algerian Governor General Jacques Soustelle and his activist allies.
 W
WThe 14 July Revolution, also known as the 1958 Iraqi coup d'état, took place on 14 July 1958 in Iraq, and resulted in the overthrow of the Hashemite monarchy in Iraq that had been established by King Faisal I in 1921 under the auspices of the British. King Faisal II, Prince 'Abd al-Ilah, and Prime Minister Nuri al-Said were killed during the uprising.
 W
WThe 1958 Lebanon crisis was a Lebanese political crisis caused by political and religious tensions in the country that included a United States military intervention. The intervention lasted for around three months until President Camille Chamoun, who had requested the assistance, completed his term as president of Lebanon. American and Lebanese government forces successfully occupied the Port of Beirut and Beirut International Airport. With the crisis over, the United States withdrew.
 W
WThe 1958 Pakistani coup d'état refers to the events between October 7, when the President of Pakistan Iskander Mirza abrogated the Constitution of Pakistan and declared martial law, and October 27, when Mirza himself was deposed by Gen. Ayub Khan, the Commander-in-Chief of the Pakistan Army. There were a number of Prime Ministers between 1956 and 1958 and it reached a stage when General Ayub Khan felt the army should take control to restore stability. East Pakistan’s politicians wanted more say in the running of the central government which increased tension. Iskander Mirza had lost the support of many of the leading politicians and was alarmed at a plan by Suhrawardy to unite the political leadership of Bengal and Punjab against him. Therefore he turned to Ayub Khan and the military for help.
 W
WThe Battle of Bab El Bekkouche during the Algerian War took place on 28 May 1958 in the region of Ouarsenis.
 W
WThe Battle of La Plata (11-21 July 1958) was part of Operation Verano, the summer offensive of 1958 launched by the Batista government during the Cuban Revolution. The battle resulted from a complex plan created by Cuban General Cantillo to directly attack Castro's mountain base in the Sierra Maestra. The battle ended with the humiliating surrender of the assault battalion and the loss of some 500 Cuban army soldiers.
 W
WThe Battle of Las Mercedes was the last battle which occurred during the course of Operation Verano, the summer offensive of 1958 launched by the Batista Government during the Cuban Revolution.
 W
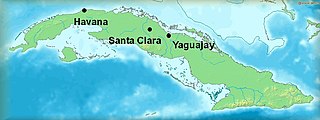
WThe Battle of Santa Clara was a series of events in late December 1958 that led to the capture of the Cuban city of Santa Clara by revolutionaries under the command of Che Guevara. The battle was a decisive victory for the rebels fighting against the regime of General Fulgencio Batista: within 12 hours of the city's capture, Batista fled Cuba and Fidel Castro's forces claimed overall victory. It features prominently on the back of the three convertible peso bill.
 W
WThe Battle of Yaguajay [(ɟ)ʝaɣwaˈxaj] was a decisive victory for the Cuban Revolutionaries over the soldiers of the Batista government near the city of Santa Clara in Cuba during the Cuban Revolution.
 W
WThe Ifni War, sometimes called the Forgotten War in Spain, was a series of armed incursions into Spanish West Africa by Moroccan insurgents that began in October 1957 and culminated with the abortive siege of Sidi Ifni.
 W
WOn 28–29 July 1958, Alix "Sonson" Pasquet, accompanied by two fellow Haitian military officers and five American soldiers of fortune, attempted to overthrow Haitian President François Duvalier by seizing an army barracks in Port-au-Prince and rallying like-minded troops for an attack on the Presidential palace. Hoped-for support failed to materialize and all eight of the insurgents were killed by troops loyal to Duvalier.
 W
WThe Kuomintang Islamic insurgency refers to a continuation of the Chinese Civil War by Chinese Muslim nationalist Kuomintang Republic of China Army forces in Northwest China, in the provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang, and another insurgency in Yunnan.
 W
WThe Mexico–Guatemala conflict was an armed conflict between the Mexico and Guatemala, in which Mexican civilian fishing boats were fired upon by the Guatemalan Air Force. Hostilities were set in motion by the installation of Miguel Ydígoras as President of Guatemala on March 2, 1958.
 W
WThe Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, also called the 1958 Taiwan Strait Crisis, was a conflict that took place between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC). In this conflict, the PRC shelled the islands of Kinmen (Quemoy) and the Matsu Islands along the east coast of mainland China to "liberate" Taiwan from the Chinese Nationalist Party, also known as the Kuomintang (KMT); and to probe the extent of the United States defense of Taiwan's territory. A naval battle also took place around Dongding Island when the ROC Navy repelled an attempted amphibious landing by the PRC Navy.
 W
WThe Snipe incident was a military incident that took place between Chile and Argentina during 1958 as a result of a disputed border line in the Beagle Channel.
 W
WIn 1958, the upswing in violence against the government of South Vietnam continued, much of which was committed by the communist-dominated insurgents now called the Viet Cong. In South Vietnam, President Ngo Dinh Diem appeared to be firmly in power, although many American officials expressed concern about the repressive nature of his regime. The United States continued to finance most of the budget of the government of South Vietnam. North Vietnam continued to campaign for reunification with the South while focusing on its internal economic development, but pressure from hard-pressed communists in the South was forcing the North to contemplate a more active military role in overthrowing the Diem government.