 W
WThe Anglo–Spanish War was a military conflict fought between Britain and Spain as part of the Seven Years' War. It lasted from January 1762 until February 1763 when the Treaty of Paris brought it to an end.
 W
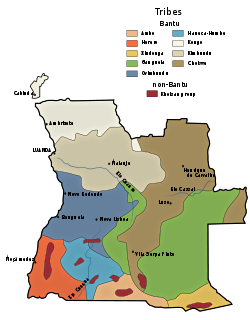
WThe Angolan War of Independence, called in Angola the Luta Armada de Libertação Nacional, began as an uprising against forced cultivation of cotton, and it became a multi-faction struggle for the control of Portugal's overseas province of Angola among three nationalist movements and a separatist movement. The war ended when a leftist military coup in Lisbon in April 1974 overthrew Portugal's Estado Novo regime, and the new regime immediately stopped all military action in the African colonies, declaring its intention to grant them independence without delay.
 W
WThe Bailundo revolt was an insurrection launched by the Ovimbundu kingdom of Bailundo and its allies against the Portuguese Empire. The revolt was prompted by the sudden decline of the price of root rubber, pitting the indigenous population against European immigrants and aboriginal loyalists. The revolt lasted between 1902 - 1904, ending in a Portuguese victory.
 W
WThe 1383–1385 Portuguese interregnum was a civil war in Portuguese history during which no crowned king of Portugal reigned. The interregnum began when King Ferdinand I died without a male heir and ended when King John I was crowned in 1385 after his victory during the Battle of Aljubarrota.
 W
WThe Dutch–Portuguese War was an armed conflict involving Dutch forces, in the form of the Dutch East India Company and the Dutch West India Company, against the Portuguese Empire. Beginning in 1602, the conflict primarily involved the Dutch companies invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, India and the Far East. The war can be thought of as an extension of the Eighty Years' War being fought in Europe at the time between Spain and the Netherlands, as Portugal was in a dynastic union with the Spanish Crown after the War of the Portuguese Succession, for most of the conflict. However, the conflict had little to do with the war in Europe and served mainly as a way for the Dutch to gain an overseas empire and control trade at the cost of the Portuguese. English forces also assisted the Dutch at certain points in the war. Because of the commodity at the center of the conflict, this war would be nicknamed the Spice War.
 W
WThe East Timor genocide refers to the "pacification campaigns" of state terrorism which were waged by the Indonesian New Order government during the Indonesian invasion and occupation of East Timor. Although some sources consider the Indonesian killings in East Timor to constitute genocide, other scholars disagree.
 W
WThe East Timorese rebellion of 1911–12, sometimes called the Great Rebellion or Rebellion of Manufahi, was a response to the efforts of Portuguese colonial authorities to collect a head tax and enforce the corvée, part of their larger effort to encourage cash crop agriculture and construct modern infrastructure. The countrywide conflict of 1911–12 was the culmination of a series of revolts led by Dom Boaventura, the liurai (chief) of the native kingdom of Manufahi. The first lasted from 1894 to 1901, the second from 1907 to 1908. In 1911 Boaventura led an alliance of local kingdoms in the last and most serious revolt against the Portuguese.
 W
WThe Eighty Years' War or Dutch War of Independence (1568–1648) was a revolt of the Seventeen Provinces of what are today the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg against Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Habsburg Netherlands. After the initial stages, Philip II deployed his armies and regained control over most of the rebelling provinces. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the northern provinces continued their resistance. They eventually were able to oust the Habsburg armies, and in 1581 they established the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. The war continued in other areas, although the heartland of the republic was no longer threatened. This included the origins of the Dutch colonial empire, which began with Dutch attacks on Portugal's overseas territories. At the time, this was conceived as carrying the war with the Spanish Empire overseas due to Portugal and Spain's being in a dynastic union.
 W
WThe English expedition to Portugal also known as the British Brigade in Portugal was a brigade raised during the reign of King Charles II for service in Portugal during the ongoing Portuguese Restoration War against Spain in August 1662. The brigade, many of which were veterans of the English Civil Wars and the Dutch Revolt, then fought in all the major battles and skirmishes under the command of Frederick Schomberg, 1st Duke of Schomberg and remained in Portugal until the end of the war being subsequently disbanded by mid 1668. The brigade under Schomberg's leadership, proved a decisive factor in winning back Portugal's independence.
 W
WThe Fernandine Wars were a series of three conflicts between the Kingdom of Portugal under King Ferdinand I and the Crown of Castile under King Henry II. They were fought over Ferdinand's claim to the Castilian succession after the death of King Peter of Castile in 1369.
 W
WThe First Carlist War was a civil war in Spain from 1833 to 1840, the first of three Carlist Wars. It was fought between two factions over the succession to the throne and the nature of the Spanish monarchy: the conservative supporters of the late king's brother, Carlos de Borbón, became known as Carlists (carlistas), while the progressive supporters of the regent, Maria Christina, acting for Isabella II of Spain, were called Liberals (liberales), cristinos or isabelinos. Aside from being a war of succession about the question who the rightful successor to king Ferdinand VII of Spain was, the Carlists’ goal was the return to an absolute monarchy, while the Liberals sought to defend the constitutional monarchy. Portugal, France and the United Kingdom supported the regency, and sent volunteer and even regular forces to confront the Carlist army.
 W
WThe French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Great Britain, Holy Roman Empire, Prussia, Russia, and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered a wide array of territories, from the Italian Peninsula and the Low Countries in Europe to the Louisiana Territory in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe.
 W
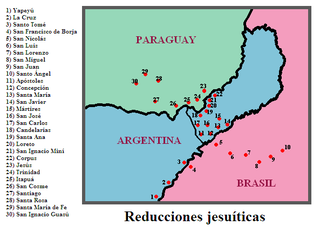
WThe Guarani War of 1756, also called the War of the Seven Reductions, took place between the Guaraní tribes of seven Jesuit Reductions and joint Spanish-Portuguese forces. It was a result of the 1750 Treaty of Madrid, which set a line of demarcation between Spanish and Portuguese colonial territory in South America.
 W
WThe Guinea-Bissau War of Independence was an armed independence conflict that took place in Portuguese Guinea between 1963 and 1974. Fought between Portugal and the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde, an armed independence movement backed by Cuba and the Soviet Union, the war is commonly referred to as "Portugal's Vietnam" due to the large numbers of men and amounts of material expended in a long, mostly guerrilla war and the internal political turmoil it created in Portugal. The war ended when Portugal, after the Carnation Revolution of 1974, granted independence to Guinea-Bissau, followed by Cape Verde a year later.
 W
WThe Hundred Years' War was a series of conflicts in Western Europe from 1337 to 1453, waged between the House of Plantagenet and its cadet House of Lancaster, rulers of the Kingdom of England, and the House of Valois over the right to rule the Kingdom of France. It was one of the most notable conflicts of the Middle Ages, in which five generations of kings from two rival dynasties fought for the throne of the largest kingdom in Western Europe. The war marked both the height of chivalry and its subsequent decline, and the development of stronger national identities in both countries.
 W
WThe Independence of Brazil comprised a series of political and military events that occurred in 1821–1824, most of which involved disputes between Brazil and Portugal regarding the call for independence presented by the Brazilian Empire.
 W
WThe Indonesian occupation of East Timor began in December 1975 and lasted until October 1999. After centuries of Portuguese colonial rule in East Timor, a 1974 coup in Portugal led to the decolonisation of its former colonies, creating instability in East Timor and leaving its future uncertain. After a small-scale civil war, the pro-independence Fretilin declared victory in the capital city of Dili and declared an independent East Timor on 28 November 1975.
 W
WThe Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict that began in 2003 with the invasion of Iraq by a United States-led coalition that overthrew the government of Saddam Hussein. The conflict continued for much of the next decade as an insurgency emerged to oppose the occupying forces and the post-invasion Iraqi government. An estimated 151,000 to 1,033,000 Iraqis were killed in the first three to four years of conflict. US troops were officially withdrawn in 2011. However, following the spread of the Syrian Civil War and the territorial gains of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Obama administration decided to redeploy US forces to Iraq in 2014. Many former soldiers are employed by defense contractors and private military companies. The U.S. became re-involved in 2014 at the head of a new coalition; the insurgency and many dimensions of the civil armed conflict continue. The invasion occurred as part of the George W. Bush administration's War on Terror, following the September 11 attacks.
 W
WThe Liberal Wars, also known as the Portuguese Civil War, the War of the Two Brothers or Miguelite War, was a war between liberal constitutionalists and conservative absolutists in Portugal over royal succession that lasted from 1828 to 1834. Embroiled parties included the Kingdom of Portugal, Portuguese rebels, the United Kingdom, France, the Catholic Church, and Spain.
 W
WThe Malayan–Portuguese war was an armed conflict involving Malacca forces, Sultanate of Johor and the Dutch East India Company, against the Portuguese Empire.
 W
WThe Mali War is an ongoing armed conflict that started in January 2012 between the northern and southern parts of Mali in Africa. On 16 January 2012, several insurgent groups began fighting a campaign against the Malian government for independence or greater autonomy for northern Mali, which they called Azawad. The National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA), an organization fighting to make this area of Mali an independent homeland for the Tuareg people, had taken control of the region by April 2012.
 W
WMoroccan–Portuguese conflicts refer to a series of battles between Morocco and Portugal throughout history.
 W
WThe Mozambican War of Independence was an armed conflict between the guerrilla forces of the Mozambique Liberation Front or FRELIMO, and Portugal. The war officially started on September 25, 1964, and ended with a ceasefire on September 8, 1974, resulting in a negotiated independence in 1975.
 W
WThe Ottoman-Portuguese conflicts of 1538 to 1559 were a series of armed military encounters between the Portuguese Empire, the Kingdom of Hormuz, and the Ethiopian Empire against the Ottoman Empire and Adal Sultanate, in the Indian Ocean, the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, and in East Africa. This is a period of battles in The Ottoman-Portuguese War.
 W
WThe Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th through the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy, which was at times supported by the Holy Roman Empire, Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Habsburg Spain. The wars were dominated by land campaigns in Hungary, including Transylvania and Vojvodina, Croatia and central Serbia.
 W
WThe Ottoman–Portuguese or Turco-Portuguese confrontations refers to a series of different military encounters between the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire, or between other European powers and the Ottoman Empire in which relevant Portuguese military forces participated. Some of these conflicts were brief, while others lasted for many years. Most of these conflicts were in the Indian Ocean, in the process of the expansion of the Portuguese Empire. These conflicts also involved regional powers, after 1538 the Adal Sultanate, with the aid of the Somali Ajuran Empire and the Ottoman Empire, fought against the Ethiopian Empire. The Ethiopians were supported by the Portuguese, under the command of Cristóvão da Gama, the son of the famous explorer Vasco da Gama. This war is known as the Ethiopian–Adal war.
 W
WThe Ottoman–Portuguese Conflicts (1586–1589) were armed military conflicts between the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire in the Indian Ocean, specifically in the east-African coast.
 W
WThe Seventh Ottoman–Venetian War was fought between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire between 1714 and 1718. It was the last conflict between the two powers, and ended with an Ottoman victory and the loss of Venice's major possession in the Greek peninsula, the Peloponnese (Morea). Venice was saved from a greater defeat by the intervention of Austria in 1716. The Austrian victories led to the signing of the Treaty of Passarowitz in 1718, which ended the war.
 W
WThe Patuleia, Guerra da Patuleia, or Little Civil War was a civil war in Portugal, so called to distinguish it from the 'great' civil war between Dom Pedro and Dom Miguel that ended in 1834. The Patuleia occurred after the Revolution of Maria da Fonte, and was closely associated with her. It was caused by the nomination, as a result of the palace coup of 6 October 1846, known as the "Emboscada", to set up a clearly Cartista government presided over by marshal João Oliveira e Daun, Duque de Saldanha.
 W
WThe Peninsular War (1807–1814) is the military conflict fought by Spain and Portugal, assisted by the United Kingdom, against the invading and occupying forces of the France for control of the Iberian Peninsula during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, it is considered to overlap with the Spanish War of Independence. The war began when the French and Spanish armies invaded and occupied Portugal in 1807 by transiting through Spain, and it escalated in 1808 after Napoleonic France had occupied Spain, which had been its ally. Napoleon Bonaparte forced the abdications of Ferdinand VII and his father Charles IV and then installed his brother Joseph Bonaparte on the Spanish throne and promulgated the Bayonne Constitution. Most Iberians rejected French rule and fought a bloody war to oust them. The war on the peninsula lasted until the Sixth Coalition defeated Napoleon in 1814, and it is regarded as one of the first wars of national liberation and is significant for the emergence of large-scale guerrilla warfare.
 W
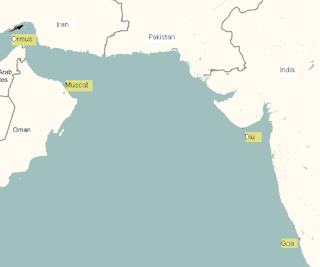
WThe Persian–Portuguese war took place from 1507 to 1622 and involved the Portuguese Empire and the Kingdom of Ormus, its vassal, on one side, and the Safavid Empire of Persia with the help of the Kingdom of England on the other side. During this era, Portugal established its rule for about more than a century in Ormuz and more than 80 years in Bahrain, capturing some other islands and ports such as Qeshm and Bandar Abbas. The conflict came to an end when the Safavid Shah, Abbas I of Persia, conquered the Portuguese Bahrain forcing them to war in the Persian Gulf.
 W
WThe Portuguese Colonial War, also known in Portugal as the Overseas War or in the former colonies as the War of Liberation, was a thirteen year long conflict fought between Portugal's military and the emerging nationalist movements in Portugal's African colonies between 1961 and 1974. The Portuguese corporatist authoritarian regime at the time, the Estado Novo, was overthrown by a military coup in 1974, and the change in government brought the conflict to an end. The war was a decisive ideological struggle in Lusophone Africa, surrounding nations, and mainland Portugal.
 W
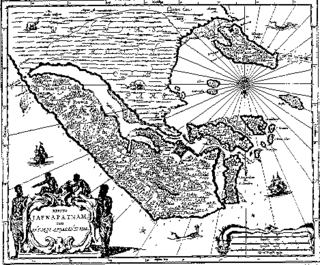
WThe Portuguese conquest of the Jaffna kingdom occurred after Portuguese traders arrived at the rival Kotte Kingdom in the southwest of modern Sri Lanka in 1505. Many kings of Jaffna, such as Cankili I, initially confronted the Portuguese in their attempts at converting the locals to Roman Catholicism, but eventually made peace with them.
 W
WThe Portuguese Restoration War was the war between Portugal and Spain that began with the Portuguese revolution of 1640 and ended with the Treaty of Lisbon in 1668, bringing a formal end to the Iberian Union. The period from 1640 to 1668 was marked by periodic skirmishes between Portugal and Spain, as well as short episodes of more serious warfare, much of it occasioned by Spanish and Portuguese entanglements with non-Iberian powers. Spain was involved in the Thirty Years' War until 1648 and the Franco–Spanish War until 1659, while Portugal was involved in the Dutch–Portuguese War until 1663.
 W
WThe War of the Portuguese Succession, a result of the extinction of the Portuguese royal line after the Battle of Alcácer Quibir and the ensuing Portuguese succession crisis of 1580, was fought from 1580 to 1583 between the two main claimants to the Portuguese throne: António, Prior of Crato, proclaimed in several towns as King of Portugal, and his first cousin Philip II of Spain, who eventually succeeded in claiming the crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.
 W
WThe Portuguese–Mamluk Naval War was a naval conflict between the Egyptian state of the Mamluks and the Portuguese in the Indian Ocean, following the expansion of the Portuguese after sailing around the Cape of Good Hope in 1498. The conflict took place during the early part of the 16th century, from 1505 to the fall of the Mamluk Sultanate in 1517.
 W
WThe Portuguese invasion of the Banda Oriental was a short-lived and failed attempt, beginning in 1811 and ending the following year, by the Portuguese Empire to annex the remaining territory of the Spanish Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata.
 W
WThe Portuguese conquest of the Banda Oriental was the armed-conflict that took place between 1816 and 1820 in the Banda Oriental, for control of what today comprises the whole of the Republic of Uruguay, the northern part of the Argentine Mesopotamia and southern Brazil. The four-year armed-conflict resulted in the annexation of the Banda Oriental into the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves as the Brazilian province of Cisplatina.
 W
WThe Reconquista was a period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula of about 780 years between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711, the expansion of the Christian kingdoms throughout Hispania, and the fall of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada in 1492.
 W
WThe Siege of Jeddah of 1517 was a battle fought between the Portuguese Empire under Lopo Soares de Albergaria against the Ottoman Empire to capture the Red Sea main port of Jeddah defended by the Mamluk garrison led by Amir Husain Al-Kurdi and the Ottoman naval force led by Selman Reis. The battle occurred in 16 December 1517 which also happened to be the Hajj season of 923 AD.
 W
WThe Sinhalese–Portuguese War was a series of conflicts waged from 1527 to 1658 during the Transitional and Kandyan periods in Sri Lanka between the Sinhalese kingdoms and their allies, against the Portuguese Empire. The Crisis of the Sixteenth Century (1521–1597), started with the Vijayabā Kollaya, the division of the Sinhala Kingdom, then centered at Kotte. The country was divided among three brothers resulting in a series of Wars of Succession. It was also at this time that the Portuguese, whose arrival in Sri Lanka was largely accidental, intruded into the internal affairs of Sri Lanka, establishing control over the maritime regions of the island and sought to control its lucrative external trade.
 W
WThe Sino-Dutch conflicts were a series of conflicts between the Ming dynasty of China and the Dutch East India Company over trade and land throughout the 1620s, 1630s, and 1662. The Dutch were attempting to compel China to accede to their trade demands, but the Chinese defeated the Dutch forces.
 W
WThe Spanish invasion of Portugal between 5 May and 24 November 1762 was a main military episode of the wider Seven Years' War, where Spain and France were heavily defeated by the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance. It initially involved the forces of Spain and Portugal, before the French and British intervened in the conflict on the side of their respective allies. The war was also strongly marked by a national guerrilla warfare in the mountainous country, cutting off supplies from Spain, and a hostile peasantry that enforced a scorched earth policy as the invading armies approached, leaving the invaders starving and short of military supplies.
 W
WThe Spanish-Portuguese War between 1735-1737 was fought over the Banda Oriental, roughly present-day Uruguay.
 W
WThe Third Fernandine War was the last conflict of the Fernandine Wars, and took place between 1381–1382, between the Crown of Castile and the Kingdoms of Portugal and England. When Henry II of Castile died in 1379, John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster claimed their rights of the throne of the Kingdom of Castile, and again found an ally in Ferdinand I of Portugal.
 W
WThe War of Independence of Brazil was waged between the newly independent Brazilian Empire and the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves, which had just undergone the Liberal Revolution of 1820. It lasted from February 1822, when the first skirmishes took place, to March 1824, with the surrender of the Portuguese garrison in Montevideo. The war was fought on land and sea and involved both regular forces and civilian militia. Land and naval battles took place in the territories of Bahia, Cisplatina and Rio de Janeiro provinces, the vice-kingdom of Grão-Pará, and in Maranhão and Pernambuco, which today are part of Ceará, Piauí and Rio Grande do Norte states.
 W
WThe War of the Emboabas was a conflict in colonial Brazil waged in 1706-1707 and 1708-1709 over newly discovered gold fields, which had set off a rush to the region between two generations of Portuguese settlers in the viceroyalty of Brazil - then the Captaincy of São Vicente. The discovery of gold set off a rush to the region, Paulistas asserted rights of discovery and non-Paulistas challenged their claims. Although the Portuguese crown sought more control in the area and the Paulistas sought protection of their claims, the Emoboabas won. The crown re-assessed its position in the region and made administrative changes subsequently.
 W
WThe War of the League of the Indies was a military conflict in which a pan-Asian alliance formed primarily by the Sultanate of Bijapur, the Sultanate of Ahmadnagar, the Kingdom of Calicut, and the Sultanate of Aceh, referred to by the Portuguese historian António Pinto Pereira as the "league of kings of India", "the confederated kings", or simply "the league", attempted to decisively overturn Portuguese presence in the Indian Ocean through a combined assault on some of the main possessions of the Portuguese State of India: Malacca, Chaul, Chale fort, and the capital of the maritime empire in Asia, Goa.
 W
WThe War of the Oranges was a brief conflict in 1801 in which Spanish forces, instigated by the government of France, and ultimately supported by the French military, invaded Portugal. It was a precursor to the Peninsular Wars, resulting in the Treaty of Badajoz, the loss of Portuguese territory, in particular Olivenza, as well as ultimately setting the stage for the complete invasion of the Iberian Peninsula by French forces.
 W
WWorld War I was a global war originating in Europe that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. Contemporaneously known as the Great War or "the war to end all wars", it led to the mobilisation of more than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, making it one of the largest wars in history. It is also one of the deadliest conflicts in history, with an estimated nine million combatant deaths and 13 million civilian deaths as a direct result of the war, while resulting genocides and the related 1918 Spanish flu pandemic caused another 17–100 million deaths worldwide, including an estimated 2.64 million Spanish flu deaths in Europe and as many as 675,000 Spanish flu deaths in the United States.