 W
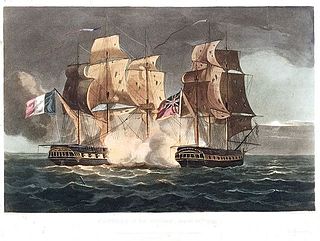
WThe Action of 8 March 1795 was a minor naval engagement in the Mediterranean theatre of the French Revolutionary Wars. The action was part of series of battles fought in the spring of 1795 between British and French fleets for control of the Ligurian Sea and thus the blockade of the French naval base of Toulon. The engagement was the first significant action of the year and was fought principally between the damaged British 74-gun ship of the line HMS Berwick and the French 32-gun frigate Alceste, with the later assistance of the frigate Vestale and the 74-gun Duquesne, distantly supported by the rest of the French Mediterranean Fleet.
 W
WThe Action of 10 April 1795 was a minor naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars in which a squadron of French Navy frigates was intercepted by a British battle squadron under Rear-Admiral John Colpoys which formed part of the blockade of the French naval base of Brest in Brittany. The French squadron split up in the face of superior British numbers, the three vessels seeking to divide and outrun the British pursuit. One frigate, Gloire was followed by the British frigate HMS Astraea and was ultimately brought to battle in a closely fought engagement. Although the ships were roughly equal in size, the British ship was easily able to defeat the French in an engagement lasting just under an hour.
 W
WThe Action of 22 August 1795 was a minor naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars between a squadron of four British Royal Navy frigates and two frigates and a cutter from the Batavian Navy. The engagement was fought off the Norwegian coastal island of Eigerøya, then in Danish Norway, the opposing forces engaged in protecting their respective countries' trade routes to the Baltic Sea. War between Britain and the Batavian Republic began, undeclared, in the spring of 1795 after the Admiralty ordered British warships to intercept Batavian shipping following the conquest of the Dutch Republic by the French Republic in January 1795.
 W
WThe Action of 24 June 1795 was a minor naval engagement fought in the Western Basin of the Mediterranean Sea on 24 June 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. During 1795 the Royal Navy and French Navy Mediterranean Fleets were vying for supremacy in the region, the French operating from the fortified port of Toulon and the British from the allied Spanish base of Port Mahon on Menorca. A minor British victory at the Battle of Genoa in March had not resolved the conflict, both sides suffering damage. The British, under Admiral William Hotham, subsequently withdrew to Menorca to meet a squadron of reinforcements while the French, under Contre-amiral Pierre Martin at Toulon, suffering from ill-discipline, had also been reinforced. By June, both fleets were ready to return to the Ligurian Sea.
 W
WThe Battle of Nuʻuanu, fought in May 1795 on the southern part of the island of Oʻahu, was a key battle in the final days of King Kamehameha I's wars to unify the Hawaiian Islands. It is known in the Hawaiian language as Kalelekaʻanae, which means "the leaping mullet", and refers to a number of Oʻahu warriors driven off the cliff in the final phase of the battle. There are "varied and sometimes conflicting histories of the Battle of Nuʻuanu."
 W
WThe Biscay campaign of June 1795 consisted of a series of manoeuvres and two battles fought between the British Channel Fleet and the French Atlantic Fleet off the Southern coast of Brittany in the Bay of Biscay during the French Revolutionary Wars. In late May 1795, a British battle squadron of six ships of the line under Vice-Admiral William Cornwallis was sent by Admiral Lord Bridport to enforce the blockade of the French port of Brest, the home port of the French Atlantic Fleet. On 8 June, Cornwallis discovered a convoy of merchant vessels travelling from Bordeaux to Brest under the protection of a small squadron under Contre-amiral Jean Gaspard Vence. Cornwallis attacked the convoy, Vence retreating under the protection of batteries on the fortified island of Belle Île as Cornwallis seized eight ships from the convoy. As Cornwallis sent his prizes back to Britain the main French fleet at Brest under Vice-amiral Villaret de Joyeuse put to sea to protect Vence's remaining ships.
 W
WThe Invasion of the Cape Colony, also known as the Battle of Muizenberg, was a British military expedition launched in 1795 against the Dutch Cape Colony at the Cape of Good Hope. The Dutch colony at the Cape, established in the seventeenth century, was at the time the only viable South African port for ships making the journey from Europe to the European colonies in the East Indies. It therefore held vital strategic importance, although it was otherwise economically insignificant. In the winter of 1794, during the French Revolutionary Wars, French troops entered the Dutch Republic, which was reformed into the Batavian Republic. In response, Great Britain launched operations against the Dutch Empire to use its facilities against the French Navy.
 W
WThe Capture of the Dutch fleet at Den Helder on the night of 23 January, 1795 presents a rare occurrence of a tactical interaction between warships and cavalry, in which a French Revolutionary Hussar regiment surrounded a Dutch fleet frozen at anchor between the 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) stretch of sea that separates the mainland port of Den Helder and the island of Texel. After a charge across the frozen Zuiderzee, the French cavalry captured all 14 Dutch warships lying at anchor. A capture of ships by horsemen is an extremely rare feat in military history.
 W
WThe Second Carib War (1795–1797) took place on the island of Saint Vincent between 1795 and 1797. The conflict pitted large numbers of British military forces against a coalition of Black Carib, runaway slaves, and French forces for control of the island.
 W
WThe Invasion of Ceylon was a military campaign fought as a series of amphibious operations between the summer of 1795 and spring of 1796 between the garrison of the Batavian colonies on the Indian Ocean island of Ceylon and a British invasion force sent from British India. The Dutch Republic had been a British ally during the French Revolutionary Wars, but was overrun by the French Republic in the winter of 1794 and reformed into the client state of the Batavian Republic. The British government, working with the exiled Stadtholder William of Orange, ordered the seizure of Batavian assets including colonies of the former Dutch Empire. Among the first territories to be attacked were those on the coast of the island of Ceylon, with operations initially focused on the trading port at Trincomalee.
 W
WCornwallis's Retreat was a naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars in which a British Royal Navy squadron of five ships of the line and two frigates was attacked by a much larger French Navy fleet of 12 ships of the line and 11 frigates. The action took place in the waters off the west coast of Brittany on 16–17 June 1795.
 W
WA slave revolt took place in the Dutch colony of Curaçao in 1795, led by Tula, a local slave, and resulted in a month-long conflict on the island between escapees and the colonial government.
 W
WThe East Indies theatre of the French Revolutionary Wars was a series of campaigns related to the major European conflict known as the French Revolutionary Wars, fought between 1793 and 1801 between the new French Republic and its allies and a shifting alliance of rival powers. Although the Indian Ocean was separated by vast distance from the principal theatre of the conflict in Western Europe, it played a significant role due to the economic importance of the region to Great Britain, France's most constant opponent, of its colonies in India and the Far Eastern trade.
 W
WThe invasion of France in 1795 or the Battle of Quiberon was a major landing on the Quiberon peninsula by émigré, counter-revolutionary troops in support of the Chouannerie and Vendée Revolt, beginning on 23 June and finally definitively repulsed on 21 July. It aimed to raise the whole of western France in revolt, bring an end to the French Revolution and restore the French monarchy. The invasion failed; it had a major negative impact, dealing a disastrous blow to the royalist cause.
 W
WGanteaume's expedition of 1795 was a French naval operation in the Aegean Sea in the autumn of 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. Commanded by Commodore Honoré Ganteaume in the ship of the line Républicain, with a squadron of four frigates and two corvettes, the French force was ordered to attack First Coalition shipping in the Aegean Sea. The principal target was the Ottoman city of Smyrna, the most significant trading port of the region, Ganteaume ordered to prey on merchant shipping sailing for European destinations and in particular a large convoy due to sail to Britain.
 W
WThe Battle of Genoa was a naval battle fought between French and allied Anglo-Neapolitan forces on 14 March 1795 in the Gulf of Genoa, a large bay in the Ligurian Sea off the coast of the Republic of Genoa, during the French Revolutionary Wars. The French fleet was led by Contre-amiral Pierre Martin and comprised 14 ships of the line while the British Royal Navy and Neapolitan fleet, under Vice-Admiral William Hotham mustered 13 ships of the line. The battle ended with a minor British-Neapolitan victory and the capture of two French ships.
 W
WThe Order of battle at the Battle of Genoa recounts the British-Neapolitan and French fleets which participated in a short campaign in the Gulf of Genoa during the French Revolutionary Wars. The campaign featured the principal Battle of Genoa on 13–14 March 1795, and an earlier smaller battle off Cap Corse on 8 March. Losses were even: although the British succeeded in capturing two French ships in the main action, two British ships were also lost elsewhere during the campaign. The French foray into the Ligurian Sea was driven back to a safe harbour, resulting in a restoration of the British blockade of Toulon, and leading to a second battle later in the year.
 W
WThe Croisière du Grand Hiver was a French attempt to organise a winter naval campaign in the wake of the Glorious First of June.
 W
WThe Battle of Groix was a large naval engagement which took place near the island of Groix off the Biscay coast of Brittany on 23 June 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. The battle was fought between elements of the British Channel Fleet and the French Atlantic Fleet, which were cruising in the region on separate missions. The British fleet, commanded by Admiral Lord Bridport, was covering an invasion convoy carrying a French Royalist army to invade Quiberon, while the French under Vice-admiral Villaret de Joyeuse had sailed a week earlier to rescue a French convoy from attack by a British squadron. The French fleet had driven off the British squadron in a battle on 17 June known as Cornwallis's Retreat, and were attempting to return to their base at Brest when Bridport's force of 14 ships of the line appeared on 22 June.
 W
WThe Hawkesbury and Nepean Wars (1794–1816) were a series of conflicts where British forces, including armed settlers and detachments of the British Army in Australia, fought against Indigenous clans inhabiting the Hawkesbury River region and the surrounding areas to the west of Sydney. The wars began in 1794, when the British started to construct farms along the river, some of which were established by soldiers.
 W
WThe Battle of the Hyères Islands was a naval engagement fought between a combined British and Neapolitan fleet and the French Mediterranean Fleet on 13 July 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. Since the start of the war in 1793 the French fleet had suffered a series of damaging defeats and was restricted to limited operations off the French Mediterranean Coast in the face of a determined allied blockade. The French fleet, commanded by Pierre Martin, had sought to test the blockade during 1795, and in March had been caught by the British, under William Hotham, in the Gulf of Genoa. At the ensuing Battle of Genoa two French ships were captured before Martin was able to retreat to a safe anchorage.
 W
WThe Battle of Krtsanisi was fought between the Qajar Iran (Persia) and the Georgian armies of the Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti and Kingdom of Imereti at the place of Krtsanisi near Tbilisi, Georgia, from September 8 to September 11, 1795, as part of Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar's war in response to King Heraclius II of Georgia’s alliance with the Russian Empire. The battle resulted in the decisive defeat of the Georgians, capture, and complete destruction of their capital Tbilisi, as well as the temporary absorption of eastern parts of Georgia into the Iranian Empire.
 W
WThe Battle of Loano occurred on 23–24 November 1795 during the War of the First Coalition. The French Army of Italy led by Barthélemy Schérer defeated the combined Austrian and Sardinian forces under Olivier, Count of Wallis.
 W
WThe siege of Luxembourg was a siege by France of the Habsburg-held Fortress of Luxembourg that lasted from 1794 until 7 June 1795, during the French Revolutionary Wars. Although the French army failed to breach the walls of the city, which were renowned as amongst the best in the world, the fortress was forced to surrender after more than seven months.
 W
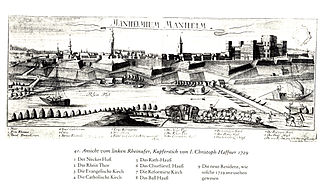
WThe Action at Mannheim 1795 began in April 1795 when two French armies crossed the Rhine and converged on the confluence of the Main and the Rhine. Initial action at Mannheim resulted in a minor skirmish, but the Bavarian commander negotiated a quick truce with the French and withdrew. On 17 October 1795, 17,000 Habsburg Austrian troops under the command of Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser engaged 12,000 soldiers, led by Jean-Charles Pichegru in the grounds outside the city of Mannheim. In a combination of maneuvers, the Habsburg army forced 10,000 of the French forces to withdraw into the city itself; other French troops fled to join neighboring Republican armies. First Coalition forces then laid siege to Mannheim. Subsequent action at neighboring cities forced the French to withdraw further westward toward France; after a month's siege, the 10,000-strong Republican French garrison now commanded by Anne Charles Basset Montaigu surrendered to 25,000 Austrians commanded by Wurmser. This surrender brought the 1795 campaign in Germany to an end. The battle and siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Situated on the Rhine River at its confluence with the Neckar River, Mannheim lies in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in modern-day Germany.
 W
WThe Mediterranean campaign of 1793–1796 was a major theater of conflict in the early years of the French Revolutionary Wars. Fought during the War of the First Coalition, the campaign was primarily contested in the Western Mediterranean between the French Navy's Mediterranean Fleet, based at Toulon in Southern France, and the British Royal Navy's Mediterranean Fleet, supported by the Spanish Navy and the smaller navies of several Italian states. Major fighting was concentrated in the Ligurian Sea, and focused on British maintenance of and French resistance to a British close blockade of the French Mediterranean coast. Additional conflict spread along Mediterranean trade routes, contested by individual warships and small squadrons.
 W
WRichery's expedition was a French naval operation during 1795 and 1796 as part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The operation was led by Commodore Joseph de Richery and comprised two separate cruises; the first was an operation off Cádiz in Southern Spain in which Richery attacked and defeated a large British merchant convoy with a weak escort, taking many prizes. Forced to anchor at Cádiz, the French squadron was subsequently blockaded in the port for almost a year. Richery was enabled to escape in August 1796 by a Spanish fleet, and went on to attack British fisheries off Newfoundland and Labrador before returning to France having inflicted severe damage to British Atlantic trade.
 W
WThe Siege of Roses began on 28 November 1794 and lasted until 4 February 1795 when the Spanish garrison abandoned the port and the forces of the First French Republic took control. Dominique Catherine de Pérignon commanded the French army and Domingo Salvator Izquierdo led the Spanish defenders. The siege took place during the War of the Pyrenees which was part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The war ended in July 1795 and Roses was soon restored to Spain. Roses is a coastal city in northeastern Spain, located 43 kilometres (27 mi) northeast of Girona, Catalonia.
 W
WThe Battle of the Diamond was a planned confrontation between the Catholic Defenders and the Protestant Peep o' Day Boys that took place on 21 September 1795 near Loughgall, County Armagh, Ireland. The Peep o' Day Boys were the victors, killing some 6 Defenders, with some wounded Peep o day boys in return. It led to the foundation of the Orange Order and the onset of "the Armagh outrages".
 W
WThe Tripolitanian civil war was a conflict from 1793 to 1795 which occurred in what is today the country of Libya. Ali Benghul, an Ottoman officer, deposed Hamet Karamanli, the ruler of Tripolitania, who had ruled since the end of the corrupt and ineffective rule of Ali I in 1793. Hamet and his brother Yusuf returned to Tripoli with the aid of the Bey of Tunis and took control of the throne.