 W
WThe Adams County Courthouse is located in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, United States. It was built in 1858, first occupied in 1859, and added to the National Register of Historic Places on October 1, 1974.
 W
WThe Armory Square Hospital formally known as the District Armory or Armory of the District of Columbia was a military hospital for the Union Army located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., which operated from 1862 to 1865. It stood at the intersection of 6th Street SW and B Street SW between the Smithsonian Castle and the Capitol. The 12 wards extended across the Mall, all the way to the Canal. Today, the National Air and Space Museum stands in its place.
 W
WThe Auburn University Chapel is the second-oldest building and oldest building in its original location on the campus of Auburn University in Auburn, Alabama.
 W
WBenton Barracks was a Union Army military encampment, established during the American Civil War, in St. Louis, Missouri, at the present site of the St. Louis Fairground Park. Before the Civil War, the site was owned and used by the St. Louis Agricultural and Mechanical Association, which at the time was located on the outskirts of St. Louis. The barracks was used primarily as a training facility for Union soldiers attached to the Western Division of the Union Army.
 W
WBethesda Presbyterian Church is a historic church in Russellville, Tennessee, US, that was used as a hospital during the American Civil War. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WCamp Joe Holt was a Union base during the American Civil War in Jeffersonville, Indiana, across the Ohio River from Louisville, Kentucky, on land that is now part of Clarksville, Indiana, near the Big Eddy. It was a major staging area for troops in the Western Theatre of the War, in preparation for invading the Confederate States of America. Its establishment was the first major step performed by Kentucky Unionists to keep Kentucky from seceding to the Confederacy.
 W
WCampbell General Hospital was a Union Civil War hospital which operated from September 1862 to July 20, 1865, in northwest Washington, D.C..
 W
WCarnton is a historic home and museum in Franklin, Williamson County, Tennessee, United States. The sprawling farm and its buildings played an important role during and immediately after the Battle of Franklin during the American Civil War. It is managed by the non-profit organization The Battle of Franklin Trust.
 W
WThe original campus of Centenary College of Louisiana is located along College Street in Jackson, Louisiana. It is operated and preserved as a museum by the Louisiana Office of State Parks as the Centenary State Historic Site, offering educational interpretive programs and guided tours.
 W
WCharleston Cumberland Presbyterian Church is a historic church on Railroad Street in Charleston, Tennessee.
 W
WChimborazo Hospital was an American Civil War era facility built in Richmond, Virginia to service the medical needs of the Confederate Army. It functioned between 1862 and 1865 in what is now Chimborazo Park, treating over 76,000 injured Confederate soldiers. During its existence, the hospital admitted nearly 78,000 patients and between 6,500 and 8,000 of these patients died. This mortality rate of between 8.3 and 10.3 percent is among the lowest such rates of period military hospitals.
 W
WThe Church of the Epiphany, built in 1844, is an historic Episcopal church located at 1317 G Street, N.W., in Washington, D.C.. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on September 10, 1971.
 W
WDavids Island is a 78-acre (320,000 m2) island off the coast of New Rochelle, New York, in Long Island Sound. Currently uninhabited, it was previously the site of Fort Slocum. The island is home to the endangered Kemp's ridley sea turtle, and birds such as osprey and least terns. Davids Island also supports valuable wetlands, rare rocky intertidal areas, and sandy beaches. The waters surrounding the island are home to winter flounder, Atlantic herring, and Atlantic silverside.
 W
WCamp Dennison was a military recruiting, training, and medical post for the United States Army during the American Civil War. It was located near Cincinnati, Ohio, not far from the Ohio River. The camp was named for Cincinnati native William Dennison, Ohio's governor at the start of the war.
 W
WDepot Field Hospital was one of seven hospitals operated at City Point, Virginia during the Siege of Petersburg during the American Civil War.
 W
WThe Dobbin House Tavern, known also as Dobbin House, on 89 Steinwehr Avenue in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania is a tavern which is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WFinley General Hospital was a Union Army hospital which operated near Washington, D.C., during the Civil War. It operated from 1862 to 1865.
 W
WFort Crawford was an outpost of the United States Army located in Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin, during the 19th century.
 W
WThe Gettysburg Lincoln Railroad Station, also known as the "Gettysburg Train Station," "Lincoln Train Station" or "Western Maryland Railroad Station," is a historic train station with depot, platform, museum and offices on Carlisle Street in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Operable from 1858 to 1942, it contributes to the Gettysburg Battlefield Historic District and is most notable as President Abraham Lincoln's point of arrival on November 18, 1863 and departure, following delivery of the Gettysburg Address. The station served as both a hospital during the battle and hub for outgoing wounded soldiers and incoming resources and supplies following the end of the war. On 2015, following several years of delays, the station, which was originally owned by the Borough of Gettysburg but was bought by the Gettysburg Foundation, the non-profit partner to the National Park Service, was placed under the purview of the National Park Service.
 W
WGood Samaritan Hospital, the oldest and largest private teaching and specialty health care facility in Cincinnati, Ohio, United States, was opened in 1852 under the sponsorship of the Sisters of Charity. The hospital is member of TriHealth, a joint operating agreement between Catholic Health Initiatives and Bethesda, Inc. Cincinnati to manage Good Samaritan. The Hospital of the Good Samaritan, at Sixth and Lock streets, was originally the Cincinnati Marine Hospital, built at a cost of $300,000, from a generic pattern by American Architect, Robert Mills. Because there was already a place for merchant seamen (rivermen) to go, there were insufficient numbers of such men to warrant opening the hospital.
 W
WHarewood General Hospital was one of several purpose-built pavilion style hospitals operating in the Washington, D.C., area during the Civil War which rendered care to Union military personnel. A purpose-built pavilion style hospital, it was in use from September 4, 1862, to May 5, 1866.
 W
WHarper House is a historic home located near Harper, Johnston County, North Carolina. It was built about 1850, and is a two-story, three-bay, vernacular Greek Revival style frame dwelling. It sits on a brick pier foundation and has a hipped roof and interior end chimneys. The front facade features a two-story pedimented portico. The house served as a Union field hospital during the Battle of Bentonville and is located adjacent to the Bentonville Battlefield museum, which offers tours of its interior. It was also bought by the state. Before the state's acquisition of the property, it was privately owned by the Dunn family. It served as a home for 5 children, John J. Dunn Jr. being the last child born in the Harper House in 1950.
 W
WThe Henderson House is a historic U.S. home located in Dumfries, Virginia. Alexander Henderson built this home in the late 18th century near the Old Post Road. Alexander Henderson was the father of Archibald Henderson, fifth Commandant of the Marine Corps. During the American Revolutionary War, the Henderson's entertained many important officers and men in this house. During the American Civil War, both the Confederate and the Union armies used the house as a hospital depending on which occupied the area. A cannonball struck the house during the American Civil War and remained lodged in the west wall for about 100 years until a souvenir hunter stole it the 1960s.
 W
WHoly Trinity Catholic Church is a Catholic church located in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C., in the United States. Holy Trinity Parish was founded in 1787 and is the oldest Roman Catholic community and house of worship in continuous operation in both Georgetown and the larger city of Washington, D.C. The original church building was completed in 1794. It is now called the Chapel of St. Ignatius, and is used for smaller ecclesiastical celebrations and as an auxiliary space for parish activities. A larger church building, necessitated by the growing community, was dedicated in 1851, and still serves as the parish church today.
 W
WFrederick Law Olmsted, the executive director of the United States Sanitary Commission, set up a system of hospital ships for wounded and sick soldiers during the American Civil War. The USSC was a private agency that cooperated closely with the U.S. Army.
 W
WHoward University Hospital, previously known as Freedmen's Hospital, is a major hospital located in Washington, D.C., built on the site of the previous Griffith Stadium. The hospital has served the African-American community in the area for over 150 years, having been established in 1862 to cater for the medical needs of the thousands of African Americans who came to Washington during the Civil War, seeking their freedom. The first hospital of its kind to provide medical treatment for former slaves, it later became the major hospital for the area's African American community.
 W
WThe Jefferson Barracks Military Post is located on the Mississippi River at Lemay, Missouri, south of St. Louis. It was an important and active U.S. Army installation from 1826 through 1946. It is the oldest operating U.S. military installation west of the Mississippi River, and it is now used as a base for the Army and Air National Guard. A Veterans Affairs healthcare system campus is located on the southern portion of the base and is also the headquarters for the Veterans Canteen Service.
 W
WJefferson General Hospital was the third-largest hospital during the American Civil War, located at Port Fulton, Indiana and was active between February 21, 1864 and December 1866. The land was owned by U.S. Senator from Indiana Jesse D. Bright. Bright was sympathetic to the Confederates, and was expelled from his position as Senator in 1862. Union authorities took the property without compensation, similar to what happened at Arlington National Cemetery.
 W
WYale New Haven Hospital (YNHH) is a 1,541-bed hospital located in New Haven, Connecticut. It is owned and operated by the Yale New Haven Health System. YNHH includes the 168-bed Smilow Cancer Hospital at Yale New Haven, the 201-bed Yale New Haven Children's Hospital, and the 76-bed Yale New Haven Psychiatric Hospital, making it one of the largest hospitals in the world and the largest in Connecticut. It is the primary teaching hospital for Yale School of Medicine and Yale School of Nursing.
 W
WLebanon is a historic plantation house located near Dunn, Harnett County, North Carolina. It was built about 1824, and is a two-story, three bay, Greek Revival style frame dwelling with a one-story wing. It is sheathed in weatherboard and rests on a brick foundation. The front facade features a three bay, two-tier porch. During the American Civil War, the Battle of Averasboro occurred in the immediate vicinity of plantation house and it was used as a hospital.
 W
WLincoln Park is the largest urban park located in the Capitol Hill neighborhood of Washington, D.C. It was known historically as Lincoln Square. From 1862 to 1865, it was the site of the largest hospital in Washington, DC: Lincoln Hospital.
 W
WThe Martha Washington Inn is a historic hotel located in Abingdon, Virginia. Originally built in 1832 by General Francis Preston, hero of the War of 1812, for his family of nine children, over the course of the last 174 years, the building has served as an upscale women's college, a Civil War hospital and barracks, and as a residence for visiting actors of the Barter Theatre. In addition to hotel services, the inn now offers spa treatments. Many people say the house might be haunted by ghosts from the area.
 W
WMobile City Hospital, also known as Old Mobile General Hospital, is a historic Greek Revival hospital building in Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was built in 1830 by Thomas S. James and served as a hospital for the city of Mobile from 1831 until 1966. It was administered for the city by the Sisters of Charity throughout a large part of its history. Residents of the city were treated here during epidemics of yellow fever and during the American Civil War. It was converted to office space after 1966. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on February 26, 1970. The building is adjacent to the old U.S. Marine Hospital, which is also on the National Register.
 W
WMount Pleasant General Hospital was a Union Civil War hospital in northwest Washington, D.C., which operated from March 28, 1862, to August 10, 1865.
 W
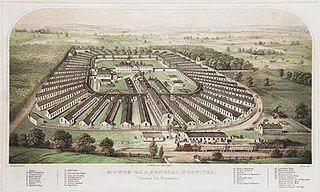
WMower General Hospital was one of the largest Federal military hospitals during the American Civil War. Located across from the Reading Railroad depot in the Chestnut Hill section of Philadelphia, it operated from January 1863 through May 1865, and was closed with the cessation of the war.
 W
WNewport Barracks was a military barracks on the Ohio River, across from Cincinnati, Ohio in Newport, Kentucky. It was operational from 1803 until 1894.
 W
WThe Old Marine Hospital is a historic medical building at 20 Franklin Street in Charleston, South Carolina. Built 1831-33 to a design by Robert Mills, it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1973 for its association with Mills, and as a high-quality example of Gothic Revival architecture. The hospital was built as a public facility for the treatment of sick sailors and other transient persons.
 W
WThe Old North Building, or simply Old North, is the oldest extant academic building on the campus of Georgetown University in Washington, D.C. and was the second major building built on the campus. To the east, the building is joined to Healy Hall and to the west, it is joined to New North, while the southern façade of the building encloses Dahlgren Quadrangle. Built in the Georgian style, Old North was one of the grandest buildings in Washington at the time of its completion in 1795. It served as the flagship of the university until the construction of Healy Hall. Old North currently houses the McCourt School of Public Policy.
 W
WThe Orton Plantation is a historic plantation house in the Smithville Township of Brunswick County, North Carolina, United States. Located beside the Cape Fear River between Wilmington and Southport, Orton Plantation is considered to be a near-perfect example of Southern antebellum architecture. Built in 1735 by the co-founder of Brunswick Town, the Orton Plantation house is one of the oldest structures in Brunswick County. During its history Orton Plantation has been attacked by Native Americans, used as a military hospital, and been home to lawyers, physicians, military leaders, and a Colonial governor. Although the home is privately owned and closed to the public, the Orton Plantation Gardens and family-owned chapel have become a tourist destination in Southeastern North Carolina, attracting thousands of visitors each year. On April 11, 1973, the Orton Plantation was added to the National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WOxford College of Emory University, also called Oxford College and founded in 1836 as Emory College, is an American two-year residential college in Oxford, Georgia, specializing in the foundations of liberal arts education. It is the birthplace and one of nine academic divisions of Emory University. The college is located on Emory University's original campus 38 miles (61 km) east of Emory's current Atlanta campus. Students who enroll in Oxford College complete an associate of the arts degree there, after which they can continue their studies at Emory's Atlanta campus to pursue a bachelor degree without any additional applications.
 W
WPennsylvania Hall is the Gettysburg College central administrative building and the college's oldest building. Designed in 1835 by John Cresson Trautwine, it was built in 1838 as a "temple-style edifice with four columns in the portico".
 W
WPennsylvania Hospital is a private, non-profit, 515-bed teaching hospital located in Center City Philadelphia and is part of the University of Pennsylvania Health System. Founded on May 11, 1751, by Benjamin Franklin and Dr. Thomas Bond, Pennsylvania Hospital is one of the earliest established public hospitals in the United States. It is also home to America's first surgical amphitheatre and its first medical library. The hospital's main building, dating to 1756, is a National Historic Landmark.
 W
WRoberts Chapel is a historic chapel in Nicholasville, Kentucky.
 W
WRock Creek-White Run Union Hospital Complex is a national historic district located at Cumberland Township, Gettysburg, and Mount Joy Township in Adams County, Pennsylvania. The district includes 11 contributing buildings and 13 contributing sites, on 13 contiguous properties including 8 farmsteads and White's Church. The farmsteads are Schwartz Farm, Shaeffer Farm, Trostle Farm, Lewis Bushman Farm, Diener Farm, Conover Farm, Lightner Farm, and Beitler Farm. The properties served as hospitals for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, 6th, and 12th corps of the Army of the Potomac during the weeks immediately following the Battle of Gettysburg.
 W
WRomney Presbyterian Church is a historic Presbyterian church in Romney, West Virginia.
 W
WSt. Elizabeths Hospital is a psychiatric hospital in Southeast, Washington, D.C. operated by the District of Columbia Department of Behavioral Health. It opened in 1855 with the name Government Hospital for the Insane, the first federally operated psychiatric hospital in the United States. Housing over 8,000 patients at its peak in the 1950s, the hospital had a fully functioning medical-surgical unit, a school of nursing, accredited internships and psychiatric residencies. Its campus was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1990. The west portion of the campus is home to over 1,000 U.S. Department of Homeland Security personnel and serves as its headquarters. St. Elizabeth’s Hospital campus also has the joint tenant of the Douglas A. Munro Coast Guard Headquarters Building with hundreds of Coast Guard personnel.
 W
WSt. Thomas Chapel, also known as St. Thomas Episcopal Church or St. Thomas Protestant Episcopal Chapel, is a historic building located at 7854 Church Street in Middletown, Frederick County, Virginia, United States. Built in the 1830s, regular services were held at the Episcopal church for almost 100 years. The building has been restored twice, once after being heavily damaged during the Civil War, and again in the 1960s. The church was added to the Virginia Landmarks Register (VLR) and the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1973.
 W
WSatterlee General Hospital was the largest Union Army hospital during the American Civil War. Operating from 1862 to 1865 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, its physicians and nurses rendered care to thousands of Union soldiers and Confederate prisoners. After its patient population spiked following the battles of Bull Run and Gettysburg, this hospital became the second-largest in the country with 34 wards and hundreds of tents containing 4,500 beds.
 W
WSchmucker Hall is an American Civil War site listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Adams County, Pennsylvania, that was constructed as the original Gettysburg Theological Seminary building. Used as both a Union and Confederate hospital during the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg, the facility served as the seminary's main building from 1832 to 1895, then as a dedicated dormitory for students until 1951. In 1960, it was leased by the Adams County Historical Society. Beginning in 2006, the Historical Society, along with the Seminary Seminary Ridge Historic Preservation Foundation, rehabilitated the building for adaptive reuse as the Seminary Ridge Museum. The Adams County Historical Society moved into the nearby Wolf House on the seminary campus preceding the renovation. In 2013, on the 150th anniversary of the battle, the Seminary, the Adams County Historical Society and the Seminary Ridge Historic Preservation Foundation opened the building as the Seminary Ridge Museum. The Museum houses displays about many different aspects of the battle, the seminary, the town, and the civil war, and the struggle among faith groups over slavery, as well as offering tours of the cupola. The exhibit and museum have earned international, national and regional awards and the rehabilitation achieved LEED Certification in 2013.
 W
WThe Sidney & Lois Eskenazi Hospital is located in Indianapolis, Indiana. The hospital is the flagship medical center for Eskenazi Health, founded in 1859 as Indiana's oldest public healthcare system. The hospital is operated by Health & Hospital Corporation of Marion County. The current hospital opened December 7, 2013, less than 1,300 feet (400 m) to the west of the original campus, replacing Wishard Memorial Hospital.
 W
WThe United States Marine Hospital, formerly known as Frank S. Keeler Memorial Hospital, is a historic Greek Revival hospital building in Mobile, Alabama, United States. Construction began in 1838 and was completed in 1842. It was designed by architect Frederick Bunnell and was operated by the Marine Hospital Service from its opening until it closed, in 1952. It treated injured Confederate and Union soldiers during the American Civil War. It shares some design features, such as its two-story colonnades, with its neighbor, the old Mobile City Hospital.
 W
WThe United States Marine Hospital in Louisville, Kentucky, in the Portland neighborhood was built in 1845, and is considered by the National Park Service to be the best remaining antebellum hospital in the United States. Of the seven hospitals built in the mid-19th century by the Marine Hospital Service "for the benefit of sick seamen, boatmen, and other navigators on the western rivers and lakes." It is the only one still standing, even after surviving two tornadoes. The building has been extensively restored to match its appearance in 1899.
 W
WWiley Memorial United Methodist Church, now known as Bethlehem Wiley United Methodist Church, is a historic church at 504 Lookout Street in Chattanooga, Tennessee, affiliated with the Holston Conference of the United Methodist Church.
 W
WThe York U.S. Army Hospital was one of Pennsylvania's largest military hospitals during the American Civil War. It was established in York, Pennsylvania, to treat wounded and sick soldiers of the Union army.