 W
WList of conflicts in Canada is a timeline of events that includes wars, battles, skirmishes, major terrorist attacks, riots and other related items that have occurred in the country of Canada's current geographical area. A complete list of terrorist attacks can be found at terrorism in Canada.
 W
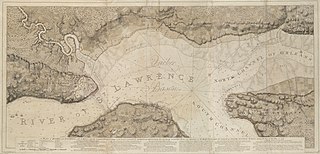
WThe Battle of Beauport, also known as the Battle of Montmorency, fought on 31 July 1759, was an important confrontation between the British and French Armed Forces during the Seven Years' War of the French province of Canada. The attack conducted by the British against the French defense line of Beauport, some 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) east of Quebec was checked, and the British soldiers of General James Wolfe retreated with 443 casualties and losses.
 W
WThe Battle of Bloody Creek was fought on 10/21 June 1711 during Queen Anne's War. An Abenaki militia successfully ambushed British and New England soldiers at a place that became known as Bloody Creek after the battles fought there. The creek empties into the Annapolis River at present day Carleton Corner, Nova Scotia, and was also the location of a battle in 1757.
 W
WThe Battle of Carillon, also known as the 1758 Battle of Ticonderoga, was fought on July 8, 1758, during the French and Indian War. It was fought near Fort Carillon on the shore of Lake Champlain in the frontier area between the British colony of New York and the French colony of New France.
 W
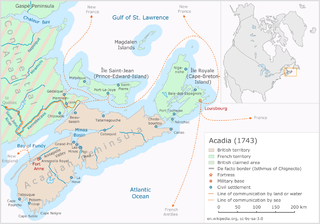
WThe Battle of Chedabucto occurred against Fort St. Louis in Chedabucto on June 3, 1690 during King William's War (1689–97). The battle was part of Sir William Phips and New England's military campaign against Acadia. New England sent an overwhelming force to conquer Acadia by capturing the capital Port Royal, Chedabucto, and attacking other villages. The aftermath of these battles was unlike any of the previous military campaigns against Acadia. The violence of the attacks alienated many of the Acadians from the New Englanders, broke their trust, and made it difficult for them to deal amicably with the English-speakers.
 W
WThe Chilcotin War, the Chilcotin Uprising or the Bute Inlet Massacre was a confrontation in 1864 between members of the Tsilhqot'in (Chilcotin) people in British Columbia and white road construction workers. Fourteen men employed by Alfred Waddington in the building of a road from Bute Inlet were killed, as well as a number of men with a pack-train near Anahim Lake and a settler at Puntzi Lake.
 W
WThe Cypress Hills Massacre occurred on June 1, 1873, near Battle Creek in the Cypress Hills region of Canada's North-West Territories. It involved a group of American bison hunters, American wolf hunters or "wolfers", American and Canadian whisky traders, Métis cargo haulers or "freighters", and a camp of Assiniboine people. Thirteen or more Assiniboine warriors and one wolfer died in the conflict. The Cypress Hills Massacre prompted the Canadian government to accelerate the recruitment and deployment of the newly formed North-West Mounted Police.
 W
WFather Le Loutre's War (1749–1755), also known as the Indian War, the Micmac War and the Anglo-Micmac War, took place between King George's War and the French and Indian War in Acadia and Nova Scotia. On one side of the conflict, the British and New England colonists were led by British Officer Charles Lawrence and New England Ranger John Gorham. On the other side, Father Jean-Louis Le Loutre led the Mi'kmaq and the Acadia militia in guerrilla warfare against settlers and British forces.
 W
WThe Fenian raids were carried out by the Fenian Brotherhood, an Irish Republican organization based in the United States, on British Army forts, customs posts and other targets in Canada, in 1866, and again from 1870 to 1871. A number of separate incursions by the Fenian Brotherhood into Canada were undertaken to bring pressure on Great Britain to withdraw from Ireland, although none of these raids achieved their aims.
 W
WFort Defiance was a small outpost built by the crew of the Columbia Rediviva for use as winter quarters during 1791-1792 on Meares Island in present-day British Columbia, Canada. They were under the command of American merchant and maritime fur trader Captain Robert Gray.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Pitt was part of a Cree uprising coinciding with the Métis revolt that started the North-West Rebellion in 1885. Cree warriors began attacking Canadian settlements on April 2. On April 15, they captured Fort Pitt from a detachment of North-West Mounted Police.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort St. Jean was conducted by American Brigadier General Richard Montgomery on the town and fort of Saint-Jean in the British province of Quebec during the American Revolutionary War. The siege lasted from September 17 to November 3, 1775.
 W
WThe Battle of Grand Pré, also known as the Battle of Minas and the Grand Pré Massacre, was a battle in King George's War that took place between New England forces and Canadian, Mi'kmaq and Acadian forces at present-day Grand-Pré, Nova Scotia in the winter of 1747 during the War of the Austrian Succession. The New England forces were contained to Annapolis Royal and wanted to secure the head of the Bay of Fundy. Led by Nicolas Antoine II Coulon de Villiers and Louis de la Corne, Chevalier de la Corne under orders from Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Roch de Ramezay, the French forces surprised and defeated a force of British troops, Massachusetts militia and rangers that were quartered in the village.
 W
WThe Battle of Hudson's Bay, also known as the Battle of York Factory, was a naval battle fought during the War of the Grand Alliance. The battle took place on 5 September 1697, when a French warship commanded by Captain Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville defeated an English squadron commanded by Captain John Fletcher. As a result of this battle, the French took York Factory, a trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company.
 W
WThe Invasion of Quebec in 1775 was the first major military initiative by the newly formed Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. The objective of the campaign was to gain military control of the British Province of Quebec, and convince French-speaking Canadiens to join the revolution on the side of the Thirteen Colonies. One expedition left Fort Ticonderoga under Richard Montgomery, besieged and captured Fort St. Johns, and very nearly captured British General Guy Carleton when taking Montreal. The other expedition left Cambridge, Massachusetts, under Benedict Arnold, and traveled with great difficulty through the wilderness of Maine to Quebec City. The two forces joined there, but they were defeated at the Battle of Quebec in December 1775.
 W
WKing George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in the British provinces of New York, Massachusetts Bay, New Hampshire, and Nova Scotia. Its most significant action was an expedition organized by Massachusetts Governor William Shirley that besieged and ultimately captured the French fortress of Louisbourg, on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, in 1745. In French, it is known as the Troisième Guerre Intercoloniale or Third Intercolonial War.
 W
WThe Lower Canada Rebellion, commonly referred to as the Patriots' War in French, is the name given to the armed conflict in 1837–38 between the rebels of Lower Canada and the government of Lower Canada. Together with the simultaneous rebellion in the neighbouring colony of Upper Canada, it formed the Rebellions of 1837–38.
 W
WThe Montreal Campaign, also known as the Fall of Montreal, was a British three-pronged offensive against Montreal which took place from July 2 to 9 September 1760 during the French and Indian War as part of the global Seven Years' War. The campaign, pitted against an outnumbered and outsupplied French army, led to the capitulation and occupation of Montreal, the largest remaining city in French Canada.
 W
WThe Newfoundland expedition was a series of fleet manoeuvres and amphibious landings in the coasts of Newfoundland, Labrador and Saint Pierre and Miquelon carried out by the combined French and Spanish fleets during the French Revolutionary Wars. This expedition, composed of seven ships of the line and three frigates under the orders of Rear-Admiral Richery sailed from Cadiz in August 1796 accompanied by a much stronger Spanish squadron, commanded by General Solano, which had the aim of escorting it to the coast of Newfoundland.
 W
WThe Nootka Crisis, also known as the Spanish Armament, was an international incident and political dispute between the Spanish Empire, the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the fledgling United States of America triggered by a series of events that took place during the summer of 1789 at the Spanish outpost Santa Cruz de Nuca, in Nootka Sound, present-day British Columbia, Canada. The commander of the outpost, Jose Esteban Martínez, seized some British commercial ships which had come for the maritime fur trade and to build a permanent post at Nootka Sound. Public outcry in England led to the mobilization of the British and Spanish navies and the possibility of war. Both sides called upon allies, and although Spain's key ally France also mobilized their navy, they soon announced they would not go to war. Without French help Spain had little hope against the allied forces of the British and the Dutch, resulting in Spain seeking a diplomatic solution and making concessions.
 W
WThe North-West Rebellion of 1885 was a rebellion by the Métis people under Louis Riel and an associated uprising by First Nations Cree and Assiniboine of the District of Saskatchewan against the Canadian government. Many Métis felt that Canada was not protecting their rights, their land, and their survival as a distinct people.
 W
WThe Pemmican War was a series of armed confrontations during the North American fur trade between the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and the North West Company (NWC) in the years following the establishment of the Red River Colony in 1812 by Lord Selkirk. It ended in 1821 when the NWC merged with the HBC.
 W
WThe Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the United States and the United Kingdom over the British–U.S. border in the San Juan Islands, between Vancouver Island and the State of Washington. The Pig War, so called because it was triggered by the shooting of a pig, is also called the Pig Episode, the Pig and Potato War, the San Juan Boundary Dispute and the Northwestern Boundary Dispute. Aside from the death of one pig, this dispute was a bloodless conflict.
 W
WThe Siege of Quebec, also known as the Second Siege of Quebec, was an unsuccessful French attempt to retake Quebec City in New France which had been captured by Britain the previous year. The siege lasted from 29 April until 15 May when British ships arrived to relieve the city which compelled the French commander Francis de Gaston, Chevalier de Lévis to break off the siege and retreat.
 W
WQueen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in England's Thirteen American Colonies during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In Europe, it is generally viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession; in the Americas, it is more commonly viewed as a standalone conflict. It is also known as the Third Indian War or as the Second Intercolonial War in France.
 W
WThe Raid on Canso was an attack by French forces from Louisbourg on the British outpost Fort William Augustus at Canso, Nova Scotia shortly after war declarations opened King George's War. The French raid was intended to boost morale, secure Louisbourg's supply lines with the surrounding Acadian settlements, and deprive Britain of a base from which to attack Louisbourg. There were 50 English families in the settlement. While the settlement was utterly destroyed, the objective failed, since the British launched an attack on Louisbourg in 1745, using Canso as a staging area.
 W
WThe Battle of Ridgeway was fought in the vicinity of the town of Fort Erie across the Niagara River from Buffalo, New York, near the village of Ridgeway, Canada West, currently Ontario, Canada, on June 2, 1866, between Canadian troops and an irregular army of Irish-American invaders, the Fenians. It was the largest engagement of the Fenian Raids, the first modern industrial-era battle to be fought by Canadians and the first to be fought only by Canadian troops and led exclusively by Canadian officers. The battlefield was designated a National Historic Site of Canada in 1921 and is the last battle fought within the current boundaries of Ontario against a foreign invasion. The Battle of Ridgeway has the distinction of being the first victory in a pitched battle for the cause of Irish independence since the Irish Rebellion of 1798.
 W
WThe Battle of Sainte-Foy, sometimes called the Battle of Quebec, was fought on April 28, 1760 near the British-held town of Quebec in the French province of Canada during the Seven Years' War. It was a victory for the French under the Chevalier de Lévis over the British army under General Murray. The battle was notably bloodier than the Battle of the Plains of Abraham of the previous September, with 833 French casualties to 1,124 British casualties. It was the last French victory in North America.
 W
WThe Sainte-Thérèse Raid was a military raid on the town of Sainte-Thérèse in French Canada conducted by British elite forces known as Rogers' Rangers that took place during the French and Indian War from 3 to 18 June 1760. Led by Robert Rogers the raid was a pre-emptive strike ordered by Major General Jeffery Amherst as a prelude to his three pronged attack on Montreal the following month.
 W
WThe Battle of Seven Oaks was a violent confrontation in the Pemmican War between the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and the North West Company (NWC), rivals in the fur trade, that took place on 19 June 1816, the climax of a long dispute in western Canada. The Métis people fought for the North West Company, and they called it "the Victory of Frog Plain".
 W
W W
WThe Battle of Signal Hill was fought on September 15, 1762, and was the last battle of the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War. A British force under Lieutenant Colonel William Amherst recaptured St. John's, after the French had seized earlier that year in a surprise attack.
 W
WThe Battle of Sorel occurred on June 19, 1610, with Samuel de Champlain supported by the Kingdom of France and his allies, the Huron, Algonquin people and Montagnais that fought against the Mohawk people in New France at present day Sorel-Tracy, Quebec. The forces of Champlain armed with the arquebus engaged and killed or captured nearly all of the Mohawks. The battle ended major hostilities with the Mohawks for twenty years.
 W
WThe Battle of the St. Lawrence involved marine and anti-submarine actions throughout the lower St. Lawrence River and the entire Gulf of Saint Lawrence, Strait of Belle Isle, Anticosti Island and Cabot Strait from May–October 1942, September 1943, and again in October–November 1944. During this time, German U-boats sank several merchant ships and four Canadian warships. There were several near shore actions involving the drop of German spies, or the attempted pick up of escaping prisoners of war. Despite the 23 ships lost, this battle marked a strategic victory for Canadian forces as ultimately they managed to disrupt U-boat activity, protect Canadian and Allied convoys, and intercept all attempted shore operations. This marked the first time that a foreign power had inflicted casualties in Canadian inland waters since the US incursions in the War of 1812.
 W
WThe United Irish Uprising in Newfoundland began with rumours in April 1800 at St. John's, Newfoundland Colony that as many as 400 men took a secret oath of the Society of United Irishmen. The recent Irish Rebellion of 1798 had inspired some of the Irish people in the Newfoundland Colony to plan and organize a rebellion. This included soldiers located at Signal Hill, Fort William, and Fort Townshend. It was suspected that as many as eighty soldiers planned to meet and mutiny against the British Army.
 W
WThe Wolseley expedition was a military force authorized by Sir John A. Macdonald to confront Louis Riel and the Métis in 1870, during the Red River Resistance, at the Red River Colony in what is now the Canadian province of Manitoba. The expedition was also intended to counter American expansionist sentiments in northern border states. Leaving Toronto in May 1870, the expedition arrived at Fort Garry on August 24, 1870. After a journey of three months in arduous conditions, the Expedition arrived at, and captured, Fort Garry. This extinguished Riel's Provisional Government, and eradicated the threat of the American expansion into western Canada.