 W
WThe Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral ; Italian: Zona d'operazioni del Litorale adriatico; Croatian: Operativna zona Jadransko primorje; Slovene: Operacijska zona Jadransko primorje) was a Nazi German district on the northern Adriatic coast created during World War II in 1943. It was formed out of territories that were previously under Fascist Italian control until its takeover by Germany. It included parts of present-day Italian, Slovenian, and Croatian territories. The area was administered as territory attached, but not incorporated to, the Reichsgau of Carinthia. The capital of the zone was the city of Trieste.
 W
WThe Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills was a Nazi German occupation zone in the sub-Alpine area in Italy during World War II.
 W
WThe Occupation of Vojvodina from 1941 to 1944 was carried out by Nazi Germany and its client states / puppet regimes: Horthy's Hungary and Independent State of Croatia.
 W
WThe occupation of the Baltic states involved the military occupation of the three Baltic states—Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania—by the Soviet Union under the auspices of the 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact in June 1940. They were then annexed into the Soviet Union as constituent republics in August 1940, though most Western powers and nations never recognised their incorporation. On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany attacked the Soviet Union and within weeks occupied the Baltic territories. In July 1941, the Third Reich incorporated the Baltic territory into its Reichskommissariat Ostland. As a result of the Red Army's Baltic Offensive of 1944, the Soviet Union recaptured most of the Baltic states and trapped the remaining German forces in the Courland pocket until their formal surrender in May 1945. The Soviet "annexation occupation" or occupation sui generis of the Baltic states lasted until August 1991, when the three countries regained their independence.
 W
WThe occupation of Byelorussia by Nazi Germany started with the German invasion of the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941 and ended in August 1944 with the Soviet Operation Bagration. The western parts of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic became part of the Reichskommissariat Ostland in 1941, but in 1943 the German authorities allowed local collaborators to set up a client state, the Belarusian Central Rada, that lasted until the Soviets liberated the region.
 W
WThe Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was a partially annexed territory of Nazi Germany established on 16 March 1939 following the German occupation of the Czech lands on 15 March 1939. Earlier, following the Munich Agreement of September 1938, Nazi Germany had incorporated the Czech Sudetenland territory as a Reichsgau.
 W
WThe German occupation of the Channel Islands lasted for most of the Second World War, from 30 June 1940 until their liberation on 9 May 1945. The Bailiwick of Jersey and Bailiwick of Guernsey are two British Crown dependencies in the English Channel, near the coast of Normandy. The Channel Islands were the only de jure part of the British Empire to be occupied by the Wehrmacht during the war.
 W
WChief of Civil Administration was an office introduced in Nazi Germany, operational during World War II. Its task was to administer civil issues according to occupation law, with the primary purpose being the support of the military command in the operational areas of the German Army. CdZ would pass his authority to a corresponding civil government after the territory in question became in the rear of the operating armed forces.
 W
WThe German occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945) began with the German annexation of Sudetenland in 1938, continued with the March 1939 invasion of the Czech lands and creation of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, and by the end of 1944 extended to all parts of the former Czechoslovakia.
 W
WAt the outset of World War II in September 1939, Denmark declared itself neutral. For most of the war, the country was a protectorate and then an occupied territory of Germany. The decision to occupy Denmark was taken in Berlin on 17 December 1939. On 9 April 1940, Germany occupied Denmark in Operation Weserübung and the king and government functioned as normal in a de facto protectorate over the country until 29 August 1943, when Germany placed Denmark under direct military occupation, which lasted until the Allied victory on 5 May 1945. Contrary to the situation in other countries under German occupation, most Danish institutions continued to function relatively normally until 1945. Both the Danish government and king remained in the country in an uneasy relationship between a democratic and a totalitarian system until the Danish government stepped down in a protest against German demands to institute the death penalty for sabotage.
 W
WDeportations from the German-occupied Channel Islands refers to a specific wave of deportations by Nazi Germany of British citizens who were residents of the Channel Islands. The stated reason was retaliation for internment of German citizens in Persia by the British Government.
 W
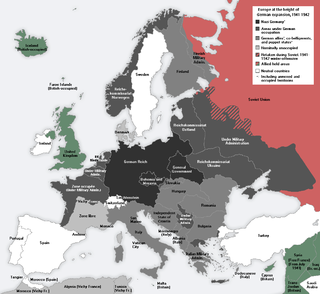
WGerman-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 and 1945, during and shortly before World War II, generally administered by the Nazi regime. The German Wehrmacht occupied European territory:as far east as the town of Mozdok in the northern Caucasus in the Soviet Union (1942–1943) as far north as the settlement of Barentsburg in Svalbard in the Kingdom of Norway as far south as the island of Gavdos in the Kingdom of Greece as far west as the island of Ushant in the French Republic
 W
WAfter the Wehrmacht occupied the Channel Islands on 30 June 1940, they assessed the existing defences to determine if they would be of use. The Germans found the Islands' fortifications antiquated and woefully inadequate for modern warfare.
 W
WThe occupation of Estonia by the German Empire occurred during the later stages of the First World War. On October 11–21, 1917, the Imperial German Army occupied the West Estonian archipelago, consisting of the islands of Saaremaa (Ösel), Hiiumaa (Dagö), and Muhu (Mühn).
 W
WAfter Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941, Army Group North reached Estonia in July. Initially the Germans were perceived by most Estonians as liberators from the USSR and its repressions, having arrived only a week after the first mass deportations from the Baltic States. Although hopes were raised for the restoration of the country's independence, it was soon realized that they were but another occupying power. The Germans pillaged the country for their war effort and unleashed The Holocaust in Estonia during which they and their collaborators murdered tens of thousands of people. For the duration of the occupation, Estonia was incorporated into the German province of Ostland.
 W
WThe occupation of Latvia by Nazi Germany was completed on July 10, 1941 by Germany's armed forces. Latvia became a part of Nazi Germany's Reichskommissariat Ostland—the Province General of Latvia. Anyone not racially acceptable or who opposed the German occupation, as well as those who had cooperated with the Soviet Union, were killed or sent to concentration camps in accordance with the Nazi Generalplan Ost.
 W
WThe occupation of Lithuania by Nazi Germany lasted from the German invasion of the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941 to the end of the Battle of Memel on January 28, 1945. At first the Germans were welcomed as liberators from the repressive Soviet regime which occupied Lithuania prior to the German arrival. In hopes of re-establishing independence or regaining some autonomy, Lithuanians organized their Provisional Government. Soon the Lithuanian attitudes towards the Germans changed into passive resistance.
 W
WThe German occupation of Luxembourg during World War I was the first of two military occupations of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg by Germany in the 20th century. From August 1914 until the end of World War I on 11 November 1918, Luxembourg was under full occupation by the German Empire. The German government justified the occupation by citing the need to support their armies in neighbouring France, although many Luxembourgers, contemporary and present, have interpreted German actions otherwise.
 W
WKarl-Siegmund Litzmann was General Commissioner for Estonia in the Reichskommissariat Ostland during the German occupation..
 W
WThe German-occupied territory of Montenegro was the area of the Italian governorate of Montenegro occupied by German forces in September 1943, after the Armistice of Cassibile; in which the Kingdom of Italy capitulated and joined the Allies. Italian forces retreated from the governorate, and from neighbouring Albania. German forces occupied Montenegro, along with Albania, and the territory remained under German occupation until Axis forces evacuated in December 1944.
 W
WThe occupation of the Baltic states by Nazi Germany occurred during Operation Barbarossa from 1941 to 1944. Initially, many Estonians, Latvians, and Lithuanians considered the Germans as liberators from the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union during World War II (1939–1945) began with the German-Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR) both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe.
 W
WThe Reichskommissariat Ostland (RKO) was established by Nazi Germany in 1941 during World War II. It became the civilian occupation regime in the Baltic states and the western part of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. German planning documents initially referred to an equivalent Reichskommissariat Baltenland. The political organization for this territory – after an initial period of military administration before its establishment – involved a German civilian administration, nominally under the authority of the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories led by Nazi ideologist Alfred Rosenberg, but actually controlled by the Nazi official Hinrich Lohse, its appointed Reichskommissar.
 W
WThe Reichsleiter Rosenberg Taskforce was a Nazi Party organization dedicated to appropriating cultural property during the Second World War. It was led by the chief ideologue of the Nazi Party, Alfred Rosenberg, from within the NSDAP Office of Foreign Affairs. Between 1940 and 1945, the ERR operated in France, the Benelux countries, Poland, the Baltic States, Greece, Italy and on the territory of the Soviet Union in the Reichskommissariat Ostland and Reichskommissariat Ukraine. Much of the looted material was recovered by the Allies after the war, and returned to rightful owners, but there remains a substantial part that has been lost or remains with the Allied powers.
 W
WThe Run for Tunis was part of the Tunisia Campaign which took place during November and December 1942 during the Second World War. Once French opposition to the Allied Operation Torch landings had ceased in mid-November, the Allies made a rapid advance by a division-sized force east from Algeria, to capture Tunis and forestall an Axis build up in Tunisia and narrowly failed. Some Allied troops were fewer than 20 miles (32 km) short of Tunis by late November but the defenders counter-attacked and pushed them back nearly 20 miles (32 km), to positions which had stabilised by the end of the year.
 W
WThe island of Sark forms part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey which with the Bailiwick of Jersey form the Channel Islands. Offered the opportunity to evacuate the island in June 1940, most locally born islanders decided to stay. The remaining 470 civilians would be subject to German rule for the next five years, until Sark was liberated on 10 May 1945. The main contact between the Sark residents and the German authorities in 1940 was 56-year old Sibyl Hathaway, the Dame of Sark, who was Seigneur of Sark from 1927 until her death in 1974.
 W
WDuring World War II, several provinces of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia corresponding to the modern-day state of Serbia were occupied by the Axis Powers from 1941 to 1944. Most of the area was occupied by the Wehrmacht and was organized as separate territory under control of the German Military Administration in Serbia. Other parts of modern Serbia that were not included in the German-administered territory were occupied and annexed by neighboring Axis countries: Syrmia was occupied and annexed by the Independent State of Croatia, Bačka was occupied and annexed by Hungary, southeastern Serbia was occupied and annexed by Bulgaria, and southwestern Serbia was occupied and annexed by Italy and included in the Italian protectorates of Albania and Montenegro.
 W
WThe Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia was the area of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia that was placed under a military government of occupation by the Wehrmacht following the invasion, occupation and dismantling of Yugoslavia in April 1941. The territory included only central Serbia, with the addition of the northern part of Kosovo, and the Banat. This territory was the only area of partitioned Yugoslavia in which the German occupants established a military government. This was due to the key rail and riverine transport routes that passed through it, and its valuable resources, particularly non-ferrous metals. On 22 April 1941, the territory was placed under the supreme authority of the German military commander in Serbia, with the day-to-day administration of the territory under the control of the chief of the military administration staff. The lines of command and control in the occupied territory were never unified, and were made more complex by the appointment of direct representatives of senior Nazi figures such as Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler, Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring, and Reichsminister Joachim von Ribbentrop. The Germans used Bulgarian troops to assist in the occupation, but they were at all times under German control. Sources variously describe the territory as a puppet state, a protectorate, a "special administrative province", or describe it as having a puppet government. The military commander in Serbia had very limited German garrison troops and police detachments to maintain order, but could request assistance from a corps of three divisions of poorly-equipped occupation troops.