 W
WThe Ballahoo class was a Royal Navy class of eighteen 4-gun schooners built under contract in Bermuda during the Napoleonic War. The class was an attempt by the Admiralty to harness the expertise of Bermudian shipbuilders who were renowned for their fast-sailing craft. The Admiralty ordered twelve vessels on 23 June 1804, and a further six on 11 December 1805.
 W
WThe Ayesha was a wooden topsail schooner, which was commandeered by a landing party of the German light cruiser SMS Emden. This landing party was able to escape being taken as prisoners of war, in November 1914, after their ship was destroyed in a battle with the Australian light cruiser HMAS Sydney.
 W
WHMS Beatrice was a 98-ton displacement, schooner launched in 1860 at Newhaven.
 W
WHMS Congo was the first steam-powered warship built for the Royal Navy. She was classified as a steam sloop and was built in 1816 at Deptford Dockyard specifically for an exploration of the Congo River. Trials with her engine proved disappointing, and it was removed before she embarked on her first voyage.
 W
WThe Cuckoo class was a class of twelve 4-gun schooners of the Royal Navy, built by contract in English shipyards during the Napoleonic War. They followed the design of the Bermuda-designed and built Ballahoo-class schooners, and more particularly, that of Haddock. The Admiralty ordered all twelve vessels on 11 December 1805. A number of different builders in different yards built them, with all launching in 1806.
 W
WHMS Dolphin was the 12-gun American privateer schooner Dolphin that Admiral John Borlase Warren's squadron captured on 13 April 1813 and that the Royal Navy took into service. As HMS Dolphin she participated in boat actions on 29 April and 5 May 1813 for which the Admiralty issued a clasp for the Naval General Service Medal. Her ultimate fate is currently undocumented.
 W
WHMS Dominica was the French letter of marque schooner Duc de Wagram, which the British captured in 1809 in the Leeward Islands and took into the Royal Navy in 1810. The American privateer Decatur captured her in 1813 in a notable single-ship action. However, Majestic recaptured her in 1814. She was wrecked in 1815
 W
WHMS Eling was one of six vessels built to an experimental design by Sir Samuel Bentham. It is not known when she was launched, though it may have been in 1796. After the Admiralty purchased her in 1798 for the Royal Navy she took part in several campaigns and captured a privateer and other vessels. She was broken up in 1814 after several years in ordinary.
 W
WThe Gaspee Affair was a significant event in the lead-up to the American Revolution. HMS Gaspee was a British customs schooner that had been enforcing the Navigation Acts in and around Newport, Rhode Island in 1772. It ran aground in shallow water while chasing the packet ship Hannah on June 9 near Gaspee Point in Warwick, Rhode Island. A group of men led by Abraham Whipple and John Brown attacked, boarded, and torched the ship.
 W
WGovernor Simcoe was a merchant schooner launched in 1793. The Provincial Marine acquired her in 1813 and renamed her after the British naval officer Sir Sidney Smith. She saw service on Lake Ontario during the War of 1812. The Royal Navy acquired her in 1814 and renamed her HMS Magnet. A few months later her captain had to blow her up to prevent the Americans from capturing the vessel.
 W
WHMS Halifax was a schooner built for merchant service at Halifax, Nova Scotia in 1765 that the British Royal Navy purchased in 1768 for coastal patrol in North America in the years just prior to the American Revolution. She is one of the best documented schooners from early North America.
 W
WHMS Harrier was a schooner of the Royal Navy. Built at Cowes, Isle of Wight and launched in 1872. She was bought by the Royal Navy for £2874 and named HMS Harrier.
 W
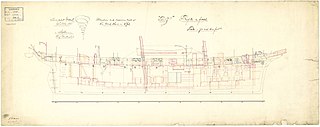
WThe French schooner Impériale was a 3-gun mercantile schooner-aviso of the French Navy commissioned at Guadeloupe on 23 September 1805. The Royal Navy captured her on 24 May 1806 and named her HMS Vigilant. The Navy renamed her HMS Subtle on 20 November 1806. She wrecked at Bermuda on 20 October 1807.
 W
WHMS Lark was a schooner of the Royal Navy, built by Westacott’s, Barnstaple and launched on 4 December 1880.
 W
WHMS Monkey was a schooner of the British Royal Navy assigned to the West Indies squadron, launched 1826 at Jamaica. She made three notable captures of slavers, one involving a single-ship action against a slaver much larger and more heavily armed than herself. She was wrecked in 1831 near Tampico.
 W
WHMS Mosquidobit was the Chesapeake-built six-gun schooner Lynx that the British Royal Navy captured and took into service in 1813. She was sold into commercial service in 1820 and nothing is known of her subsequent fate.
 W
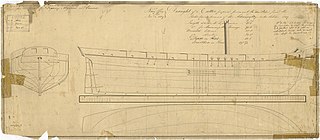
WHMS Pickle was a topsail schooner of the Royal Navy. She was originally a civilian vessel named Sting, of six guns, that Lord Hugh Seymour purchased to use as a tender on the Jamaica station. Pickle was at the Battle of Trafalgar, and though she was too small to take part in the fighting, Pickle was the first ship to bring the news of Nelson's victory to Great Britain. She also participated in a notable single-ship action when she captured the French privateer Favorite in 1807. Pickle was wrecked in 1808, but without loss of life.
 W
WHMS Pigmy was a Pigmy-class 10-gun schooner of the Royal Navy. She was launched in February 1810. She served on the North Sea and North American stations before she was sold in 1823.
 W
WHMS Redbridge was one of four schooner-rigged gunboats built to an experimental design by Sir Samuel Bentham. Her launch date is unknown, but the Admiralty purchased her in April 1798. She had a short, relatively uneventful career before the French captured her in 1803. The French Navy sold her in January 1814.
 W
WHMS Sealark was the American schooner Fly, launched in 1801 or 1811, that HMS Scylla captured in 1811. The Royal Navy took her into service as a 10-gun schooner. She participated in one notable single-ship action in 1812 that in 1847 the Admiralty recognized with a clasp to the Naval General Service Medal. She was sold in 1820.
 W
WHMS St Lawrence was a 14-gun schooner of the Royal Navy. She had been built in 1808 in St. Michaels, Talbot County, Maryland for Thomas Tennant and sold to Philadelphians in 1810. During the War of 1812 she was the American privateer Atlas. The British captured her in 1813 and renamed her St Lawrence. The American privateer Chasseur recaptured her in 1815, and then HMS Acasta re-recaptured her.
 W
WHMS Superieure was the French privateer Supérieure, which was built in 1801 in Baltimore, Maryland, and which the British captured in 1803 in the West Indies, and took into the Royal Navy. She spent most of her career on the Jamaica and Leeward Islands stations, where she captured numerous privateers. She participated in several notable single-ship actions, including one in which she harassed a frigate, and two campaigns that would, in 1847, earn her surviving crew members the Naval General Service Medal (NGSM). She was laid-up in Britain in 1810 and sold in 1814.
 W
WHMS Undine was a schooner gunboat of the Royal Navy. Built as the private yacht Morna by Camper and Nicholsons, Gosport and launched in 1869. The schooner was purchased by the Royal Navy on 15 March 1881 and was renamed Undine.