 W
WThe Action of 6 October 1779 was a minor but famous and furious naval engagement that took part in the early stages of the war between Britain and France in the American Revolutionary War between the British Royal Navy frigate HMS Quebec and the frigate Surveillante of the French Navy. The battle ended in a French victory when Quebec was destroyed by an explosion.
 W
WThe Action of 10 August 1780 was a minor naval engagement that took place off Brest during the American Revolutionary War between a Royal Navy frigate and a French Navy frigate. This was the first engagement thought to involve the use of the carronade.
 W
WThe Battle of Auray took place on 29 September 1364 at the French town of Auray. This battle was the decisive confrontation of the Breton War of Succession, a part of the Hundred Years' War.
 W
WThe Battle of Ballon took place on 22 November 845 between the forces of Charles the Bald, king of West Francia, and Nominoë Duke of Brittany. Nominoë was appropriating border territory and opposing Charles' attempt to impose Frankish authority. Nominoë defeated Charles, initiating a period of Breton expansion and consolidation of power.
 W
WThe Battle of Pouancé was a battle in Conan II of Brittany's campaigns against the rebel Rivallon I of Dol, the Count of Anjou Geoffrey III, and the Duchy of Normandy's ruler, William.
 W
WThe Battle of Trans-la-Fôret was fought on 1 August 939 between the occupying Norsemen and the Bretons, led by the joint army of Alan II, Hugh II of Maine, and Judicael Berengar.
 W
WSir Robert Bemborough (d.1351) was a medieval knight who led the Montfortist faction during the Combat of the Thirty. This was an arranged battle between thirty knights from both sides during the Breton War of Succession, a struggle for control of the duchy between the House of Montfort and the House of Blois. Bemborough was killed in the battle.
 W
WThe Battle of Blavet was an encounter between the Huguenot forces of Soubise and a French fleet under the Duke of Nevers in Blavet harbour, Brittany in January 1625, triggering the Second Huguenot rebellion against the Crown of France.
 W
WThe Breton–Norman War of 1064–66 was fought between the Sovereign Duchy of Brittany and the Duchy of Normandy.
 W
WCamp Conlie was one of eleven military camps established by the Republican Government of National Defense under Léon Gambetta during the Franco-Prussian war. It became notable because of events which have led to its being described as a "concentration camp", in which troops from Brittany were supposedly incarcerated and persecuted. This became a significant atrocity story within Breton nationalism.
 W
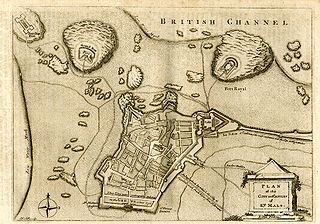
WThe Capture of Belle Île was a British amphibious expedition to capture the French island of Belle Île off the Brittany coast in 1761, during the Seven Years' War. After an initial British attack was repulsed, a second attempt under General Studholme Hodgson forced a beachhead. A second landing was made, and after a six-week siege the island's main citadel at Le Palais was stormed, consolidating British control of the island. A French relief effort from the nearby mainland was unable to succeed because of British control of the sea. The British occupied the island for two years before returning it in 1763 following the Treaty of Paris.
 W
WThe Chouannerie was a royalist uprising or counter-revolution in 12 of the western départements of France, particularly in the provinces of Brittany and Maine, against the First Republic during the French Revolution. It played out in three phases and lasted from the spring of 1794 until 1800.
 W
WThe Combat of the Thirty was an episode in the Breton War of Succession fought to determine who would rule the Duchy of Brittany. It was an arranged fight between selected combatants from both sides of the conflict, fought at a site midway between the Breton castles of Josselin and Ploërmel among 30 champions, knights, and squires on each side. The challenge was issued by Jean de Beaumanoir, a captain of Charles of Blois supported by King Philip VI of France, to Robert Bemborough, a captain of Jean de Montfort supported by Edward III of England.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort Crozon or the Siege of El Leon was a land and sea engagement that took place late in the French wars of religion and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). The siege was fought between 1 October and 19 November 1594 and was conducted by English and French troops against a Spanish fort constructed on the Crozon Peninsula near Brest. After a number of assaults were repelled, a Spanish relief force under Juan del Águila attempted to relieve the garrison, but it was delayed by French cavalry and could not reach the garrison in time.
 W
WThe battle of Fougères was a battle on 3 November 1793 at Fougères, during the Virée de Galerne. It was a Vendéen victory.
 W
WThe invasion of France in 1795 or the Battle of Quiberon was a major landing on the Quiberon peninsula by émigré, counter-revolutionary troops in support of the Chouannerie and Vendée Revolt, beginning on 23 June and finally definitively repulsed on 21 July. It aimed to raise the whole of western France in revolt, bring an end to the French Revolution and restore the French monarchy. The invasion failed; it had a major negative impact, dealing a disastrous blow to the royalist cause.
 W
WThe French–Breton War lasted from 1487 to 1491. The cause of this war was the approaching death of the Breton Duke Francis II of Brittany, who had no clear successor. If not resolved, this meant a resumption of issues from a previous War of the Breton Succession (1341–1364), which had rival claimants allying with England or France, resulting in an ambiguous peace treaty that failed to prevent future succession disputes.
 W
WThe Siege of Hennebont of 1342 was an episode of the succession of the War of Bretagne. The forces of Charles of Blois kept Jeanne of Flandre in the city, while they waited for English reinforcements. The arrival of these reinforcements in June 1342 provoked the lifting of the siege.
 W
WJosselin Castle is a medieval castle at Josselin, in the Morbihan department of Brittany, France, first built in 1008 by Guéthénoc, viscount of Porhoët. The town and castle were named after Guéthénoc's son, Goscelinus, and rebuilt at various times since. The current castle was built by Olivier de Clisson after 1370. He had acquired the land as part of the dowry on his marriage to Margaret of Rohan. It has been designated as a monument historique since 1928.
 W
WThe Battle of La Brossinière or Battle of la Gravelle was a battle of the Hundred Years' War on 26 September 1423. It occurred at La Brossinière, between the forces of England and France, shortly after hostilities had resumed, following the battle of Agincourt (1415).
 W
WThe Raid on Lorient was a British amphibious operation in the region around the town of Lorient from 29 September to 10 October 1746 during the War of the Austrian Succession. It was planned as an attempt to force the French to withdraw their forces from Flanders to reinforce their own coast. At the same time, as Lorient was used by the French East India Company as a base and supply depot, its destruction would serve British objectives in the East Indies.
 W
WThe Mad War was a late medieval conflict between a coalition of feudal lords and the French monarchy. It occurred during the regency of Anne of Beaujeu in the period after the death of Louis XI and before the majority of Charles VIII. The war began in 1485 and ended in 1488.
 W
WThe Battle of Morlaix was a battle fought in Morlaix on 30 September 1342 between England and France. The English besieged the town, but a French relief force arrived. The English constructed a strong defensive position. After repeated attacks, the French forced the English to retreat into the woods. The French force then withdrew. Notably it was the first use of a tactical withdrawal by the English in medieval warfare.
 W
WThe Siege of Morlaix took place from 6 September to 17 September 1594 during the French Wars of Religion and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). The siege was fought between the French Royal army under Jean VI d'Aumont reinforced by an English contingent under Sir John Norreys who besieged the town of Morlaix, which was held by the combined forces of Spain and the Catholic League of France. A relief force of Spanish troops under the Juan del Águila and another of Leaguers under the Duke of Mercœur were turned back by an English force under John Norreys. With the arrival of a fleet of English ships under Martin Frobisher the garrison swiftly surrendered.
 W
WThe Battle of Quiberon Bay was a decisive naval engagement during the Seven Years' War. It was fought on 20 November 1759 between the Royal Navy and the French Navy in Quiberon Bay, off the coast of France near St. Nazaire. The battle was the culmination of British efforts to eliminate French naval superiority, which could have given the French the ability to carry out their planned invasion of Great Britain. A British fleet of 24 ships of the line under Sir Edward Hawke tracked down and engaged a French fleet of 21 ships of the line under Marshal de Conflans. After hard fighting, the British fleet sank or ran aground six French ships, captured one and scattered the rest, giving the Royal Navy one of its greatest victories, and ending the threat of French invasion for good.
 W
WThe Siege of Rennes was an episode in the War of the Breton Succession during 1356-1357.
 W
WThe Battle of La Roche-Derrien was one of the battles of the Breton War of Succession; it was fought on 20th June 1347 during the night between English and French forces. Approximately 4,000–5,000 French, Breton and Genoese mercenaries laid siege to the town of La Roche-Derrien in the hope of luring Sir Thomas Dagworth, the commander of the only standing English field army in Brittany at the time, into an open pitched battle.
 W
WThe Raid on St Malo took place in June 1758 when an amphibious British naval expedition landed close to the French port of St Malo in Brittany. While the town itself was not attacked, as had been initially planned, the British destroyed large amounts of shipping before re-embarking a week later. The naval forces were under the command of Richard Howe while the army was led by the Duke of Marlborough and Lord Sackville.
 W
WThe Battle of Saint-Aubin-du-Cormier took place on 28 July 1488, between the forces of King Charles VIII of France, and those of Francis II, Duke of Brittany, and his allies. The defeat of the latter signalled the end to the "guerre folle", a feudal conflict in which French aristocrats revolted against royal power during the regency of Anne de Beaujeu. It also effectively precipitated the end of the independence of Brittany from France.
 W
WThe siege of Brest in 1386 was a siege by forces led by John IV, Duke of Brittany, against English-occupied Brest during the Hundred Years’ War. The siege was relieved by an English army commanded by John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster.
 W
WThe Battle of the Tombettes took place in 1800, between the Chouans and the Republicans during the Chouannerie.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Ushant was a naval battle fought between French and British squadrons near the island of Ushant on 12 December 1781, as part of the American Revolutionary War.
 W
WThe Battle of Ushant took place on 27 July 1778, and was fought during the American Revolutionary War between French and British fleets 100 miles (160 km) west of Ushant, an island at the mouth of the English Channel off the north-westernmost point of France.
 W
WThe Third Battle of Ushant or the Action of 20–21 April 1782 was a naval battle fought during the American Revolutionary War, between a French naval fleet of three ships of the line protecting a convoy and two British Royal naval ships of the line off Ushant, a French island at the mouth of the English Channel off the north-westernmost point of France. This was the third battle that occurred in this region during the course of the war.
 W
WThe sieges of Vannes of 1342 were a series of four sieges of the town of Vannes that occurred throughout 1342. Two rival claimants to the Duchy of Brittany, John of Montfort and Charles of Blois, competed for Vannes throughout this civil war from 1341 to 1365. The successive sieges ruined Vannes and its surrounding countryside. Vannes was eventually sold off in a truce between England and France, signed in January 1343 in Malestroit. Saved by an appeal of Pope Clement VI, Vannes remained in the hands of its own rulers, but ultimately resided under English control from September 1343 till the end of the war in 1365.
 W
WThe War of the Breton Succession was a conflict between the Counts of Blois and the Montforts of Brittany for control of the Sovereign Duchy of Brittany, then a fief of the Kingdom of France. It was fought between 1341 and 12 April 1365.