 W
WThis list of town walls in England and Wales describes the fortified walls built and maintained around these towns and cities from the 1st century AD onwards. The first town walls were built by the Romans, following their conquest of Britain in 43 AD. The Romans typically initially built walled forts, some of which were later converted into rectangular towns, protected by either wooden or stone walls and ditches. Many of these defences survived the fall of the Roman Empire in the 4th and 5th centuries, and were used in the unstable post-Roman period. The Anglo-Saxon kings undertook significant planned urban expansion in the 8th and 9th centuries, creating burhs, often protected with earth and wood ramparts. These burh walls sometimes utilised older Roman fortifications, and themselves frequently survived into the early medieval period.
 W
WAbergavenny's town walls are a sequence of defensive walls built around the town of Abergavenny in Monmouthshire, Wales.
 W
WAlnwick's town walls are a 15th-century defensive structure built around the town of Alnwick in England.
 W
WBath's city walls were a sequence of defensive structures built around the city of Bath in England. Roman in origin, then restored by the Anglo-Saxons, and later strengthened in the High medieval period, the walls formed a complete circuit, covering the historic core of the modern city, an area of approximately 23 acres (9.3 ha) including the Roman Baths and medieval Bath Abbey. In the present-day however, the walls have largely disappeared, though the route they took is evident from the street layout; one of the gates partially remains.
 W
WBeaumaris's town walls were a fifteenth-century defensive structure built around the town of Beaumaris in Wales.
 W
WBerwick's town walls are a sequence of defensive structures built around the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed in England.
 W
WBeverley's town walls are a sequence of defensive structures built around the town of Beverley in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England.
 W
WCaernarfon's town walls are a medieval defensive structure around the town of Caernarfon in North Wales. The walls were constructed between 1283 and 1292 after the foundation of Caernarfon by Edward I, alongside the adjacent castle. The walls are 734 m (2,408 ft) long and include eight towers and two medieval gatehouses. The project was completed using large numbers of labourers brought in from England; the cost of building the walls came to around £3,500, a large sum for the period. The walls were significantly damaged during the rebellion of Madog ap Llywelyn in 1294, and had to be repaired at considerable expense. Political changes in the 16th century reduced the need to maintain such defences around the town. Today the walls form part of the UNESCO world heritage site administered by Cadw. Archaeologists Oliver Creighton and Robert Higham describe the defences as "a remarkably intact walled circuit".
 W
WThe Westgate is a medieval gatehouse in Canterbury, Kent, England. This 60-foot (18 m) high western gate of the city wall is the largest surviving city gate in England. Built of Kentish ragstone around 1379, it is the last survivor of Canterbury's seven medieval gates, still well-preserved and one of the city's most distinctive landmarks. The road still passes between its drum towers. This scheduled monument and Grade I listed building houses the West Gate Towers Museum.
 W
WCanterbury city walls are a sequence of defensive walls built around the city of Canterbury in Kent, England. The first city walls were built by the Romans, probably between 270 and 280 AD. These walls were constructed from stone on top of an earth bank, and protected by a ditch and wall towers. At least five gates were placed into the walls, linked to the network of Roman roads across the region. With the collapse of Roman Britain, Canterbury went into decline but the walls remained, and may have influenced the decision of Augustine to settle in the city at the end of the 6th century. The Anglo-Saxons retained the defensive walls, building chapels over most of the gates and using them to defend Canterbury against Viking incursions.
 W
WCardiff's town walls were a Medieval defensive wall enclosing much of the present day centre of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales, which included Cardiff Castle. It measured 1280 paces or 1.280 miles in circumference and had an average thickness of between 6 feet and 8 ft (2.4 m) and a height of 10 ft (3.0 m).
 W
WCarlisle city walls were a defensive structure surrounding the centre of Carlisle, Cumbria. The city walls ran from Carlisle Castle in the north-west of the city to The Citadel in the south-east. Between these points, the city was protected by the former North and East Walls and the West Walls which remain largely intact. The line of the walls can still be followed with the exception of the southernmost end of the West Wall which has been built over. The perimeter, including the castle, is approximately 2.2 kilometres (1.4 mi) which is comparable to Southampton town walls but less than Chester city walls.
 W
WThe Port Wall in Chepstow, Monmouthshire, Wales, is a late thirteenth century stone wall, which was constructed for the twin purposes of defence and tax collection by permitting users of the town's market only one point of access through the wall at the Town Gate. The wall originally formed a semi-circle extending for some 1,100 metres (3,600 ft), roughly southwards from Chepstow Castle to the River Wye. It enclosed an area of 53 hectares, including the entire town and port as it existed at that time. Substantial sections of the wall remain intact, and both the Port Wall and the Town Gate are Grade I listed buildings. The Port Wall is a Scheduled monument.
 W
WChester city walls consist of a defensive structure built to protect the city of Chester in Cheshire, England. Their construction was started by the Romans when they established the fortress of Deva Victrix between 70 and 80 AD. It originated with a rampart of earth and turf surmounted by a wooden palisade. From about 100 AD they were reconstructed using sandstone, but were not completed until over 100 years later. Following the Roman occupation nothing is known about the condition of the walls until Æthelflæd refounded Chester as a burgh in 907. The defences were improved, although the precise nature of the improvement is not known. After the Norman conquest, the walls were extended to the west and the south to form a complete circuit of the medieval city. The circuit was probably complete by the middle of the 12th century.
 W
WThe Chester city walls surround what was the extent of the English city of Chester in the medieval period. They started as a defensive structure for the fortress of Deva Victrix during the Roman occupation of Britain. Originating between 70 and 90 AD, they consisted of earth ramparts surmounted by wooden palisades. At intervals there were wooden gates and towers. Following the arrival of the Legio XX Valeria Victrix at the end of the 1st century the walls were reconstructed in sandstone, and building work continued, with interruptions, until the Roman circuit of the walls was completed over 100 years later. During the same period the towers and gates were rebuilt in stone. Repairs were carried out on the walls throughout the Roman occupation. Chester was refortified in 907 by Æthelflæd, but how this affected the walls is not precisely known. The north and east Roman walls were certainly used in the fortification, as they are still in existence today, but it is possible that they were extended to the west and south to meet the River Dee.
 W
WConwy's town walls are a medieval defensive structure around the town of Conwy in Wales. The walls were constructed between 1283 and 1287 after the foundation of Conwy by Edward I, and were designed to form an integrated system of defence alongside Conwy Castle. The walls are 1.3 km (0.81 mi) long and include 21 towers and three gatehouses. The project was completed using large quantities of labourers brought in from England; the cost of building the castle and walls together came to around £15,000, a huge sum for the period. The walls were slightly damaged during the rebellion of Owain Glyndŵr in 1401, but political changes in the 16th century reduced the need to maintain such defences around the town. The fortifications were treated sympathetically during the development of the road and railway systems in Conwy during the 19th century and survived largely intact into the modern period. Today the walls form part of the UNESCO world heritage site administered by Cadw. Historians Oliver Creighton and Robert Higham describe the defences as "one of the most impressive walled circuits" in Europe.
 W
WCoventry's city walls are a sequence of defensive structures built around the city of Coventry in England.
 W
WCowbridge town wall is a Grade II*-listed medieval wall in the small market town of Cowbridge in the Vale of Glamorgan, south Wales. The walls were built by about 1300. It is believed that the purpose of the walls were to protect the Lord of Glamorgan's burgage plots and to provide a way of collecting tolls from the town's market, held twice-weekly.
 W
WThere have been several town walls around Edinburgh, Scotland, since the 12th century. Some form of wall probably existed from the foundation of the royal burgh in around 1125, though the first building is recorded in the mid-15th century, when the King's Wall was constructed. In the 16th century the more extensive Flodden Wall was erected, following the Scots' defeat at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. This was extended by the Telfer Wall in the early 17th century. The walls had a number of gates, known as ports, the most important being the Netherbow Port, which stood halfway down the Royal Mile. This gave access from the Canongate which was, at that time, a separate burgh.
 W
WThe fortifications of Kingston upon Hull consisted of three major constructions: the brick built Hull town walls, first established in the early 14th century, with four main gates, several posterngates, and up to thirty towers at its maximum extent; Hull Castle, on the east bank of the River Hull, protecting Hull's river harbour, constructed in the mid 16th century and consisting of two blockhouses and a castle connected by a curtain wall; and the later 17th century Citadel, an irregular triangular, bastioned, primitive star fort replacing the castle on the east river bank.
 W
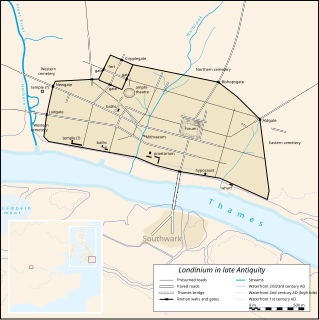
WThe London Wall was the defensive wall first built by the Romans around Londinium, their strategically important port town on the River Thames in what is now London, England, and subsequently maintained until the 18th century.
 W
WThe Monmouth town walls and defences comprise the defensive system of town walls and gates built in Monmouth, Wales between 1297 and the early part of the following century. Wye Bridge Gate, East Gate, Monk's Gate, and Monnow Bridge Gate were access points to the town. West Gate, across Monnow Street, also provided access. Only the Monnow Bridge Gatehouse survives intact, albeit in a substantially modified version from the original.
 W
WThe New Gate of Newcastle, England, was a city gate in Newcastle town wall dating to the fourteenth century or before, which for centuries housed a gaol. It gives its name to Newgate Street.
 W
WThe Newcastle town wall is a medieval defensive wall, and Scheduled Ancient Monument, in Newcastle upon Tyne, England. It was built during the 13th and 14th centuries, and helped protect the town from attack and occupation during times of conflict. It was approximately 3 kilometres (2 mi) long, at least 2 metres (6.5 ft) thick, up to 7.6 metres (25 ft) high, and had six main gates: Close Gate, West Gate, New Gate, Pilgrim Gate, Pandon Gate and Sand Gate. It also had seventeen towers, as well as several smaller turrets and postern gates. The town wall was kept in good repair whilst there was a threat of invasion from Scottish armies, and the town was successfully defended on at least two occasions; but with the decline of the border wars between England and Scotland, the wall was allowed to deteriorate.
 W
WPembroke's town walls are a Grade II*-listed medieval defensive structure around the town of Pembroke, Pembrokeshire, Wales. They were probably built beginning in the late 13th century by the Earls of Pembroke, although it is uncertain when they were finished. Most of the walls have not survived, but there are visible sections and two bastions exist, one with a restored late 18th-century gazebo atop it.
 W
WSouthampton's town walls are a sequence of defensive structures built around the town in southern England. Although earlier Roman and Anglo-Saxon settlements around Southampton had been fortified with walls or ditches, the later walls originate with the move of the town to the current site in the 10th century. This new town was defended by banks, ditches and the natural curve of the river and coastline. The Normans built a castle in Southampton but made no attempts to improve the wider defences of the town until the early 13th century, when Southampton's growing prosperity as a trading centre and conflict with France encouraged the construction of a number of gatehouses and stone walls to the north and east sides of the settlement.
 W
WThe Tenby town walls are Grade I-listed medieval defensive structures around the town of Tenby in Pembrokeshire. They are assessed as one of the most important surviving medieval city walls in Britain. The walls were built in the 13th century by the Earls of Pembroke and improved in the 1450s. They were last known to have been repaired in 1588 and have declined thereafter. Most of the town's gates were demolished beginning in the 18th century and only one survives.
 W
WWorcester's city walls are a sequence of defensive structures built around the city of Worcester in England between the 1st and 17th centuries. The first walls to be built around Worcester were constructed by the Romans. These early walls lasted beyond the fall of the Empire, and the defences encouraged several early Christian foundations to establish themselves in Worcester during the troubled 6th and 7th centuries. The Anglo-Saxons expanded Worcester in the 890s, forming a new walled, planned city, called a burh. The burh utilised the southern stretches of the old Roman walls, but pushed further north to enclose a much larger area. The Anglo-Saxon city walls were maintained by a share of taxes on a local market and streets, in an agreement reinforced by a royal charter.
 W
WYork has, since Roman times, been defended by walls of one form or another. To this day, substantial portions of the walls remain, and York has more miles of intact wall than any other city in England. They are known variously as York City Walls, the Bar Walls and the Roman walls. The walls are generally 13 feet (4m) high and 6 feet (1.8m) wide.