 W
WThe Second Hundred Years' War is a periodization or historical era term used by some historians to describe the series of military conflicts between Great Britain and France that occurred from about 1689 to 1815. For the context see International relations, 1648–1814.
 W
WThis is a list of wars that began between 1500 and 1799. Other wars can be found in the historical lists of wars and the list of wars extended by diplomatic irregularity. Conflicts of this era include the Thirty Years' War in Europe, the Kongo Civil War in Africa, the Qing conquest of the Ming in Asia, the Spanish conquest of Peru in South America, and the American Revolutionary War in North America.
 W
WThe American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, the First Nations Wars in Canada and the Indian Wars is the collective name for the various armed conflicts that were fought by European governments and colonists, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settlers, against various American Indian and First Nation tribes. These conflicts occurred in North America from the time of the earliest colonial settlements in the 17th century until the early 20th century. The various wars resulted from a wide variety of factors, including cultural clashes, land disputes, and criminal acts committed. The European powers and their colonies also enlisted Indian tribes to help them conduct warfare against each other's colonial settlements. After the American Revolution, many conflicts were local to specific states or regions and frequently involved disputes over land use; some entailed cycles of violent reprisal.
 W
WThe Anglo–Mysore Wars were a series of wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Kingdom of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company, Maratha Empire and the Nizam of Hyderabad on the other. Hyder Ali and his successor Tipu Sultan fought a war on four fronts with the British attacking from the west, south and east, while the Nizam's forces attacked from the north. The fourth war resulted in the overthrow of the house of Hyder Ali and Tipu, and the dismantlement of Mysore to the benefit of the East India Company, which took control of much of the Indian subcontinent.
 W
WThe Australian frontier wars is a term applied by some historians to violent conflicts between Indigenous Australians and white settlers during the British colonisation of Australia. The first fighting took place several months after the landing of the First Fleet in January 1788 and the last clashes occurred in the early 20th century, as late as 1934. A minimum of 40,000 Indigenous Australians and between 2,000 and 2,500 settlers died in the wars. However, recent scholarship on the frontier wars in what is now the state of Queensland indicates that Indigenous fatalities may have been significantly higher. Indeed, while battles and massacres occurred in a number of locations across Australia, they were particularly bloody in Queensland, owing to its comparatively larger pre-contact Indigenous population.
 W
WThe 1740 to 1748 War of the Austrian Succession was the last Great Power conflict with the Bourbon-Habsburg dynastic conflict at its heart, and marked the rise of Prussia as a major power. Related conflicts include King George's War, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War, as well as the First and Second Silesian Wars.
 W
WCamisards were Huguenots of the rugged and isolated Cévennes region and the Vaunage in southern France. In the early 1700s, they raised an insurrection against the persecutions which followed Louis XIV's Revocation of the Edict of Nantes, making Protestantism illegal. The Camisards operated throughout the mainly Protestant Cévennes region including the Vaunage and the parts of the Camargue around Aigues Mortes. The revolt broke out in 1702, with the worst of the fighting continuing until 1704, then skirmishes until 1710 and a final peace by 1715. The Edict of Tolerance was not finally signed until 1787.
 W
WThe campaigns of Nader Shah, or the Naderian Wars, were a series of conflicts fought in the early to mid-eighteenth century throughout Central Eurasia primarily by the Iranian conqueror Nader Shah. His campaigns originated from the overthrow of the Iranian Safavid dynasty by the Hotaki Afghans. In the ensuing collapse and fragmentation of the empire after the capture of the Iranian capital of Isfahan by the Afghans, a claimant to the Safavid throne, Tahmasp II, accepted Nader into his service. After having subdued north-west Iran as well as neutralising the Abdali Afghans to the east as well as turning Tahmasp II into a vassal, Nader marched against the Hotaki Afghans in occupation of the rest of the country. In a series of incredible victories the Afghans were decimated and Tahmasp II returned to the throne as a restored Safavid monarch.
 W
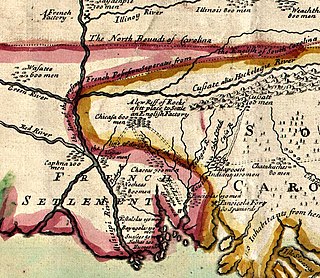
WThe Chickasaw Wars were fought in the 18th century between the Chickasaw allied with the British against the French and their allies the Choctaws and Illinois Confederation. The Province of Louisiana extended from Illinois to New Orleans, and the French fought to secure their communications along the Mississippi River. The Chickasaw, dwelling in northern Mississippi and western Tennessee, lay across the French path. Much to the eventual advantage of the British and the later United States, the Chickasaw successfully held their ground. The wars came to an end only with the French cession of New France to the British in 1763 according to terms of the Treaty of Paris.
 W
WColonial American military history is the military record of the Thirteen Colonies from their founding to the American Revolution in 1775.
 W
WBetween 1550 and 1795, there were a series of wars between the regency of Algiers and its allies—local sultanates or tribal confederations—and the Sherifian dynasties that ruled Morocco. The origins of these conflicts are multiple and overlapping. The state-owned enterprise of the regency of Algiers in the central Maghreb around Algiers as a new political center and its integration with the Ottoman Empire was at the expense of the Zayyanids of Tlemcen in the west. The latter in recurrent conflicts at the beginning of the sixteenth century with the regency on the one hand and the Spaniards on the other end up seeing their domain integrated with the regency. Their weakening stirred the Saadian lusts and their claim on the western Algerian. If the regency of Algiers confirms its control over Tlemcen and Orania it does not have the means to launch long campaigns in the Saharan confines that it delegates to various tribal confederations like the Ouled Sidi Cheikh. The Saadians blocked to the north by the Spanish Empire and the Regency of Algiers then find a South-Saharan outlet for the extension of their Empire. These conflicts and the resulting agreements foreshadow the borders and delimitations between the modern nation-states of the Maghreb.
 W
WThe Dzungar–Qing Wars (1687–1757) were a decades-long series of conflicts that pitted the Dzungar Khanate against the Qing dynasty of China and their Mongolian vassals. Fighting took place over a wide swath of Inner Asia, from present-day central and eastern Mongolia to Tibet, Qinghai, and Xinjiang regions of present-day China. Qing victories ultimately led to the incorporation of Outer Mongolia, Tibet and Xinjiang into the Qing Empire that was to last until the fall of the dynasty in 1911–1912, and the genocide of much of the Dzungar population in conquered areas.
 W
WThe European wars of religion were a series of Christian religious wars which were waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic countries of Europe. However, religion was only one of the causes, which also included revolts, territorial ambitions, and Great Power conflicts. For example, by the end of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), Catholic France was allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy. The wars were largely ended by the Peace of Westphalia (1648), establishing a new political order now known as Westphalian sovereignty.
 W
WJean de Forcade de Biaix, aka Jean de Forcade, Marquis de Biaix, aka Jean-Quirin de Forcade de Biaix, aka Jean Quérin von Forcade, Herr von Biaix, aka Johann Querin de Forcade, Herr zu Biaix, aka Johann Quirin von Forkade de Biaix was a Huguenot, a descendant of the noble family of Forcade and Lieutenant General in the service of the Kingdom of Prussia. He was the Regimentschef of the 23rd Prussian Infantry Regiment, Commandant of the Royal Residence in Berlin, Gouverneur militaire of Berlin, a Knight of the Order of the Black Eagle a member of King Frederick I of Prussia's "Tobacco Collegium". and president of the Grand Directoire 1718–1729, the deliberative and decision-making body responsible for all Huguenot affairs in the kingdom.
 W
WFrench assistance to Nguyễn Phúc Ánh, the future Emperor of Vietnam and the founder of the Nguyễn Dynasty, covered a period from 1777 to 1820. From 1777, Mgr Pigneau de Behaine, of the Paris Foreign Missions Society, had taken to protecting the young Vietnamese prince who was fleeing from the offensive of the Tây Sơn. Pigneau de Behaine went to France to obtain military aid, and secured a France-Vietnam alliance that was signed through the 1787 Treaty of Versailles between the king of France, Louis XVI, and Prince Nguyễn Phúc Ánh. As the French regime was under considerable strain at the eve of the French Revolution, France was unable to follow through with the application of the treaty. However, Mgr Pigneau de Behaine persisted in his efforts and, with the support of French individuals and traders, mounted a force of French soldiers and officers that would contribute to the modernization of the armies of Nguyễn Ánh, making possible his victory and his reconquest of all of Vietnam by 1802. A few French officers would remain in Vietnam after the victory, becoming prominent mandarins. The last of them left in 1824 following the enthronement of Minh Mạng, Gia Long's successor. The terms of the 1787 Treaty of Alliance would still remain one of the justifications of French forces when they demanded the remittance of Đà Nẵng in 1847.
 W
WThe Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony–Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715.
 W
WThe haidamakas, also haidamaky or haidamaks were Ukrainian cossack paramilitary outfits composed of commoners, and impoverished noblemen in the eastern part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was a reaction to the Commonwealth's actions that were directed to reconstitute its orders on territory of right-bank Ukraine, which was secured following ratification of the Treaty of Perpetual Peace with Muscovy in 1710.
 W
WThere were several Mongol invasions of Tibet. The earliest is the alleged plot to invade Tibet by Genghis Khan in 1206, which is considered anachronistic; there is no evidence of Mongol-Tibetan encounters prior to the military campaign in 1240. The first confirmed campaign is the invasion of Tibet by the Mongol general Doorda Darkhan in 1240, a campaign of 30,000 troops that resulted in 500 casualties. The campaign was smaller than the full-scale invasions used by the Mongols against large empires. The purpose of this attack is unclear, and is still in debate among Tibetologists. Then in the late 1240s Mongolian prince Godan invited Sakya lama Sakya Pandita, who urged other leading Tibetan figures to submit to Mongol authority. This is generally considered to have marked the beginning of Mongol rule over Tibet, as well as the establishment of patron and priest relationship between Mongols and Tibetans. These relations were continued by Kublai Khan, who founded the Mongol Yuan dynasty and granted authority over whole Tibet to Drogon Chogyal Phagpa, nephew of Sakya Pandita. The Sakya-Mongol administrative system and Yuan administrative rule over the region lasted until the mid-14th century, when the Yuan dynasty began to crumble.
 W
WThe Kandyan Wars refers generally to the period of warfare between the British colonial forces and the Kingdom of Kandy, on the island of what is now Sri Lanka, between 1796 and 1818. More specifically it is used to describe the expeditionary campaigns of the British Army in the Kingdom of Kandy in 1803 and 1815.
 W
WThe Mughal–Maratha Wars, also called the Maratha War of Independence, were fought between the Maratha Empire and the Mughal Empire from 1680 to 1707. The Deccan Wars started in 1680 with the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb’s invasion of the Maratha enclave in Bijapur established by Chatrapati Shivaji. After the death of Aurangzeb, Marathas defeated the Mughals in Delhi and Bhopal, and extended their empire till Peshawar by 1758.
 W
WThe term Navajo Wars covers at least three distinct periods of conflict in the American West: the Navajo against the Spanish ; the Navajo against the Mexican government ; and the Navajo against the United States. These conflicts ranged from small-scale raiding to large expeditions mounted by governments into territory controlled by the Navajo. The Navajo Wars also encompass the widespread raiding that took place throughout the period; the Navajo raided other tribes and nearby settlements, who in return raided into Navajo territory, creating a cycle of raiding that perpetuated the conflict.
 W
WThe Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th through the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy, which was at times supported by the Holy Roman Empire, Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Habsburg Spain. The wars were dominated by land campaigns in Hungary, including Transylvania and Vojvodina, Croatia and central Serbia.
 W
WThe persecution of Huguenots under Louis XV refers to hostile activities against French Protestants between 1715 and 1774 during the reign of Louis XV.
 W
WThe War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–1720) was caused by Spanish attempts to recover territorial losses agreed by the 1713 Peace of Utrecht. Conducted primarily in Italy, it included minor engagements in the Americas and Northern Europe as well as the Spanish-backed 1719 Jacobite Rising. Spain recaptured Sardinia in 1717 without opposition, followed by a landing on Sicily in July 1718. That led to the Quadruple Alliance on 2 August 1718 of Britain, France, Emperor Charles VI and the Dutch Republic. The war ended with the 1720 Treaty of The Hague, which restored the position prior to 1717 but with Savoy and Austria exchanging Sardinia and Sicily. Spain regained the Kingdom of Naples during the War of the Polish Succession (1733-1735).
 W
WQueen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in England's Thirteen American Colonies during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In Europe, it is generally viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession; in the Americas, it is more commonly viewed as a standalone conflict. It is also known as the Third Indian War or as the Second Intercolonial War in France.
 W
WThe Second Hundred Years' War is a periodization or historical era term used by some historians to describe the series of military conflicts between Great Britain and France that occurred from about 1689 to 1815. For the context see International relations, 1648–1814.
 W
WThe Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict, "a struggle for global primacy between Britain and France," which also had a major impact on the Spanish Empire. In Europe, the conflict arose from issues left unresolved by the War of the Austrian Succession, with Prussia seeking greater dominance. Long standing colonial rivalries between Britain against France and Spain in North America and the Caribbean islands valuable for sugar were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. In Europe, the war broke out over territorial disputes between Prussia and Austria, which wanted to regain Silesia after it was captured by Prussia in the previous war. Britain, France, and Spain fought both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power.
 W
WThe Sino-Burmese War, also known as the Qing invasions of Burma or the Myanmar campaign of the Qing dynasty, was a war fought between the Qing dynasty of China and the Konbaung dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). China under the Qianlong Emperor launched four invasions of Burma between 1765 and 1769, which were considered as one of his Ten Great Campaigns. Nonetheless, the war, which claimed the lives of over 70,000 Chinese soldiers and four commanders, is sometimes described as "the most disastrous frontier war that the Qing dynasty had ever waged", and one that "assured Burmese independence". Burma's successful defense laid the foundation for the present-day boundary between the two countries.
 W
WThe Battle of Sonipat was fought between Sikhs and Mughal Empire in 1709.
 W
WThe Tây Sơn Wars, often known as the Vietnamese civil war of 1771-1802 were a series of military conflicts association followed the Vietnamese peasant uprising of Tây Sơn led three brothers Nguyễn Nhạc, Nguyễn Huệ, and Nguyễn Lữ. They began in 1771 and end in 1802 when Nguyễn Phúc Ánh or Emperor Gia Long, an descendant of the Nguyễn lord, defeated the Tay Son and reunited Đại Việt, then renamed the country to Vietnam.
 W
WThe Three Hundred and Thirty Five Years' War was an alleged state of war between the Netherlands and the Isles of Scilly, and its existence is disputed. It is said to have been extended by the lack of a peace treaty for 335 years without a single shot being fired, which would make it one of the world's longest wars, and a bloodless war. Despite the uncertain validity of the declaration of war, and thus uncertainty about whether or not a state of war ever actually existed, peace was finally declared in 1986, bringing an end to any hypothetical war that may have been legally considered to exist.
 W
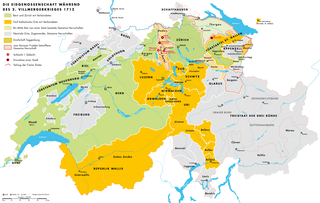
WThe Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy, that took place from 12 April until 11 August 1712. On the one hand there were the Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint Gall, on the other the Protestant cantons of Bern and Zürich as well as the abbatial subjects of Toggenburg. The conflict was simultaneously a religious war, a war for the hegemony within the Confederacy and an uprising of subjects. The war ended in a Protestant victory and toppled the balance of political power within the Confederacy.
 W
WThe War of the Polish Succession was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of their own national interests. France and Spain, the two Bourbon powers, attempted to test the power of the Austrian Habsburgs in western Europe, as did the Kingdom of Prussia, whilst Saxony and Russia mobilized to support the eventual Polish victor. The fighting in Poland resulted in the accession of Augustus III, who in addition to Russia and Saxony, was politically supported by the Habsburgs.
 W
WThe Xhosa Wars were a series of nine wars or flare-ups between the Xhosa Kingdom and European settlers in what is now the Eastern Cape in South Africa. These events were the longest-running military action in the history of African colonialism.