 W
WThe Action of 4 February 1781 was a minor naval engagement that occurred on 4 February, 1781 off Sombrero, Anguilla, between a British force of two ships of the line and one frigate under the command of Captain Francis Reynolds-Moreton, 3rd Baron Ducie and a Dutch frigate escorting thirty merchant ships under the command of Rear-Admiral Willem Krul, and resulted in the capture of all Dutch vessels present by the British. The battle occurred soon after a British expeditionary force under the command of Admiral George Brydges Rodney had captured the Dutch colony of Sint Eustatius during the opening stages of the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War, a conflict resulting from tensions between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Dutch Republic over Dutch support for the American rebels during the Revolutionary War.
 W
WThe Action of 21 July 1781 was a naval skirmish off the harbour of Spanish River, Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, during the War of American Independence. Two light frigates of the French Navy, captained by La Pérouse and Latouche Tréville, engaged a convoy of 18 British ships and their Royal Navy escorts. The French captured two of the British escorts while the remainder of the British convoy escaped.
 W
WThe Action of 25 February 1781 was a naval engagement fought off Cape Finisterre between the Spanish naval frigate sixth rate Graña of 30 guns and the Royal Navy fifth-rate frigate HMS Cerberus of 32 guns. Graña surrendered after a hard fight.
 W
WThe Action of 30 May 1781 was a naval battle fought between two frigates of the Royal Navy and two of the Dutch Republic off the Barbary Coast. In the Netherlands it is known as the zeegevecht bij Kaap Sint-Marie. In a battle lasting more than two hours, Captain William Peere Williams-Freeman of the Flora, compelled Captain Pieter Melvill's Castor to strike her colours. Shortly after, Captain Gerardus Oorthuys of den Briel compelled Thomas Pakenham to strike Crescent. However, Flora came to Crescent's rescue before Oorthuys could board her, and forced him to retreat.
 W
WThe American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), also known as the American War of Independence or the Revolutionary War, was initiated by delegates from the thirteen American colonies in Congress against Great Britain over their objection to Parliament's taxation policies and lack of colonial representation. From their founding in the 1600s, the colonies were largely left to govern themselves. With the capture of New France in the French and Indian War and confirmation of British victory through the 1763 Treaty of Paris, the British government was left deeply in debt, and the colonial legislatures vigorously disputed being forced to pay the expenses of the war. The Stamp Act and Townshend Acts provoked colonial opposition and unrest, leading to the 1770 Boston massacre and 1773 Boston Tea Party. When Parliament imposed the Intolerable Acts upon Massachusetts, twelve colonies sent delegates to the First Continental Congress to organize a boycott of British goods.
 W
WThe Second Anglo–Mysore War was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784. At the time, Mysore was a key French ally in India, and the conflict between Britain against the French and Dutch in the American Revolutionary War sparked Anglo–Mysorean hostilities in India. The great majority of soldiers on the company side were raised, trained, paid and commanded by the company, not the British government. However, the company's operations were bolstered by Crown troops sent from Britain, and by troops sent from Hanover, which was also ruled by Britain's King George III.
 W
WSpain played an important role in the independence of the United States, as part of its conflict with Britain. Spain declared war on Britain as an ally of France, itself an ally of the American colonies. Most notably, Spanish forces attacked British positions in the south and captured West Florida from Britain in the Siege of Pensacola. This secured the southern route for supplies and closed off the possibility of any British offensive through the western frontier of United States via the Mississippi River. Spain also provided money, supplies and munitions to the American forces.
 W
WThe Battle of Cape Henry was a naval battle in the American War of Independence which took place near the mouth of Chesapeake Bay on 16 March 1781 between a British squadron led by Vice Admiral Mariot Arbuthnot and a French fleet under Admiral Charles René Dominique Sochet, Chevalier Destouches. Destouches, based in Newport, Rhode Island, had sailed for the Chesapeake as part of a joint operation with the Continental Army to oppose the British army of Brigadier General Benedict Arnold that was active in Virginia.
 W
WThe Battle of Cowpens was an engagement during the American Revolutionary War fought on January 17, 1781 near the town of Cowpens, South Carolina, between U.S. forces under Brigadier General Daniel Morgan and British forces under Lieutenant Colonel Sir Banastre Tarleton, as part of the campaign in the Carolinas. The battle was a turning point in the American reconquest of South Carolina from the British.
 W
WThe Battle of Groton Heights was a battle of the American Revolutionary War fought on September 6, 1781 between a small Connecticut militia force led by Lieutenant Colonel William Ledyard and the more numerous British forces led by Brigadier General Benedict Arnold and Lieutenant Colonel Edmund Eyre.
 W
WThe Battle of Guilford Court House was fought on March 15, 1781, during the American Revolutionary War, at a site which is now in Greensboro, the seat of Guilford County, North Carolina. A 2,100-man British force under the command of Lieutenant General Charles Cornwallis defeated Major General Nathanael Greene's 4,500 Americans. The British Army, however, suffered a considerable number of casualties during the battle.
 W
WThe Battle of Mobile was a British attempt to recapture the town of Mobile, in the British province of West Florida, from the Spanish during the Anglo-Spanish War. The Spanish had previously captured Mobile in March 1780. On January 7, 1781, a British attack against a Spanish outpost on the east side of Mobile Bay was repulsed, and the German leader of the expedition was killed.
 W
WThe Battle of Spencer's Ordinary was an inconclusive skirmish that took place on 26 June 1781, late in the American Revolutionary War. British forces under Lieutenant Colonel John Graves Simcoe and American forces under Colonel Richard Butler, light detachments from the armies of General Lord Cornwallis and the Marquis de Lafayette respectively, clashed near a tavern at a road intersection not far from Williamsburg, Virginia.
 W
WThe Battle of the Chesapeake, also known as the Battle of the Virginia Capes or simply the Battle of the Capes, was a crucial naval battle in the American Revolutionary War that took place near the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay on 5 September 1781. The combatants were a British fleet led by Rear Admiral Sir Thomas Graves and a French fleet led by Rear Admiral Francois Joseph Paul, the Comte de Grasse. The battle was strategically decisive, in that it prevented the Royal Navy from reinforcing or evacuating the besieged forces of Lieutenant General Lord Cornwallis at Yorktown, Virginia. The French were able to achieve control of the sea lanes against the British and provided the Franco-American army with siege artillery and French reinforcements. These proved decisive in the Siege of Yorktown, effectively securing independence for the Thirteen Colonies.
 W
WThe Battle of Torrence's Tavern was a minor engagement of the American Revolutionary War that took place in what was the western portion of Rowan County, North Carolina, approximately 10 miles (16 km) east of the Catawba River near modern-day Mooresville in Iredell County. Torrence's Tavern was a part of the larger Southern campaign of the American Revolution, which, by 1780–1781 involved a series of clashes between the British Army and Loyalist militia and the Continental Army and Patriot militia in the Piedmont region of North and South Carolina.
 W
WThe Battle of Blandford, also called the Battle of Petersburg, took place near Petersburg, Virginia on 25 April 1781, late in the American War of Independence. Roughly 2,300 British regulars under the command of Brigadier General William Phillips defeated about 1,000 militia under Major General Baron von Steuben.
 W
WBrodhead's Coshocton Expedition was a campaign in April, 1781, by the United States against the Delaware Indians near Coshocton, Ohio. Led by Daniel Brodhead IV, the Americans massacred the Delawares as well as peaceful Moravian converts.
 W
WThe Battle of Blomindon took place on 21 May 1781 during the American Revolutionary War. The naval battle involved three armed U.S. privateer vessels against three Nova Scotian vessels off Cape Split, Nova Scotia. American Privateers caught two Nova Scotia Vessels. The first Nova Scotia vessel was re-captured by Lieut Benjamin Belcher. The second Nova Scotia vessel was overtaken by the captured crew under the command of Captain Bishop. The privateers were taken to Cornwallis and put on trial.
 W
WThe Capture of Sint Eustatius took place in February 1781 during the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War when British army and naval forces under General John Vaughan and Admiral George Rodney seized the Dutch-owned Caribbean island of Sint Eustatius. The capture was controversial in Britain, as it was alleged that Vaughan and Rodney had used the opportunity to enrich themselves and had neglected more important military duties. The island was subsequently taken by Dutch-allied French forces in late 1781, ending the British occupation.
 W
WThe Battle of Dogger Bank was a naval battle that took place on 5 August 1781 during the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War, contemporaneously related to the American Revolutionary War, in the North Sea. It was a bloody encounter between a British squadron under Vice Admiral Sir Hyde Parker and a Dutch squadron under Vice Admiral Johan Zoutman, both of which were escorting convoys.
 W
WThe Dutch West Indies campaign was a series of minor conflicts in 1781 and 1782, in the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War and the American Revolutionary War. Following Great Britain's declaration of war on the Dutch Republic in December 1780, British Admiral George Brydges Rodney, the commander of the Royal Navy in the West Indies, was notified by a fast-sailing packet ship of the declaration. He immediately acted to ensure control over as many of the Dutch colonies as possible, capturing Sint Eustatius, a vital entrepot of French and Dutch trade between their colonies and Europe, in early February 1781. He also captured Saba and Sint Maarten, and orchestrated the capture of the Dutch colonial outposts of Berbice, Demerara, and Essequibo in South America. A planned expedition by Samuel Hood against Curaçao was called off on rumors that a French fleet was approaching. A French expedition in 1782 captured Demerara and Essequibo, although the fate of the other colonies were settled at the conclusion of the war.
 W
WThe Battle of Eutaw Springs was a battle of the American Revolutionary War, and was the last major engagement of the war in the Carolinas. Both sides claimed victory.
 W
WThe First Anglo-Maratha War (1775–1782) was the first of three Anglo-Maratha Wars fought between the British East India Company and Maratha Empire in India. The war began with the Treaty of Surat and ended with the Treaty of Salbai.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Royal was a naval battle fought off Fort Royal, Martinique in the West Indies during the Anglo-French War on 29 April 1781, between fleets of the British Royal Navy and the French Navy. After an engagement lasting four hours, the British squadron under Sir Samuel Hood broke off and retreated. Grasse offered a desultory chase before seeing the French convoys safe to port.
 W
WThe Battle of Fort Slongo was fought on October 3, 1781 between American Continental Army forces, under the command of Benjamin Tallmadge, and the British defenders of Fort Salonga, in the American Revolutionary War. The fort was located near the border of present-day Huntington Township and Smithtown, New York, overlooking Long Island Sound.
 W
WFrancisco's Fight is the name commonly given to an alleged skirmish between a detachment of Tarleton's Raiders and Peter Francisco, a Continental Army soldier with a long service record, during the American Revolutionary War in July 1781. The skirmish, which is only known to be documented by Francisco, resulted in the death of at least one man and the wounding of several others.
 W
WThe Great Siege of Gibraltar was an unsuccessful attempt by Spain and France to capture Gibraltar from the British during the War of the American Revolution. The American war had ended with the British defeat at Yorktown in October 1781, but the Bourbon defeat in their great final assault on Gibraltar would not come until September 1782. The siege was suspended in February 1783 at the beginning of peace talks with the British.
 W
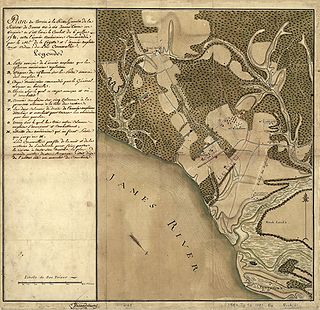
WThe Battle of Green Spring took place near Green Spring Plantation in James City County, Virginia during the American Revolutionary War. On July 6, 1781 United States Brigadier General "Mad" Anthony Wayne, leading the advance forces of the Marquis de Lafayette, was ambushed near the plantation by the British army of Earl Charles Cornwallis in the last major land battle of the Virginia campaign prior to the Siege of Yorktown.
 W
WThe Gulf Coast campaign or the Spanish conquest of West Florida in the American Revolutionary War, was a series of military operations primarily directed by the governor of Spanish Louisiana, Bernardo de Gálvez against the British province of West Florida. Begun with operations against British positions on the Mississippi River shortly after Britain and Spain went to war in 1779, Gálvez completed the conquest of West Florida in 1781 with the successful siege of Pensacola.
 W
WThe Capture of HMS Savage was a naval battle of the Revolutionary War involving the American privateer Congress and the British sloop-of-war HMS Savage. It occurred in September 1781 off South Carolina and is considered one of the hardest-fought single ship actions of the war.
 W
WThe Invasion of Tobago was a French invasion of the British-held island of Tobago during the Anglo-French War. On May 24, 1781, the fleet of Comte de Grasse landed troops on the island under the command of General Marquis de Bouillé. By June 2, 1781, they had successfully gained control of the island.
 W
WIn the Jahriyya revolt of 1781 sectarian violence between two suborders of the Naqshbandi Sufis, the Jahriyya Sufi Muslims and their rivals, the Khafiyya Sufi Muslims, led to Qing intervention to stop the fighting between the two, which in turn led to a Jahriyya Sufi Muslim rebellion which the Qing dynasty in China crushed with the help of the Khufiyya (Khafiyya) Sufi Muslims.
 W
WThe Battle of Jersey was an attempt by French forces during the American Revolutionary War to invade Jersey and remove the threat the island posed to French and American shipping. Jersey provided a base for British privateers, and France, engaged in the war as an ally of the United States, sent an expedition to gain control of the island.
 W
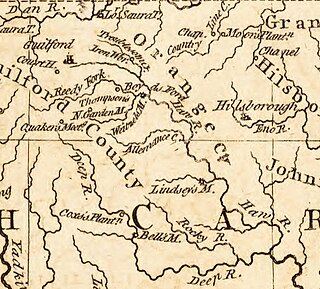
WThe Battle of Lindley's Mill took place in Orange County, North Carolina, on September 13, 1781, during the American Revolutionary War. The battle took its name from a mill that sat at the site of the battle on Cane Creek, which sat along a road connecting what was then the temporary state capital, Hillsborough, with Wilmington, North Carolina.
 W
WLochry's Defeat, also known as the Lochry massacre, was a battle fought on August 24, 1781, near present-day Aurora, Indiana, in the United States. The battle was part of the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), which began as a conflict between Great Britain and the Thirteen Colonies before spreading to the western frontier, where American Indians entered the war as British allies. The battle was short and decisive: about one hundred Indians of local tribes led by Joseph Brant, a Mohawk military leader who was temporarily in the west, ambushed a similar number of Pennsylvania militiamen led by Archibald Lochry. Brant and his men killed or captured all of the Pennsylvanians without suffering any casualties.
 W
WThe Long Run massacre occurred on 13 September 1781 at the intersection of Floyd's Fork creek with Long Run Creek, along the Falls Trace, a trail in what is now eastern Jefferson County, Kentucky.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort Motte was a military operation during the American Revolutionary War. A force of Patriots led by General Francis "Swamp Fox" Marion and Lt. Colonel "Light Horse" Harry Lee set out to capture the British post at Fort Motte, the informal name of a plantation mansion fortified by the British for use as a depot because of its strategic location at the confluence of the Congaree and Wateree rivers. The British garrisoned roughly 175 British soldiers under Lt. Daniel McPherson at the fort.
 W
WThe Battle of Porto Novo was fought on 1 July 1781 between forces of the Kingdom of Mysore and British East India Company in the place called Porto Novo on the Indian subcontinent, during the Second Anglo-Mysore War. The British force, numbering more than 8,000 under the command of Sir Eyre Coote defeated a force estimated at 40,000 under the command of Hyder Ali.
 W
WThe Battle of Porto Praya was a naval battle that took place during the American Revolutionary War on 16 April 1781 between a British squadron under Commodore George Johnstone and a French squadron under the Bailli de Suffren.
 W
WThe Raid on Annapolis Royal took place on 29 August 1781 during the American Revolutionary War. The raid involved two American privateers - the Resolution and the Reprisal - attacking and pillaging Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia in revenge of the British destruction of the Penobscot Expedition. The privateers took captive the Commander of the militia John Ritchie, described as the "Governor of Annapolis." One historian described it as "one of the most daring and dramatic raids upon Nova Scotia."
 W
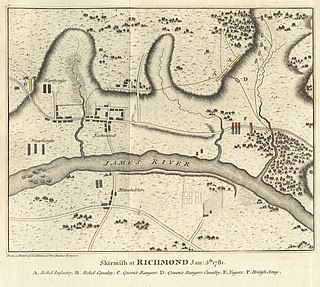
WThe Raid on Richmond was a series of British military actions against the capital of Virginia, Richmond, and the surrounding area, during the American Revolutionary War. Led by American turncoat Benedict Arnold, the Richmond Campaign is considered one of his greatest successes while serving under the British Army, and one of the most notorious actions that Arnold ever performed.
 W
WThe Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II was an uprising of native and mestizo peasants against the Bourbon reforms in the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru. While Túpac Amaru II, an early leader of the rebellion, was captured and executed in 1781, the rebellion continued for at least another year under other leaders.
 W
WThe Battle of Saldanha Bay was a naval action that occurred off the Dutch Cape Colony on 21 July 1781 during the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War. A squadron of Royal Navy warships under the command of commodore George Johnstone captured five Dutch East India Company ships; her own crew destroyed a sixth. Casualties on the Dutch side were minimal if any, and there were no British casualties.
 W
WThe Battle of Sholinghur was fought on 27 September 1781 at Sholinghur, 80 kilometres (50 mi) West of Chennai (Madras), between forces of the Kingdom of Mysore led by Hyder Ali and East India Company forces led by General Eyre Coote. Haider Ali's forces were surprised by the company forces and they were expelled from the Carnatic with heavy casualties.
 W
WThe Siege of Fort Watson was an American Revolutionary War confrontation in South Carolina that began on April 15, 1781 and lasted until April 23, 1781. Continental Army forces under Henry "Light Horse Harry" Lee and South Carolina militia under Francis Marion besieged Fort Watson, a fortified British outpost that formed part of the communication and supply chain between Charleston and other British outposts further inland.
 W
WThe Siege of Ninety Six was a siege in western South Carolina late in the American Revolutionary War. From May 22 to June 18, 1781, Continental Army Major General Nathanael Greene led 1,000 troops in a siege against the 550 Loyalists in the fortified village of Ninety Six, South Carolina. The 28-day siege centered on an earthen fortification known as Star Fort. Despite having more troops, Greene was unsuccessful in taking the town, and was forced to lift the siege when Lord Rawdon approached from Charleston with British troops.
 W
WThe Siege of Pensacola was a siege fought in 1781, the culmination of Spain's conquest of the British province of West Florida during the Gulf Coast campaign.
 W
WThe Siege of Yorktown, also known as the Battle of Yorktown, the surrender at Yorktown, or the German Battle, ending on October 19, 1781, at Yorktown, Virginia, was a decisive victory by a combined force of American Continental Army troops led by General George Washington and French Army troops led by the Comte de Rochambeau over a British army commanded by British peer and Lieutenant General Charles Cornwallis. The culmination of the Yorktown campaign, the siege proved to be the last major land battle of the American Revolutionary War in the North American region, as the surrender by Cornwallis, and the capture of both him and his army, prompted the British government to negotiate an end to the conflict. The battle boosted faltering American morale and revived French enthusiasm for the war, as well as undermining popular support for the conflict in Great Britain.
The Skirmish at Waters Creek was a minor action fought on March 8, 1781, during the American Revolutionary War. It was fought near Waters Creek in Newport News, Virginia between a group of local Patriot militia and British Army troops.
 W
WThe Capture of HMS St Fermin was a naval engagement that took place off Málaga on 4 April 1781, during the American Revolutionary War. Spanish xebecs San Antonio and San Luis captured the sloop-of-war HMS St Fermin.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Ushant was a naval battle fought between French and British squadrons near the island of Ushant on 12 December 1781, as part of the American Revolutionary War.
 W
WThe Yorktown or Virginia campaign was a series of military maneuvers and battles during the American Revolutionary War that culminated in the decisive Siege of Yorktown in October 1781. The result of the campaign was the surrender of the British Army force of General Charles Earl Cornwallis, an event that led directly to the beginning of serious peace negotiations and the eventual end of the war. The campaign was marked by disagreements, indecision, and miscommunication on the part of British leaders, and by a remarkable set of cooperative decisions, at times in violation of orders, by the French and Americans.