 W
WThe 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, sometimes called the Treaty of Aachen, ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
 W
WThe Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle or Aachen ended the War of Devolution between France and Spain. It was signed on 2 May 1668 in Aachen. Spain acceded on 7 May 1669.
 W
WThe Treaty of Amiens temporarily ended hostilities between France and Great Britain during the French Revolutionary Wars. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it set the stage for the Napoleonic Wars. Britain gave up most of its recent conquests; France was to evacuate Naples and Egypt. Britain retained Ceylon and Trinidad. It was signed in the city of Amiens on 27 March 1802 by Joseph Bonaparte and Marquess Cornwallis as a "Definitive Treaty of Peace." The consequent peace lasted only one year and was the only period of general peace in Europe between 1793 and 1814.
 W
WThe Treaty of Badajoz was signed by Spain and Portugal on 6 June 1801. Portugal ceded the border town of Olivença to Spain and closed its ports to British military and commercial shipping.
 W
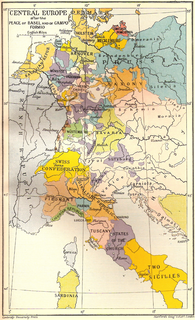
WThe Peace of Basel of 1795 consists of three peace treaties involving France during the French Revolution.The first was with Prussia on 5 April; The second was with Spain on 22 July, ending the War of the Pyrenees; and The third was with the Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel on 28 August, concluding the stage of the French Revolutionary Wars against the First Coalition.
 W
WThe Boxer Protocol was signed on September 7, 1901, between the Qing Empire of China and the Eight-Nation Alliance that had provided military forces ; after China's defeat in the intervention to put down the Boxer Rebellion. It is often regarded as one of the Unequal Treaties.
 W
WThe Convention of Vergara was a treaty successfully ending the major fighting in Spain's First Carlist War. The treaty, also known by many other names including the Embrace of Vergara, was signed by Baldomero Espartero for the Isabelines and Rafael Maroto for the Carlists.
 W
WThe Treaty of Córdoba established Mexican independence from Spain at the conclusion of the Mexican War of Independence. It was signed on August 24, 1821 in Córdoba, Veracruz, Mexico. The signatories were the head of the Army of the Three Guarantees, Agustín de Iturbide, and, acting on behalf of the Spanish government, Jefe Político Superior Juan O'Donojú. The treaty has 17 articles, which developed the proposals of the Plan of Iguala. The Treaty is the first document in which Spanish and Mexican officials accept the liberty of what will become the First Mexican Empire, but it is not today recognized as the foundational moment, since these ideas are often attributed to the Grito de Dolores. The treaty was rejected by the Spanish government. Spain did not recognize Mexico's independence until December 28, 1836.
 W
WThe Definitive treaty of peace and friendship between Mexico and Spain, also called Santa María–Calatrava Treaty was an international treaty between Mexico and Spain on December 28, 1836, by which the Spanish monarchy recognized the independence of Mexico as a "free, sovereign and independent nation". It ended the tensions between both nations that emerged from the Mexican War of Independence, which began in 1810. It was signed by Mexican Miguel Santa María and Spaniard José María Calatrava.
 W
WThe 1720 Treaty of The Hague was signed on 17 February 1720 between Spain and the Quadruple Alliance, established by the 1718 Treaty of London. Its members included Britain, France, the Dutch Republic and Austria.
 W
WThe Treaty of Paris of 1898 was a treaty signed by Spain and the United States on December 10, 1898, that ended the Spanish–American War. Under it, Spain relinquished all claim of sovereignty over and title to Cuba and also ceded Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines to the United States. The cession of the Philippines involved a compensation of $20 million from the United States to Spain.
 W
WThe Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the United Netherlands and the Spanish Crown, the terms of which were agreed on 30 January 1648. The Treaty is a key event in Dutch history marking formal recognition of the independent Dutch Republic and formed part of the Peace of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War and the Eighty Years' War.
 W
WThe Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France, and the Grand Alliance, which included England, Spain, Emperor Leopold, and the Dutch Republic.
 W
WThe Peace of Vervins or Treaty of Vervins was signed between the representatives of Henry IV of France and Philip II of Spain under the auspices of the papal legates of Clement VIII, on 2 May 1598 at the small town of Vervins in Picardy, northern France, close to the territory of the Habsburg Netherlands.
 W
WThe Plan of Iguala, also known as The Plan of the Three Guarantees or Act of Independence of North America, was a revolutionary proclamation promulgated on 24 February 1821, in the final stage of the Mexican War of Independence from Spain. The Plan stated that Mexico was to become a constitutional monarchy, whose sole official religion would be Roman Catholicism, in which the Peninsulares and Creoles of Mexico would enjoy equal political and social rights. It took its name from the city of Iguala in the modern-day state of Guerrero.
 W
WThe Treaty of the Pyrenees,, was signed on 7 November 1659, and ended the 1635 to 1659 Franco-Spanish war.
 W
WThe Sentencia Arbitral de Guadalupe was a legal decree delivered by King Ferdinand II of Aragon at the Monastery of Santa María de Guadalupe in Extremadura, Spain on 21 April 1486 to free the Catalan remensa peasants who were subjects of the lord of the manor and tied to his lands and subject to numerous onerous fees and maltreatment under the so-called evil customs.
 W
WThe Treaty of Seville was signed on 9 November 1729 between Britain, France, and Spain, formally ending the 1727–1729 Anglo-Spanish War; the Dutch Republic joined the Treaty on 29 November.
 W
WThe Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and October 1679. The treaties ended various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Republic, Spain, Brandenburg, Sweden, Denmark, the Prince-Bishopric of Münster, and the Holy Roman Empire. The most significant of the treaties was the first, which established peace between France and the Dutch Republic and placed the northern border of France very near its modern position.
 W
WThe Treaty of Granada was signed and ratified on November 25, 1491, between Boabdil, the sultan of Granada, and Ferdinand and Isabella, the King and Queen of Castile, León, Aragon and Sicily. It ended the Granada War which had started in 1482, culminating in the siege and battle of Granada beginning in spring 1491.
 W
WThe Twelve Years' Truce was the name given to the cessation of hostilities between the Habsburg rulers of Spain and the Southern Netherlands and the Dutch Republic as agreed in Antwerp on 9 April 1609. It was a watershed in the Eighty Years' War, marking the point from which the independence of the United Provinces received formal recognition by outside powers. For Spain the Truce was seen as a humiliating defeat as they were forced to make several sacrifices but they scarcely got anything in return. For the time of its duration however the Truce allowed King Philip III and his favorite minister the Duke of Lerma to disengage from the conflict in the Low Countries and devote their energies to the internal problems of the Spanish Monarchy. The Archdukes Albert and Isabella used the years of the Truce to consolidate Habsburg rule and to implement the Counter-Reformation in the territories under their sovereignty.
 W
WThe Peace of Utrecht is a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of Spain, and involved much of Europe for over a decade. The main action saw France as the defender of Spain against a multinational coalition. The war was very expensive and bloody and finally stalemated. Essentially, the treaties allowed Philip V to keep the Spanish throne in return for permanently renouncing his claim to the French throne, along with other necessary guarantees that would ensure that France and Spain should not merge, thus preserving the balance of power in Europe.
 W
WThe Treaty of Venlo of 7 September 1543 concluded the Guelders Wars (1502–1543), and the definitive acquisition of the Duchy of Guelders and the adjoining County of Zutphen by the House of Habsburg, adding them to the Habsburg Netherlands. William V, Duke of the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg had to relinquish his claims to Guelders and Zutphen in favour of the Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain, Charles V of Habsburg.
 W
WThe Peace of Westphalia is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire, closing a calamitous period of European history that killed approximately eight million people.
 W
WThe Treaty of Zaragoza, also called the Capitulation of Zaragoza was a peace treaty between Castile and Portugal, signed on 22 April 1529 by King John III of Portugal and the Castilian emperor Charles V, in the Aragonese city of Zaragoza. The treaty defined the areas of Castilian and Portuguese influence in Asia, in order to resolve the "Moluccas issue", which had arisen because both kingdoms claimed the Moluccas Islands for themselves, asserting that they were within their area of influence as specified in 1494 by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The conflict began in 1520, when expeditions of both kingdoms reached the Pacific Ocean, because no agreed meridian of longitude had been established in the Orient.