 W
WThe Selton Hill Ambush took place on 11 March 1921, during the Irish War of Independence. An Irish Republican Army (IRA) flying column was ambushed by members of the RIC Auxiliary Division at Selton Hill, County Leitrim. Six IRA officers of the Leitrim Brigade were killed.
 W
WThe Battle of (the) Annaberg was the biggest battle of the Silesian Uprisings. The battle, which took place between May 21–26, 1921, was fought at the Annaberg, a strategic hill near the village of Annaberg O.S., located southeast of Oppeln (Opole) in Upper Silesia, Weimar Germany. After the hill had been captured by irregular Polish-Silesian units in the Third Silesian Uprising, German Freikorps pushed the Polish forces back. The final border was determined by political and diplomatic efforts.
 W
WThe Battle of Annual was fought on July 22, 1921, at Annual in northeastern Morocco, between the Spanish Army and Berber Riffian combatants during the Rif War. The Spanish suffered a major military defeat, almost always referred to by the Spanish as the Disaster of Annual, which led to major political crises and a redefinition of Spanish colonial policy toward the Rif.
 W
WThe Battle of Blair Mountain was the largest labor uprising in United States history and the largest armed uprising since the American Civil War. The conflict occurred in Logan County, West Virginia, as part of the Coal Wars, a series of early-20th-century labor disputes in Appalachia. Up to 100 people were killed, and many more arrested. The United Mine Workers saw major declines in membership, but the long-term publicity led to some improvements in working conditions.
 W
WThe Battle of Kütahya–Eskişehir, was fought between July 10 and July 24, 1921 when the Greek Army of Asia Minor defeated the Turkish troops commanded by İsmet Pasha in defence of the line of Kara Hisâr-ı Sahib -Kütahya-Eskişehir.
 W
WThe Battle of Sakarya, also known as the Battle of the Sangarios, was an important engagement in the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922), the western front of the Turkish War of Independence.
 W
WBozner Blutsonntag refers to the events of 24 April 1921 in Bozen. It was the first climax of fascist violence in South Tyrol, a German-speaking province that was annexed by Italy after World War I.
 W
WAfter Miklós Horthy was chosen Regent of Hungary on 1 March 1920, Charles I of Austria, who reigned in Hungary as Charles IV, made two unsuccessful attempts to retake the throne. His attempts are also called the "First" and "Second Royal coups d'état" respectively.
 W
WThe Clonbanin ambush was an ambush carried out by the Irish Republican Army (IRA) on 5 March 1921, during the Irish War of Independence. It took place in the townland of Clonbanin, County Cork.
 W
WThe Coto War was a conflict between Panama and Costa Rica fought between 21 February and 5 March 1921. The casus belli occurred when an expeditionary force led by Colonel Héctor Zúñiga Mora occupying on behalf of Costa Rica the town of Pueblo Nuevo de Coto, a hamlet on the banks of the river of the same name that belonged at that time to the district of Alanje, in the Panamanian province of Chiriquí. Zúñiga justified the incursion by the fact that there was no definite border between Costa Rica and Panama.
 W
WThe Crossbarry Ambush or Battle of Crossbarry occurred on 19 March 1921 and was one of the largest engagements of the Irish War of Independence. It took place near the small village of Crossbarry in County Cork, about 20 km south-west of Cork city. About a hundred Irish Republican Army (IRA) volunteers, commanded by Tom Barry, escaped an attempt by about 1,200 British troops to encircle them. During the hour-long battle, ten British troops and three IRA volunteers were killed.
 W
WThe Dagestan uprising of 1920-1921 was an event during the Russian Civil War.
 W
WThe Dromkeen ambush took place on 3 February 1921, during the Irish War of Independence, at Dromkeen in County Limerick. The Irish Republican Army (IRA) ambushed a Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) patrol, killing 11 policemen.
 W
WThe East Karelian Uprising and the Soviet–Finnish conflict 1921–1922 were an attempt by a group of East Karelian separatists to gain independence from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. They were aided by a number of Finnish volunteers, starting from 6 November 1921. The conflict ended on 21 March 1922 with the Agreements between the governments of Soviet Russia and Finland about the measures of maintenance of the inviolability of the Soviet–Finnish border. The conflict is regarded in Finland as one of the heimosodat – "Kinship Wars".
 W
WThe February Uprising was an anti-Bolshevik rebellion by the nationalist Armenian Revolutionary Federation which started on February 13 and was suppressed on April 2, 1921 by the recapture of Yerevan by Bolshevik forces.
 W
WThe Franco–Turkish War, known as the Cilicia Campaign in France and as the Southern Front of the Turkish War of Independence in Turkey, was a series of conflicts fought between France and the Turkish National Forces from December 1918 to October 1921 in the aftermath of World War I. French interest in the region resulted from the Sykes-Picot Agreement and returning Armenian refugees of the Armenian Genocide back to their homes.
 W
WThe Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922 was fought between Greece and the Turkish National Movement during the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire in the aftermath of World War I, between May 1919 and October 1922.
 W
WThe Headford Ambush was carried out by the Irish Republican Army (IRA) on 21 March 1921, during the Irish War of Independence. The IRA's 2nd Kerry Brigade ambushed a train carrying British troops of the Royal Fusiliers at Headford Junction railway station near Killarney, County Kerry. This sparked a battle lasting almost an hour, in which at least 14 people were killed – nine British soldiers, two IRA volunteers and three civilians. The IRA withdrew after another train carrying British troops arrived.
 W
WThe Irish War of Independence or Anglo-Irish War was a guerrilla war fought in Ireland from 1919 to 1921 between the Irish Republican Army and British forces: the British Army, along with the quasi-military Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) and its paramilitary forces the Auxiliaries and Ulster Special Constabulary (USC). It was an escalation of the Irish revolutionary period into warfare.
 W
WThe Kilmeena ambush was an action during the Irish War of Independence that took place at Kilmeena, County Mayo on 19 May 1921. The ambush ended in defeat for the local West Mayo Irish Republican Army (IRA), with six IRA volunteers killed and seven wounded. Two members of the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) and one Black and Tan were also killed in the action.
 W
WThe Kronstadt rebellion or Kronstadt mutiny was an insurrection of the Soviet sailors, soldiers and civilians of the port city of Kronstadt against the Bolshevik government of the Russian SFSR. It was the last major revolt against the Bolshevik regime on Russian territory during the Russian Civil War that ravaged the country. The revolt began on March 1, 1921, in the city's naval fortress, located on the island of Kotlin in the Gulf of Finland. Traditionally, Kronstadt served as the base of the Russian Baltic fleet and as defense for the approaches to Petrograd, located 55 kilometres (34 mi) from the island. For sixteen days, the rebels rose in opposition to the Soviet government they had helped to consolidate.
 W
WThe Malabar rebellion in 1921 started as resistance against the British colonial rule, the prevailing feudal system, and in favour of the Khilafat Movement in South Malabar but ended in communal violence against Hindus. There were a series of clashes between the Mappila peasantry and their landlords, supported by the British, throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries. The heavy-handed crackdown of the Khilafat Movement by the British Authorities was met by resistance in the Eranad and Valluvanad taluks of Malabar. In the initial stages, the movement had the support of Mohandas Gandhi and other Indian nationalist leaders, and a number of clashes took place between Khilafat volunteers and other religious communities, but the violence soon spread across the region. The Mappilas attacked and took control of police stations, British government offices, courts and government treasuries. Though the crowds who attacked and destroyed the public offices in Eranad, Valluvanad, and Ponnani Taluks were Mappilas, sometimes Nambudiris, Nairs and Thiyyas also acted as leaders in many parts of Valluvanad. However the British historians called the rebellion as Mappila revolt.
 W
WThe Mongolian Revolution of 1921 was a military and political event by which Mongolian revolutionaries, with the assistance of the Soviet Red Army, expelled Russian White Guards from the country, and founded the Mongolian People's Republic in 1924. Although nominally independent, the Mongolian People's Republic was a satellite state of the Soviet Union until a third Mongolian revolution in January 1990. The revolution also ended Chinese Beiyang government's occupation of Mongolia, which had existed since 1919. The official Mongolian name of the revolution is "People's Revolution of 1921" or simply "People's Revolution".
 W
WOperation Nemesis was a covert operation and an assassination campaign by the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (Dashnaktsutyun) carried out between 1920 and 1922, during which a number of former Ottoman political and military figures were assassinated for their role in the Armenian Genocide, as well as Azerbaijani figures for the 1918 massacre of Armenians in Baku. Shahan Natalie and Armen Garo are considered its masterminds. It was named after the Greek goddess of divine retribution, Nemesis.
 W
WPatagonia Rebelde was the name given to the uprising and violent suppression of a rural workers' strike in the Argentine province of Santa Cruz in Patagonia between 1920 and 1922. The uprising was put down by Colonel Héctor Benigno Varela's 10th Cavalry Regiment of the Argentine Army under the orders of President Hipólito Yrigoyen. Approximately 300-1,500 rural workers were shot and killed by the 10th Cavalry Regiment in the course of the operations, many of them executed by firing squads after surrendering. Most of the executed were Spanish and Chilean workers who had sought refuge in Argentina's Patagonia after their violent strike in the city of Puerto Natales in southern Chile on 27 July 1920 was crushed by the Chilean authorities, at the cost of four carabineers killed. At least two Argentine soldiers, three local policemen and a number of ranch owners and their relatives also died during the strife. Several of the captured women were raped in the uprising as the rebel forces fought for control of the territory. The most detailed narrative of these events is that by Osvaldo Bayer, summarized in English by Bruce Chatwin in 1976.
 W
WThe Rand Rebellion was an armed uprising of white miners in the Witwatersrand region of South Africa, in March 1922. Jimmy Green, a prominent politician in the Labour Party, was one of the leaders of the strike.
 W
WThe Red Army invasion of Georgia, also known as the Soviet–Georgian War or the Soviet invasion of Georgia, was a military campaign by the Russian Red Army aimed at overthrowing the Social-Democratic (Menshevik) government of the Democratic Republic of Georgia (DRG) and installing a Bolshevik regime in the country. The conflict was a result of expansionist policy by the Russians, who aimed to control as much as possible of the lands which had been part of the former Russian Empire until the turbulent events of the First World War, as well as the revolutionary efforts of mostly Russian-based Georgian Bolsheviks, who did not have sufficient support in their native country to seize power without external intervention.
 W
WThe Rif War was an armed conflict fought from 1920 to 1927 between the colonial power Spain and the Berber tribes of the Rif mountainous region of Morocco. Led by Abd el-Krim, the Riffians at first inflicted several defeats on the Spanish forces by using guerrilla tactics and captured European weapons. After France's military intervention against Abd el-Krim's forces and the major landing of Spanish troops at Al Hoceima, considered the first amphibious landing in history to involve the use of tanks and aircraft, Abd el-Krim surrendered to the French and was taken into exile.
 W
WThe Scramoge ambush was an ambush carried out by the Irish Republican Army (IRA) on 23 March 1921, during the Irish War of Independence. The IRA ambushed a lorry carrying British troops and Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) officers at Scramoge, near Strokestown in County Roscommon. Three British soldiers and an RIC officer were killed, while two RIC 'Black and Tans' were captured and shot dead shortly after.
 W
WThe Sheemore ambush was an ambush carried out by the Irish Republican Army (IRA) on 4 March 1921, during the Irish War of Independence. It took place at Sheemore near Carrick-on-Shannon, County Leitrim.
 W
WThe Simko Shikak revolt refers to an armed Ottoman-backed tribal Kurdish uprising against the Qajar dynasty of Iran from 1918 to 1922, led by Kurdish chieftain Simko Shikak from the Shekak tribe. The revolt is often referred as the first modern conflict involving Iranian Kurds with separatist ambitions.
 W
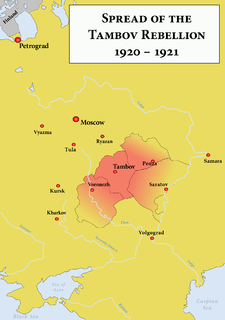
WThe Tambov Rebellion of 1920–1921 was one of the largest and best-organized peasant rebellions challenging the Bolshevik regime during the Russian Civil War. The uprising took place in the territories of the modern Tambov Oblast and part of the Voronezh Oblast, less than 300 miles southeast of Moscow.
 W
WThe Ukrainian War of Independence, a period of sustained warlike conflict, lasted from 1917 to 1921 and resulted in the establishment and development of a Ukrainian republic, most of which was later absorbed into the Soviet Union as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic of 1922–1991.
 W
WThe Civil War in Ukraine is the term commonly used in post-Soviet Ukraine for the events taking place between 1917–21, nowadays regarded essentially as a war between the Ukrainian People's Republic and the bolsheviks. The war ensued soon after the October Revolution when Lenin dispatched the Antonov's expeditionary group to Ukraine and Southern Russia.
 W
WAccording to the Treaty of Trianon, the city of Sopron in western Hungary and its surroundings were assigned to Austria. After an uprising in 1921 in this region, a referendum was held and 65.8% of the votes were in favor of belonging to Hungary. This referendum was accepted by the major powers and the transition of Sopron and its surrounding 8 villages from Austria to Hungary was the only serious territorial revision in the years following the Treaty of Trianon.
 W
WThe Zaian War was fought between France and the Zaian confederation of Berber tribes in Morocco between 1914 and 1921 during the French conquest of Morocco. Morocco had become a French protectorate in 1912, and Resident-General Louis-Hubert Lyautey sought to extend French influence eastwards through the Middle Atlas mountains towards French Algeria. This was opposed by the Zaians, led by Mouha ou Hammou Zayani. The war began well for the French, who quickly took the key towns of Taza and Khénifra. Despite the loss of their base at Khénifra, the Zaians inflicted heavy losses on the French, who responded by establishing groupes mobiles, combined arms formations that mixed regular and irregular infantry, cavalry and artillery into a single force.