 W
WThe Uprising of Peter Delyan, which took place in 1040–1041, was a major Bulgarian rebellion against the Byzantine Empire in the Theme of Bulgaria. It was the largest and best-organised attempt to restore the former Bulgarian Empire until the rebellion of Ivan Asen I and Petar IV in 1185.
 W
WThe Chiprovtsi uprising was an uprising against Ottoman rule organized in northwestern Bulgaria by Roman Catholic Bulgarians, but also involving many Eastern Orthodox Christians. It broke out after the capture of Belgrade by Austria on 6 September 1688 and ended unsuccessfully, with the centre of insurrectionary activity, Chiprovtsi, being completely destroyed by Ottoman forces.
 W
WThe First Tarnovo uprising was a Bulgarian uprising against the Ottoman rule based in the former Bulgarian capital, Tarnovo, that broke out in 1598 and was severely crushed by the Ottoman authorities.
 W
WThe Gorna Dzhumaya Uprising was an anti-Ottoman rebellion that broke out and spread throughout the Pirin region of Ottoman Macedonia in 1902. The uprising broke out on September 23, along the middle reaches of the Struma River in modern-day Bulgaria. It was poorly organized, premature and had a small scope. The uprising was held under the leadership of the Supreme Macedonian-Adrianople Committee (SMAC). The organizers were General Ivan Tsonchev and Stoyan Mihaylovski. The Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) disagreed with the SMAC plan and refused to take part in the fighting. The Bulgarian government also did not support the actions of the insurgents, because it was under strong international pressure. The Uprising was suppressed and ca. 2,000 refugees escaped to Bulgaria. With the appearance of the first refugees in many cities of the country, rallies were convened, which appealed to Europe and the Bulgarian government for intervention. The atrocities committed against the local population in the region provoked a reaction among the European public and it pressed the Sublime Porte for the adoption of some reforms. However, these reforms were not actually implemented.
 W
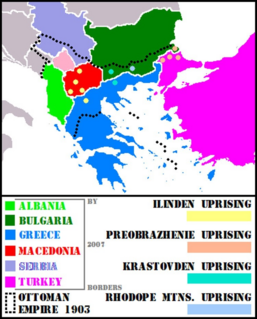
WThe Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising, or simply the Ilinden Uprising of August 1903, was an organized revolt against the Ottoman Empire, which was prepared and carried out by the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization. The name of the uprising refers to Ilinden, a name for Elijah's day, and to Preobrazhenie which means Transfiguration. The revolt lasted from the beginning of August to the middle of October and covered a vast territory from the eastern Black Sea coast to the shores of Lake Ohrid.
 W
WThe Uprising of Ivaylo was a rebellion of the Bulgarian peasantry against the incompetent rule of Emperor Constantine Tikh and the Bulgarian nobility. The revolt was fuelled mainly by the failure of the central authorities to confront the Mongol menace in north-eastern Bulgaria. The Mongols had looted and ravaged the Bulgarian population for decades, especially in the region of Dobrudzha. The weakness of the state institutions was a result of the accelerating process of feudalisation of the Second Bulgarian Empire.
 W
WThe Kresna–Razlog Uprising named by the insurgents the Macedonian Uprising, was a Bulgarian uprising against the Ottoman rule, predominantly in the areas of Kresna and Razlog in late 1878 and early 1879. It broke out following the protests and spontaneous opposition to the decisions of the Congress of Berlin, which, instead of ceding the Bulgarian-populated parts of Macedonia to the newly reestablished Bulgarian suzerain state per the Treaty of San Stefano, returned them to Ottoman control. It was prepared by the "Edinstvo" Committee.
 W
WThe Kruševo Republic was a short-lived political entity proclaimed in 1903 by rebels from the Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) in Kruševo during the anti-Ottoman Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising. According to subsequent Bulgarian and Macedonian narratives, it was one of the first modern-day republics in the Balkans.
 W
WPetrova Niva is a historic area in the Strandzha mountains of southeastern Bulgaria where, between 11 and 13 July 1903, a group of Bulgarian Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO) delegates announced the outbreak of an anti-Ottoman uprising aimed at liberating southern Thrace from Ottoman rule and proclaimed the Strandzha Republic.
 W
WThe Razlovtsi insurrection was a rebellion in the areas of Maleshevo and Piyanets in Ottoman Macedonia during 1876.
 W
WThe Second Tarnovo uprising, according to a unique Russian source published in 1847, is thought to be a Bulgarian uprising against Ottoman rule based in the former Bulgarian capital, Tarnovo, that broke out in 1686 and was severely crushed by the Ottoman authorities.
 W
WThe September Uprising was an armed insurgency staged in September 1923 by the Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP) under Comintern pressure and attempted to overthrow Alexander Tsankov's new government of Bulgaria that had come to power with the coup d'état of 9 June. Besides its communist base, the uprising was also supported by agrarians and anarchists. The uprising's goal was the "establishment of a government of workers and peasants" in Bulgaria.
 W
WThe Supreme Macedonian Committee chetas' action in 1895 was an armed expedition of several chetas from Bulgaria into the Ottoman-ruled Macedonia in the period of June-August 1895. Its aim was to provoke a general uprising in the area and to draw the attention of the Great Powers to non-compliance of the Treaty of Berlin (1878), and the provided reforms in European Turkey. The Supreme Macedonian Committee invited about 40 active and reserve officers from the Bulgarian army, as well as some old vojvodes from Macedonia. Among them were Boris Sarafov, Toma Davidov, Mihail Apostolov, Yordan Venedikov, etc. The number of the rebels was about 800 people, divided into four detachments. After invading Macedonia, the separate detachments headed to Strumica, Melnik and Dospat, respectively, but generally did not achieve much success. The failure of the action caused disagreements in the organization. The Ottoman government took advantage of the attack of the Pomaks populated Dospat and spread information about the atrocities in the European press. The Great Powers did not react as expected to the raising of the Macedonian question and instead of putting pressure on the Ottoman Empire, they put pressure on the Bulgarian government.
 W
WTikvesh uprising was an uprising in the Tikveš region of Macedonia in late June 1913.
 W
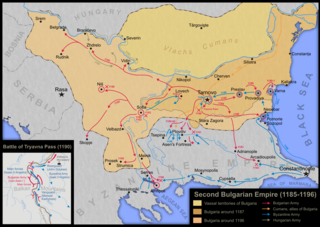
WThe Uprising of Asen and Peter was a revolt of Bulgarians and Vlachs living in Moesia and the Balkan Mountains, then the theme of Paristrion of the Byzantine Empire, caused by a tax increase. It began on 26 October 1185, the feast day of St. Demetrius of Thessaloniki, and ended with the restoration of Bulgaria with the creation of the Second Bulgarian Empire, ruled by the Asen dynasty.
 W
WThe Uprising of Georgi Voyteh was a Bulgarian uprising against the Byzantine theme of Bulgaria in 1072. It was the second major attempt to restore the Bulgarian Empire after the Uprising of Peter Delyan in 1040-1041.
 W
WThe Uprising of Konstantin and Fruzhin was the earliest Bulgarian uprising against Ottoman rule. It was organized in the early 15th century by two Bulgarian nobles and was supported by a Christian coalition, but failed to liberate Bulgaria.