 W
WThe 12 January 1879 action at Sihayo's Kraal was an early skirmish in the Anglo-Zulu War. The day after his invasion of Zululand, the British General Lord Chelmsford led a reconnaissance in force to the kraal of Zulu Chief Sihayo. This force had orders to burn the kraal to the ground as punishment for two of Sihayo's sons having entered the British Colony of Natal to kill two of Sihayo's wives who had fled there.
 W
WThe Battle of Angamos was a naval encounter of the War of the Pacific fought between the navies of Chile and Perú at Punta Angamos, on 8 October 1879. The battle was the culminating point of a naval campaign that lasted about five months in which the Chilean Navy had the sole mission of eliminating its Peruvian counterpart. In the struggle, two armored frigates, led by Commodore Galvarino Riveros and Navy Captain Juan José Latorre battered and later captured the Peruvian monitor Huáscar, under Rear Admiral Miguel Grau Seminario.
 W
WThe Battle of Chipana took place on 12 April 1879, during the War of the Pacific between Chile and Peru. It was the first naval engagement between both navies and it took place in front of Huanillos, off the (then) Bolivian coast, as the Peruvian corvette Unión and gunboat Pilcomayo found the Chilean corvette Magallanes on its way to Iquique. After a two-hour running artillery duel, Unión suffered engine problems, the pursuit was called off and Magallanes escaped with minor damage. Magallanes was able to complete part of its mission of delivering commissioned papers to Iquique, but unable to complete its reconnaissance mission of finding if there were any guano ships still making commerce in the zone.
 W
WThe First Battle of Geok Tepe was the main event in the 1879 Russian expedition against the Akhal Tekke Turcomans during the Russian conquest of Turkestan. Lomakin marched 275 miles to the Goek Teppe fortress, mismanaged the attack and was forced to retreat. Next year, this was reversed by Skobelev by the second Battle of Geok Tepe.
 W
WThe Battle of Iquique was a naval engagement that occurred between a Chilean corvette under the command of Arturo Prat and a Peruvian ironclad under the command of Miguel Grau Seminario on 21 May 1879, during the naval stage of the War of the Pacific, and resulted in a Peruvian victory. The War of the Pacific was a conflict that pitted Chile against Peru and Bolivia. The battle took place off the then-Peruvian port of Iquique. The Peruvian ironclad Huáscar, commanded by Miguel Grau Seminario, sank the Esmeralda, a Chilean wooden corvette captained by Arturo Prat Chacón, after four hours of combat.
 W
WThe Battle of Isandlwana on 22 January 1879 was the first major encounter in the Anglo-Zulu War between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Eleven days after the British commenced their invasion of Zululand in South Africa, a Zulu force of some 20,000 warriors attacked a portion of the British main column consisting of about 1,800 British, colonial and native troops and perhaps 400 civilians. The Zulus were equipped mainly with the traditional assegai iron spears and cow-hide shields, but also had a number of muskets and old rifles.
 W
WThe Jementah Civil War broke out in 1879 in Jementah in northern Johor when Tengku Alam Shah, the heir of Sultan Ali of the autonomous principality of Muar refused to surrender the principality to the central administration of Sultan Abu Bakar of Johor.
 W
WThe Kresna–Razlog Uprising named by the insurgents the Macedonian Uprising, was a Bulgarian uprising against the Ottoman rule, predominantly in the areas of Kresna and Razlog in late 1878 and early 1879. It broke out following the protests and spontaneous opposition to the decisions of the Congress of Berlin, which, instead of ceding the Bulgarian-populated parts of Macedonia to the newly reestablished Bulgarian suzerain state per the Treaty of San Stefano, returned them to Ottoman control. It was prepared by the "Edinstvo" Committee.
 W
WThe Nauruan Civil War was fought from 1878 to 1888, between forces loyal to incumbent King Aweida of Nauru and those seeking to depose him in favour of a rival claimant. The war was preceded by the introduction of firearms to Nauru. For the majority of the war, the loyalists and the rebels found themselves in a stalemate, with one side controlling the north and the other controlling the south. In 1888, The German Empire intervened and restored Aweida to the throne, although the island was annexed in the process. By the end of the war, about 500 people had died, around a third of the population.
 W
WThe Battle of Novšiće ) was a battle for control over Plav and Gusinje fought on 4 December 1879 between the forces of Principality of Montenegro led by Marko Miljanov and local pro-Ottoman forces which included irregulars of the League of Prizren, both commanded by Ali Pasha, the Kaymekam of Gusinje. The League of Prizren consisted of the local Albanians and Bosniaks from Plav and Gusinje in Scutari Vilayet and irregulars from Kosovo Vilayet. Some of them where Muslims of Montenegrin origin like Husein Bektešević.
 W
WThe Battle of Pisagua, was a landing operation of the War of the Pacific, fought on November 2, 1879, between Chile and the combined forces of Bolivia and Peru. The Chilean army commanded by Erasmo Escala, supported by the Chilean Fleet, launched an amphibious assault on the port of Pisagua and successfully drove the defending Bolivian-Peruvian forces, led by Gen. Juan Buendia, back from the shore. They established a beachhead that allowed an initial force of about 1,000 Chilean soldiers in two assault waves to disembark onto Peruvian territory at Pisagua in Tarapacá Department. This region was the principal territory in dispute.
 W
WThe Battle of Punta Gruesa was a naval action that took place on May 21, 1879, during the War of the Pacific between Chile and Peru. This may be labelled as the second part of the Naval Battle of Iquique, although it is described in many sources as a separate battle.
 W
WThe Battle of Río Grande was a small military engagement that took place on 10 September 1879, during the War of the Pacific. A picket of Chilean soldiers and a Bolivian montonera clashed in Rio Grande, around San Pedro de Atacama. Bolivians are defeated, which eliminates local resistance to Chilean occupation in the Litoral Department.
 W
WThe Battle of Rorke's Drift, also known as the Defence of Rorke's Drift, was an engagement in the Anglo-Zulu War. The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke's Drift, under the command of Lieutenants John Chard of the Royal Engineers and Gonville Bromhead, began when a large contingent of Zulu warriors broke off from their main force during the final hour of the British defeat at the day-long Battle of Isandlwana on 22 January 1879, diverting 6 miles (9.7 km) to attack Rorke's Drift later that day and continuing into the following day.
 W
WThe Battle of San Francisco, also known as the Battle of Dolores, was a major battle in the Tarapacá Campaign of the War of the Pacific, fought on November 19, 1879, in the Peruvian department of Tarapacá. A Chilean army under Colonel Emilio Sotomayor had moved via Dolores rail road deep into the desert and was encamped at San Francisco Saltpeter Office, about 30 kilometers south east of the port of Pisagua. Allied forces under General Juan Buendía launched an attack on Sotomayor's army. At the beginning, Bolivian General Carlos Villegas pressed the attack over a poorly defended battery right in the Chilean centre and almost succeeded. Only the arrival of infantry support allowed Colonel José Domingo Amunátegui to hold the position.
 W
WMeeker Massacre and the White River War, Ute War, or the Ute Campaign, were conflicts that began when the Utes attacked an Indian agency on September 29, 1879, killing the Indian agent Nathan Meeker and his 10 male employees, and taking women and children as hostages. United States Army forces were called in from Fort Steele in Wyoming. Following the massacre of Meeker and others, there was an attack at Milk Creek on U.S. troops, led by Major Thomas T. Thornburgh, killing the major and 13 troops within minutes. Relief troops were called in, which resulted in a further conflict.
 W
WThe Siege of the British Residency in Kabul was a military engagement of the Second Anglo-Afghan War. The British resident, Sir Louis Cavagnari and his escort were massacred after an 8-hour siege by mutinous Afghan troops inside their Residency in Kabul. This event triggered the second phase of the war, during which an Anglo-Indian army invaded Afghanistan and captured Kabul.
 W
WThe Siege of the Sherpur Cantonment was a battle fought in December 1879, during the Second Anglo-Afghan War.
 W
WThe Battle of Tarapacá occurred on November 27, 1879, during the Tarapacá Campaign of the War of the Pacific. A Chilean column of 2,300 soldiers led by Colonel Luis Arteaga recklessly attacked an outnumbering Peruvian contingent of 4,500 troops at Tarapacá commanded by Gen Juan Buendía, resulting in a harsh defeat. The Chilean 2nd Line Regiment was the most damaged unit, losing almost half of its force, along with its commander Col. Eleuterio Ramírez and his second in command, Lt. Col. Bartolomé Vivar. Also, the unit lost its banner, which was recovered six months later after the battle of Tacna. Despite the victory, the Allies could not contest for the domination of the Tarapacá department, abandoning it to Chilean control.
 W
WThe Battle of Calama or Battle of Topáter was fought on March 23, 1879 between Chile and Bolivia, and was the first battle of the War of the Pacific.
 W
WThe ʻUrabi revolt, also known as the ʻUrabi Revolution, was a nationalist uprising in Egypt from 1879 to 1882. It was led by and named for Colonel Ahmed ʻUrabi and sought to depose the Khedive Tewfik Pasha and end British and French influence over the country. The uprising was ended by an Anglo-Egyptian War and takeover of the country. Thus began the History of Egypt under the British.
 W
WDuring the implementation of the Congress of Berlin, when the Principality of Montenegro had received Plav and Gusinje, the surrounding Albanian populace under the guise of the Ottomans attacked the Montenegrin forces in Velika at two occasions, on October 9 and November 22, 1879. The Ottomans were defeated.
 W
WVictorio's War, or the Victorio Campaign, was an armed conflict between the Apache followers of Chief Victorio, the United States, and Mexico beginning in September 1879. Faced with arrest and forcible relocation from his homeland in New Mexico to San Carlos Indian Reservation in southeastern Arizona, Victorio led a guerrilla war across southern New Mexico, west Texas and northern Mexico. Victorio fought many battles and skirmishes with the United States Army and raided several settlements until the Mexican Army killed him and most of his warriors in October 1880 in the Battle of Tres Castillos. After Victorio's death, his lieutenant Nana led a raid in 1881.
 W
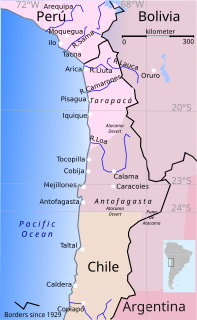
WThe War of the Pacific, also known as the Saltpeter War and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with a Chilean victory, which gained for the country a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. The Chilean Army took Bolivia's nitrate-rich coastal region, and Peru was defeated by the Chilean Navy.